On March 15, archaeologists announced the discovery of a collection of Paleolithic tools in northwestern China.
According to a report from the Shaanxi Archaeological Institute, this discovery is the result of a year-long excavation project that began in March 2021 at the Yeyuan site in the Lintong District of Shaanxi Province.
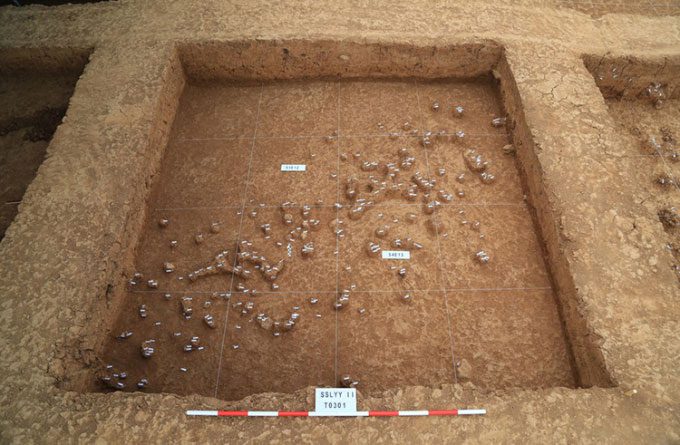

A large number of stone tools found at Yeyuan. (Photo: Xinhua)
Approximately 12,000 artifacts were discovered in an area of 500m2, including hand axes, scrapers, and other sharp stone tools.
Preliminary estimates suggest that ancient humans inhabited this area at least 600,000 years ago. Their activities began to flourish around 250,000 years ago and continued until about 70,000 years ago.
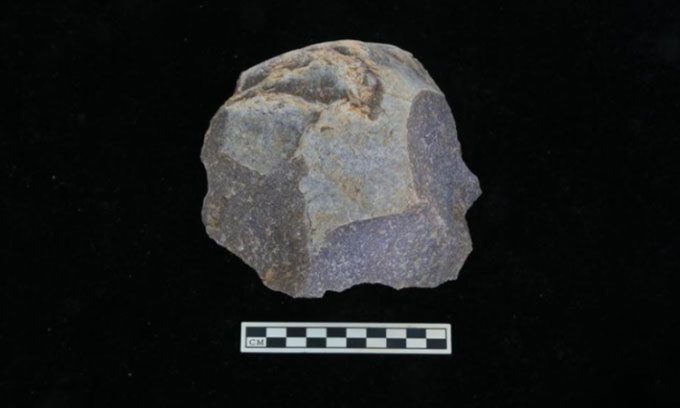

A sharp stone tool used for cutting. (Photo: Xinhua)
Expert Zhang Gaike from the Shaanxi Archaeological Institute stated that the excavation is significant for studying the development of cultures in the Qinling Mountains, as well as the interactions among humans in different regions during the Paleolithic era.
The Paleolithic era, or the early stage of the Stone Age, encompasses a large portion of human history on Earth, lasting from approximately 2.5 million years ago to 12,000 years ago. This period is characterized by the development of chipped stone tools.