The asteroid that collided with Earth at Vredefort, South Africa, is estimated to be one of the largest asteroids ever, believed to have a diameter of about 10 km.
The Vredefort Crater is one of the largest and oldest impact craters on Earth, located in the impact area of South Africa. It was formed millions of years ago during the Cretaceous period and is a natural wonder of immense scientific value. The crater is situated in the Free State province of South Africa and is named after the town of Vredefort, which lies near the center of the crater.
According to scientists’ estimates, this crater is approximately 2 billion years old, and its formation may stem from the impact of a massive meteorite during the Cretaceous period.
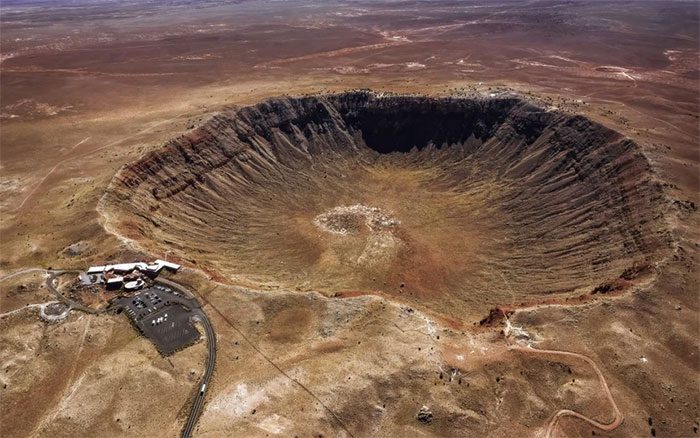

The Vredefort Crater is a massive and long-lasting crater, one of Earth’s striking geological natural wonders. Its existence provides scientists with valuable opportunities to study planetary formation and the collisions between celestial bodies.
Scientists believe that about 2 billion years ago, a meteorite with a diameter of approximately 10 km collided with Earth at high speed, creating this gigantic crater. The impact released tremendous energy, resulting in a shockwave and extreme heat that devastated surrounding ecosystems and altered the geological structure of the entire area.
The crater has a diameter of 300 km. Its shape resembles a large basin surrounded by fertile plains and sand dunes. For a long time, the crater was covered by a thick layer of rock until modern technological developments revealed its existence.
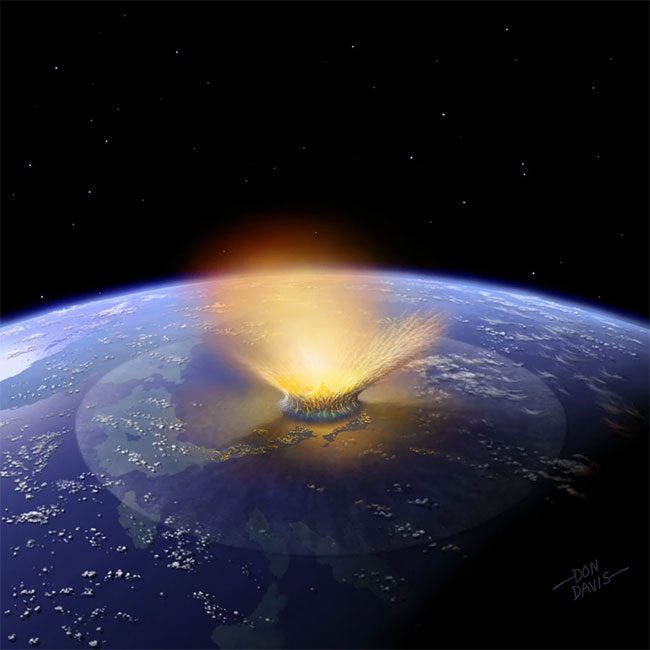

Its colossal scale astonishes visitors, and its existence surpasses human imagination. This also allows scientists to better study the Earth’s surface and the changes during its formation.
For scientists, the crater provides a rare opportunity to research the evolutionary history of Earth. By analyzing sediments and geological structures at the bottom of the crater, they can gain a deeper understanding of changes on the Earth’s surface and the evolution of biological adaptations following the impact event. The crater may also have the potential to store groundwater, mineral resources, and potential life forms, which has attracted the attention of many researchers.
In addition to its scientific research value, the Vredefort Crater has become a popular tourist destination. Visitors can explore volcanic rocks and formations at the bottom of the crater and admire the stunning desert landscapes. Additionally, the nearby wildlife reserve offers opportunities to observe rare animals such as African lions, giraffes, and zebras.
Through meteorite research, scientists can understand the composition and structure of extraterrestrial materials. These meteorites contain matter from space that may be products of supernova explosions or other cosmic events. By analyzing the ratios of elements and isotopes in meteorites, scientists can infer the chemical evolutionary processes of the universe at different times, thereby gaining a deeper understanding of the origins and evolution of the universe.
To protect the unique ecosystem and landscape of the crater, local authorities have established a nature reserve and implemented a series of protective measures. Additionally, South Africa’s tourism department provides safe guiding services to ensure the safety and convenience of visitors.
As one of the largest and oldest craters on Earth, the Vredefort Crater is renowned for its colossal scale, vast landscapes, and rich scientific research value. It holds memories of Earth’s evolutionary history and offers visitors a unique travel experience. The crater symbolizes the magnificent wonders of Earth, and its existence will continue to spark curiosity and exploration desires among people.

The Vredefort Crater also provides research data on cosmic radiation and cosmic rays. Traces left by cosmic rays and radiation will remain in meteorites, and these traces can be used by scientists to study the radiation environment and particle physics processes in the universe. This is critical for our understanding of the origins and nature of cosmic rays, and it may help scientists gain a better understanding of the physical properties of the universe.
The Vredefort Crater is considered an important window into the origins and evolution of the universe. Through meteorite research, scientists can obtain crucial information about extraterrestrial materials, cosmic ages, cosmic chemical evolution, and cosmic radiation, all of which play a significant role in enhancing our understanding of the origins and evolution of the universe. With the continuous advancement of science and technology, this crater will continue to reveal many mysteries of the universe to us.