A powerful earthquake measuring 6.6 on the Richter scale struck on the morning of May 27, shaking sparsely populated areas, including the islands of Kao and Tofua.
An earthquake with a magnitude of 6.6 jolted the Pacific nation of Tonga on the morning of May 27, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
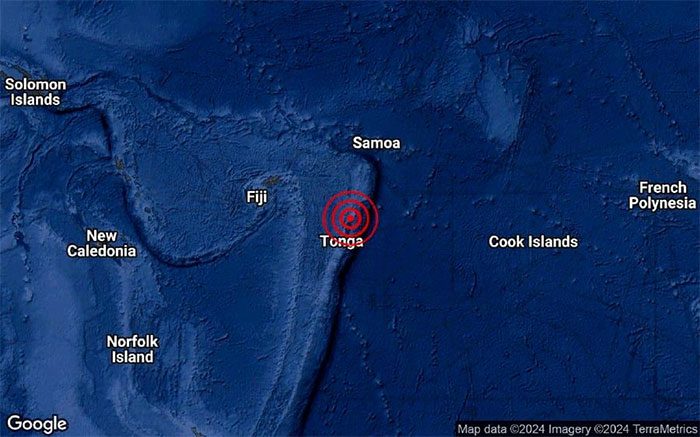
6.6 magnitude earthquake in the Pacific Ring of Fire on May 27 (Photo: Terra Metrics).
The earthquake occurred at 9:47 AM local time at a depth of approximately 112 km. The epicenter was located in the ocean about 198 km north of Tonga’s capital, Nuku’alofa, according to the USGS.
The quake shook sparsely populated areas, including the islands of Kao and Tofua. However, the USGS reported that there was no tsunami threat in the region.
With an epicenter over 9,200 km away, Vietnam was not affected by this earthquake. Nevertheless, experts warn that earthquakes or volcanic eruptions along the Pacific Ring of Fire can trigger chain reactions, making other tectonic plates more susceptible to breaking and causing tremors.
Previously, from late March to early April, a series of earthquakes were recorded in Papua New Guinea, Indonesia, Japan, and Taiwan. These areas are all located along the Pacific Ring of Fire—a collection of ocean trenches, archipelagos, and volcanic ranges stretching approximately 40,000 km.
Over the past decade, this region has witnessed about 90% of the world’s earthquakes.
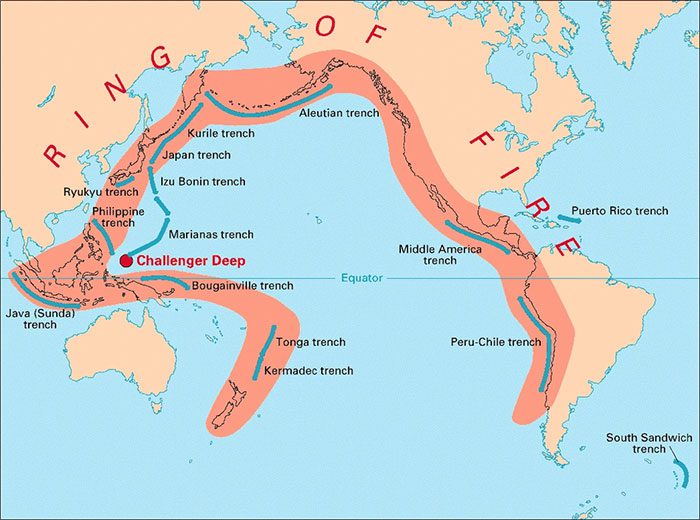
The Pacific Ring of Fire is a hotspot for earthquakes (Photo: USGS).
According to geological experts, this ring frequently experiences volcanic activity due to tectonic plates colliding and converging at subduction zones. Here, the lower plates are pushed down by the upper plates and submerge into the Earth’s mantle.
Over time, these plates melt and turn into magma. When molten rock erupts to the surface through cracks in the Earth’s crust, it creates volcanoes.
Scientists believe that climate change is one of the factors contributing to the increase in earthquakes and volcanic eruptions in recent years, due to the relationship between rainfall and seismic activity.
This occurs when certain areas face droughts, destabilizing the substrate and creating more magma. Additionally, melting ice in polar regions could also potentially increase volcanic activity in the future.