Dr. Tâm warns that many patients are complacent and do not seek treatment until the tumor has grown large, making it too late for effective intervention.
Dr. Đinh Hữu Tâm from the Department of Pathology at the Central Military Hospital 108 states that salivary gland cancer is a rare type of tumor. It can occur in the salivary glands located in the oral cavity and can affect individuals of all ages, significantly impacting their health. In reality, many patients are complacent and do not seek treatment until the tumor has enlarged, at which point it is often too late.
Unlike other head and neck cancers caused by known factors such as tobacco, alcohol, and HPV, Dr. Tâm notes that the causes of salivary gland cancer are mostly unclear. Exposure to radiation, such as low-dose radiation therapy and frequent dental X-rays, is often suspected to contribute to the development of salivary gland tumors.
Other potential contributing factors include workplace exposure (to substances like nickel, rubber, and silica), diet, age, and genetics. Additionally, about 2% of benign pleomorphic adenomas can transform into malignant tumors.
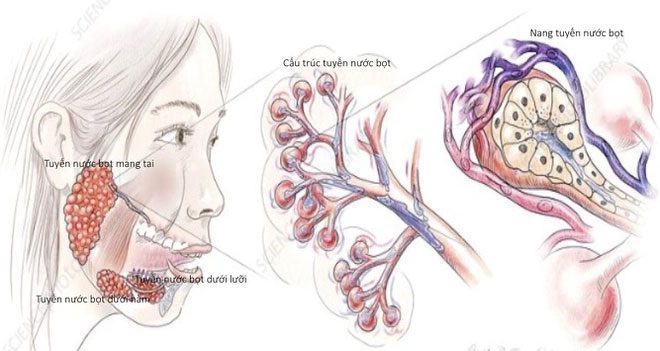
Anatomy of salivary glands. (Image: BVCC).
Symptoms of Salivary Gland Cancer
The majority of salivary gland cancers arise from the parotid and submandibular glands, typically presenting as a swelling in the salivary gland.
- Parotid gland cancer: Often painful, with loss of sensation or difficulty opening the jaw.
- Suspicious symptoms of cancer: Rapid tumor growth, facial nerve paralysis, poor mobility of the tumor, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Submandibular gland cancer: Typically presents as a painless mass in the front of the neck; if painful, it is usually due to inflammation. Less common signs include limited mobility, skin invasion, facial nerve paralysis, and enlarged lymph nodes.
- Sublingual gland cancer: Often manifests as a mass on the floor of the mouth.
- Accessory salivary gland tumors usually present as a non-ulcerated, painless submucosal mass in the oral cavity.
Treatment
Dr. Hữu Tâm states that complete surgical resection of the tumor is currently the primary treatment method for salivary gland cancer. Reconstructive surgery involving nerves, skin, bone, and soft tissue may be performed during the surgery to ensure functionality and aesthetics for the patient.
Adjuvant radiation therapy is indicated for patients in advanced or terminal stages. For some patients with accessory salivary gland cancer, radiation therapy may be considered as the initial treatment method.


















































