Stroke is a very common emergency condition. However, many patients (P) are unaware of the warning signs of a stroke, often arriving at the hospital (H) late or taking incorrect home remedies…
18% Mortality Rate
|
Caring for stroke patients |
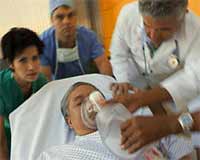
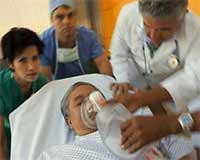
On April 26, at the Stroke Center of Trưng Vương Emergency Hospital (Ho Chi Minh City), about ten patients were receiving treatment. All patients were in a deep coma and required oxygen support or mechanical ventilation.
Ms. T.M.C., relative of patient L.T.T. (64 years old, Tân Bình District, Ho Chi Minh City), stated that Mr. T. had suffered two strokes but drank alcohol and smoked heavily every day. On April 23, while sitting and drinking, Mr. T. suddenly experienced twitching in his hands, became unsteady, and was about to fall. Ms. C. quickly took him to Trưng Vương Hospital. Dr. Trần Quang Thắng, deputy head of the neurology department at Trưng Vương Hospital, reported that Mr. T. was in a coma and in very critical condition due to a recurrent stroke. Ms. C. mentioned that for the past two years, Mr. T. had not followed his doctor’s prescribed medication but only took traditional Chinese and herbal medicine.
According to Dr. Quang Thắng, a stroke (also known as a cerebrovascular accident) occurs when part of the brain is suddenly damaged due to loss of blood supply, causing brain cells to gradually die. The consequences can lead to paralysis on one side of the body, coma, or death. The World Health Organization reports that the annual incidence rate of stroke in the community is between 1.27% and 7.46%.
Globally, stroke is the third leading cause of death, following coronary artery disease and cancer. According to a study from Chợ Rẫy Hospital and the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City, the mortality rate from stroke is 18%. Notably, patients transferred from other provinces to these two medical units have an extremely high mortality rate, reaching 70%, meaning that out of 100 stroke patients, 70 cases result in death.
Five Symptoms to Recognize a Stroke 1. Sudden weakness or numbness of the face, arms, or legs. If a patient shows signs of a stroke, urgently call 115 for immediate assistance. |
Do Not Delay!
The cause of a stroke is damage to blood vessels leading to cerebral hemorrhage (ruptured blood vessels) or cerebral infarction (blocked blood vessels). Among those who survive a stroke, about 50% will recover well, while the remaining 50% may suffer disabilities or other lasting effects.
To detect a stroke early, patients, family members, friends, and colleagues must recognize that this is an emergency condition and be aware of the symptoms to promptly take the patient to the emergency room.
Dr. Quang Thắng advises that when a patient is experiencing a stroke, they should be transferred to the hospital as quickly as possible. Avoid using oils, scraping the skin, or traditional remedies, as these are ineffective and can delay necessary treatment. Early emergency care is crucial since many life-threatening complications can arise within the first few hours after a stroke, but they can be prevented or treated.
Risk Factors
According to Dr. Thắng, stroke commonly occurs in older adults, particularly males. The leading risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, heart diseases (such as atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease…), atherosclerosis, previous strokes, transient ischemic attacks, and peripheral vascular diseases…
Additionally, other factors that may cause stroke include high blood lipid levels, lack of physical activity, obesity, alcohol addiction, and stress. Numerous studies show a strong correlation between high blood pressure and stroke risk. Therefore, regular monitoring and management of high blood pressure is the best preventive measure against stroke. Following high blood pressure, elevated blood lipids leading to atherosclerosis also significantly increase the risk of stroke.
Preventing Recurrence
The risk of stroke recurrence among surviving patients is 30% within the first five years after the initial stroke. Therefore, stroke patients, after treatment and discharge, need to monitor for the possibility of recurrence. According to Dr. Quang Thắng, to prevent stroke, patients must control vascular risk factors (high blood pressure, cholesterol levels, smoking, diabetes).
Moreover, lifestyle and dietary changes are essential. Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of stroke. Engaging in physical exercise, losing weight, consuming less fat, eating more fruits and vegetables, limiting salt intake, and following the doctor’s medication instructions are also necessary actions to take.
LÊ THANH HÀ