While the race for 6G technology is still in its infancy, China Mobile, the world’s largest telecommunications operator, launched a 6G experimental satellite into low Earth orbit in early February.
This initiative aims to reduce latency and enable extremely high data transmission speeds, supporting advanced technology applications deployed on Earth.
Currently, 5G networks are the technology prioritized by most countries around the world, offering significantly improved performance compared to 4G.

China’s 6G experimental satellite in space. (Photo: China Mobile/X).
China has begun testing 6G technology in space. Recently, China Mobile launched the world’s first satellite dedicated to 6G experimentation, a fact confirmed by China Daily.
Towards 1 Terabit per Second Throughput
This satellite is positioned in low Earth orbit (LEO), approximately 500 km from Earth. It is the world’s first satellite serving 6G testing, developed by China Mobile in collaboration with the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The low orbit enhances rapid data transmission and reduces latency compared to other satellites operating at 36,000 km away.
The idea is that when 6G networks are deployed, they will fill the “gaps” on Earth via a space-based satellite system, meaning that 6G will be usable anywhere on the globe.
Theoretically, 6G technology promises transmission speeds of up to 1 Terabit per second (1,000 Gigabits per second) with nearly zero latency.
Moreover, 6G will be particularly suited for the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling the detection and connection of numerous devices or vehicles within a certain radius.
Despite the ongoing experimental implementation of 6G technology in China, scientists believe it will not be commercially available before 2030.
This technology is expected to transmit data 100 times faster than 5G, with latency reduced to less than one millisecond.
6G will also improve data transmission reliability and reduce energy consumption. In addition, while 5G operates on millimeter-wave frequencies up to 30 gigahertz, 6G will utilize terahertz bands, deemed suitable for ultra-high-speed data transmission.
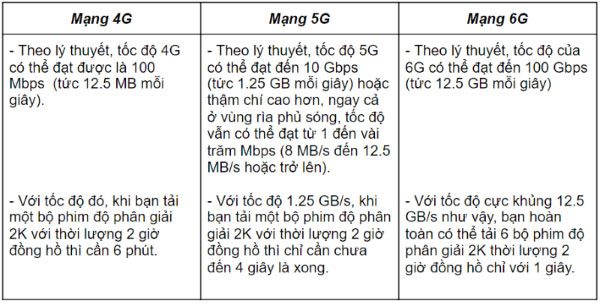
What is 6G?6G is the sixth generation of mobile networks, following the 5G generation. The specific standards are not yet clear, but we can speculate on the characteristics that 6G networks will have. According to PCMag, new generations of mobile networks utilize advanced digital encoding techniques. Additionally, 6G networks will support wider bandwidths and be smarter. What Makes 6G Different?The most apparent difference is speed. With each new generation of mobile networks, speed is a key factor of improvement, and 6G is no exception. The sixth-generation mobile network will use more advanced devices with greater and more diverse waveforms. This includes high-frequency bands (Extreme High Frequency) that provide substantial speed and capacity. To visualize this, you can refer to the comparison of speeds between 4G, 5G, and 6G as follows:
|