Recently, in the Facebook group “Loving Wild Nature” with over 326 thousand members, a post by member N.H attracted the attention of other members with the title “Giant Bat Captured in Africa.
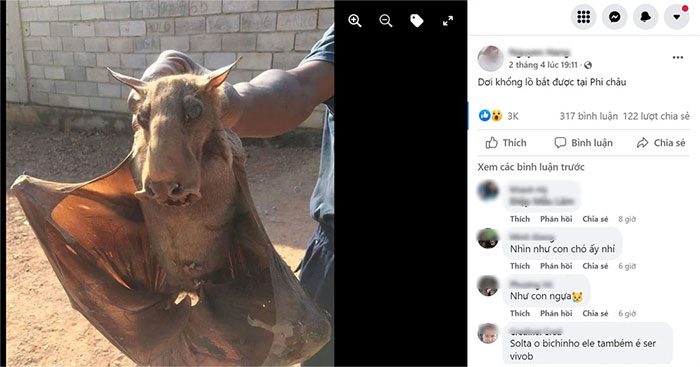
A giant bat captured in Africa. (Photo: Screenshot)
The post garnered over 3,000 likes, more than 300 comments, and 122 shares within just two days due to the bat’s unusual appearance. One member, M.G, even commented: ‘Looks like a dog,’ while another member, P.V, remarked: ‘Like a horse.‘
So, what species of bat was captured in Africa, and is it dangerous to humans?
In fact, the image of the captured bat has been circulating on social media since July 2018. This bat is a hammer-headed bat (scientific name: Hypsignathus monstrosus) – the largest bat species in Africa.
They typically inhabit tropical rainforests in Central Africa (near the equator). This species can have a wingspan of up to 97 cm, with males being significantly larger than females.
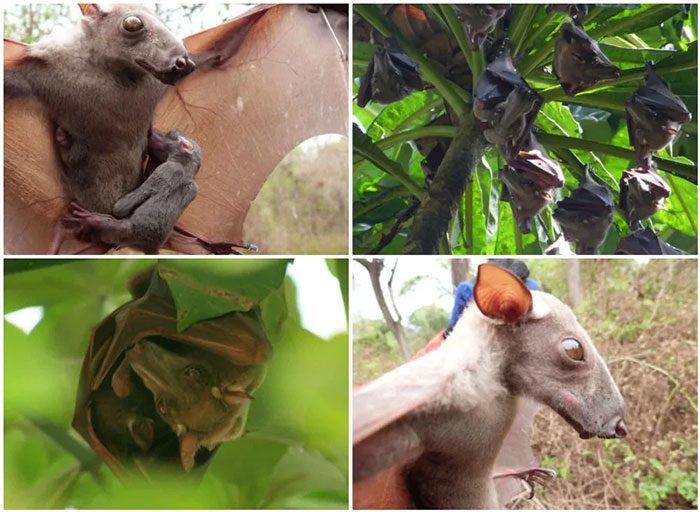

Hammer-headed bat. (Photo: Snopes)
Despite their intimidating appearance, this bat species primarily feeds on fruit, thus posing no direct threat to humans or livestock. However, they are considered one of three host species (also fruit bats) responsible for transmitting the Ebola virus.
Specifically, in 2005, when researchers studied over 1,000 small specimens (679 bats, 222 birds, and 129 vertebrates) in Gabon and Congo – the two countries hardest hit by Ebola outbreaks, they found that only three species of fruit bats served as hosts for the virus.
These three bat species are: hammer-headed bat, Epomops franqueti, and Myonycteris torquata (according to Live Science). Scientists warn that considering bats as food in Africa could lead to the transmission of the Ebola virus from bats to humans.





















































