The phenomenon of swelling, itching, and rashes on the arm after receiving the Moderna vaccine, also known as “Covid arm,” is uncomfortable but harmless and will disappear within a few days.
Dr. Esther Freeman, the director of dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, stated that this is merely a natural immune response of the body.
“This phenomenon is normal. Many people will experience swelling and redness in the arm for a few days. It is somewhat uncomfortable, but there is no need to panic or hesitate when receiving the second dose of the vaccine,” she said.
As the chief investigator at the Global Covid-19 Dermatology Agency, Dr. Freeman has noted cases of rashes and redness in the arm after vaccination. So far, only 14 people have reported this condition, but there may be many more unreported cases. Other post-vaccination reactions are listed on the V-safe page of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Dermatologists and allergists refer to “Covid arm” as a “delayed hypersensitivity reaction.” In this case, the area where the vaccine was injected will develop a red, itchy rash that is painful to touch, with the rash measuring 13-15 cm in length.
“At first, it looks quite alarming, but it will disappear within 24 hours to a week,” Dr. Freeman said.
“Covid arm” only occurs in individuals who receive the Moderna vaccine, as reported in clinical trials. Recipients of the Pfizer vaccine do not experience this condition.
“This does not mean you should choose Pfizer over Moderna,” Dr. Freeman added.
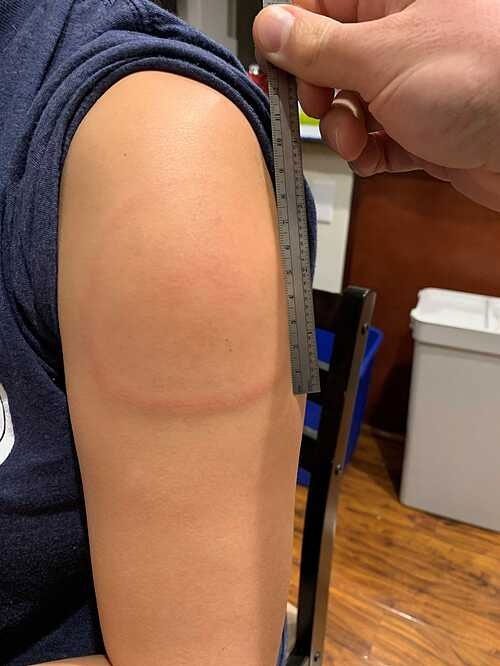
A 15cm rash on the arm of a Moderna vaccine recipient. (Photo: Mass General Brigham Hospital).
The rash is more common in women (77%). This may be due to the fact that healthcare workers, who are a priority group, are predominantly female. Professor Kim Blumenthal, an allergy and epidemiology expert at Harvard Medical School, believes that women are often more likely to report post-vaccination symptoms.
The average age of those experiencing “Covid arm” is 43. This is also the common age for healthcare workers, who were among the first to receive the vaccine, according to Dr. Tom Shimabukuro from the Immunization Agency of the Public Health Service.
Side effects from different vaccines are similar, except for this particular symptom. Data shows that older individuals have a weaker immune response after vaccination. Therefore, a rash on the arm may indicate a strong immune response in the younger group, according to Dr. Freeman.
“It is not surprising to see distinct symptoms in different age groups,” she said.
The rash typically manifests 5 to 9 days after the first vaccination. This differs from common side effects, which appear within 24 to 48 hours. Many people are concerned that the second vaccine dose may cause more severe symptoms. However, there is no evidence to support this. Professor Kim Blumenthal stated that “Covid arm” is a type of delayed allergic reaction, and the cause is still unclear.
Experts acknowledge that the symptom is uncomfortable but believe that individuals should not delay or avoid receiving the second vaccine dose. Doctors assert that the rash at the injection site is not an infection and does not require antibiotic treatment.
“However, if the rash spreads beyond the arm, or if you experience unusual symptoms lasting more than a week, please contact a healthcare facility,” Dr. Freeman advised.
Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital recommends that individuals receive their second Moderna vaccine dose in the opposite arm. All doctors agree on an important message that “Covid arm” is a harmless, short-term reaction to vaccination.
“People should not panic or hesitate to receive the second dose just because of this symptom,” Dr. Freeman said.
How to manage “Covid arm”
Although not serious and not a cause for concern, “Covid arm” can be uncomfortable and bothersome for those affected. Therefore, it is essential to remain calm, knowing that it poses no danger and does not affect the antibody production process against Covid-19.
Additionally, individuals should inform their healthcare provider monitoring the vaccination for appropriate guidance or treatment recommendations to alleviate discomfort. While waiting for medical advice, applying a cool compress (not cold) at home can help reduce pain, swelling, and itching.
It is important to note that treating “Covid arm” does not diminish the immune response to the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines administered. Furthermore, the occurrence of “Covid arm” lasting (if it occurs) after the first dose of the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is not a reason to delay or contraindicate the second dose, as it is necessary to achieve the best immune efficacy.
Thus, to combat Covid-19, vaccines are undoubtedly the best shield, alongside the necessity for everyone to strictly adhere to the “5K” guidelines even after being fully vaccinated. Areas currently implementing social distancing must enforce these measures rigorously.


















































