What peculiarities in these skeletons have left experts bewildered?
Strange Skeletons
In 1987, archaeologists discovered an ancient site in a field near the village of Tiao Jia in Jinan City, Shandong Province, China. A large number of stone tools, pottery, axes, sickles, knives, and various other cultural artifacts were found. These remains belong to an ancient culture known as the Longshan culture, which existed during the Neolithic period about 5,000 years ago. Among the numerous archaeological finds, scientists also uncovered many ancient human skeletons.
Surprisingly, archaeologists found that the skeletons discovered were significantly taller than the majority of people today. One skeleton measured up to 1.9 meters, while many others were 1.8 meters or even taller.
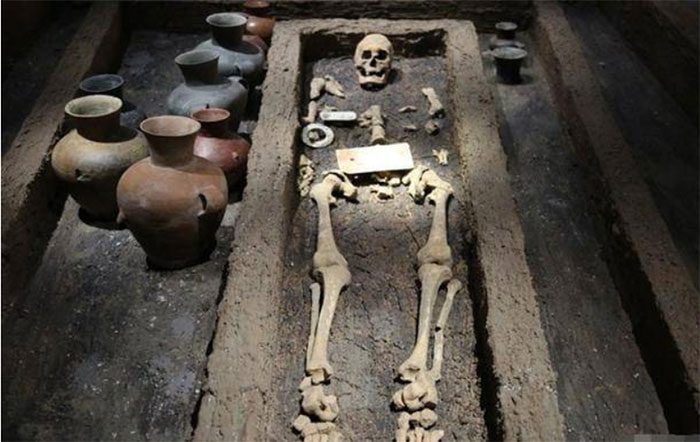

One of the skeletons found in Shandong, China. (Photo: Sohu)
In an excavation at the ‘Ubeidiya site in the Jordan Valley, located between Israel, Syria, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia, archaeologists discovered a 1.5 million-year-old fossilized vertebra of a young boy. Modern techniques helped reconstruct the physical characteristics of the boy, who was 9 to 12 years old at the time of death, and estimate how tall he would be as an adult.
The findings indicated that when he grew up, he would have reached a height of 1.98 meters.
When villagers in Scaieni, located in the Buzaului Mountains of Romania, dug the earth to plant an apple orchard, they were astonished to discover gigantic skeletons measuring up to 2.4 meters along with pieces of pottery, jewelry, and strange metal statues approximately 1 meter tall.
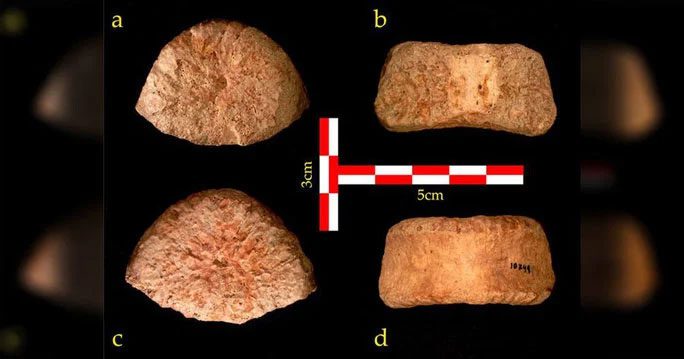
The 1.5 million-year-old vertebra of a boy found at the ‘Ubeidiya site in the Jordan Valley. (Photo: Internet).
These discoveries are puzzling because most known ancient human species were shorter than modern humans. This is attributed to their existence in a harsh environment, lacking nutrition, and struggling to find food. According to the evolutionary history of humans, height has gradually increased over time, suggesting that ancient people should have been shorter than modern individuals.
The discoveries of remains in Tiao Jia and many other sites around the world have overturned scientists’ perceptions. This has provided a new perspective to better understand the physical development of ancient humans.
Experts’ Speculations
After a period of research, Wang Fen, a professor of Cultural History at Shandong University, along with many other experts, proposed two different hypotheses.
First, the ancient humans were tall due to nutrition from their diet. According to Chinese history, the Longshan culture belongs to the era of the Five Emperors, and the climate at that time was warmer than today. In the book “The Spring and Autumn Annals of the Lu Family – Ancient Music”, it is recorded that “Merchants chased elephants to the east. They traveled all the way south of the Yangtze River and lived there.” The presence of elephants at that time also explains the weather conditions. The expert in oracle bone scripts (inscriptions on turtle shells and animal bones from the Shang Dynasty), Hu Hou, also acknowledged that “the climate during the era of the Five Emperors was not only warm but also much hotter than today.”

From the excavated skeletons, it is evident that ancient people were very tall. (Photo: Sohu)
Experts speculate that besides agriculture, ancient people also engaged in animal husbandry to ensure a stable food supply. Furthermore, the climatic conditions of that time greatly influenced food sources. At that time, the climate around Tiao Jia was warm and humid, allowing for easy plant growth and favorable conditions for livestock farming. Thanks to the abundant supply, these ancient individuals had access to nutritious food, which contributed to their remarkable height.
Second, the height of humans may have changed over time. Historical records describe the heights of people from the Qin and Han dynasties, indicating that Confucius was 1.82 meters tall; Xiang Yu was 1.9 meters; Liu Bei was about 1.82 meters; Zhuge Liang was 1.94 meters; Guan Yu was 2.18 meters… even Cao Cao, who was relatively short, was 1.69 meters tall.

According to historical descriptions, Guan Yu and Liu Bei were both over 1.8 meters tall. (Photo: Sohu)
Archaeologists have recorded the heights of ancient people based on the excavated bone fragments. The surprising conclusion is that from the pre-Qin period to the Western Han period, the average height of men was about 1.66 meters, slightly shorter than modern humans.
This result is reflected in the terracotta warriors and horses of Qin Shi Huang. These statues were made to scale, and the average height of the terracotta warriors is between 1.7 meters and 1.81 meters (after removing their bases). Given the physical requirements for soldiers in the Qin era, it is normal for their height to be slightly above average. Thus, the height of men during the Qin and Han dynasties averaged around 1.66 meters.
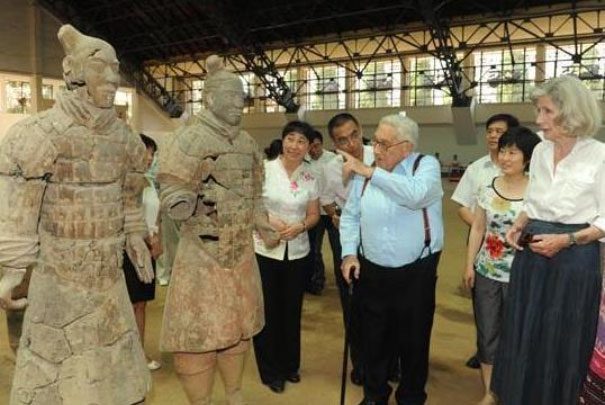

The average height of the terracotta warriors is between 1.7 meters and 1.81 meters. (Photo: Sohu)
However, the skeletons from the era of the Five Emperors are clearly much taller. Perhaps, the height of humans in later eras gradually declined. According to archaeologists’ speculations, the emergence of social classes and the increase in population after entering these eras led to a decrease in the food supply and nutrition available to common people. Hence, the physical stature of ancient humans underwent significant changes.