Deadly Nightshade is a medicinal herb in Traditional Chinese Medicine, but improper use can lead to poisoning or serious health consequences.
What You Need to Know About Deadly Nightshade
1. What is Deadly Nightshade?
Deadly Nightshade, scientifically known as Datura metel, belongs to the Nightshade family and is known by various names such as Mandala (white flower), Black Thorn, and other local names.
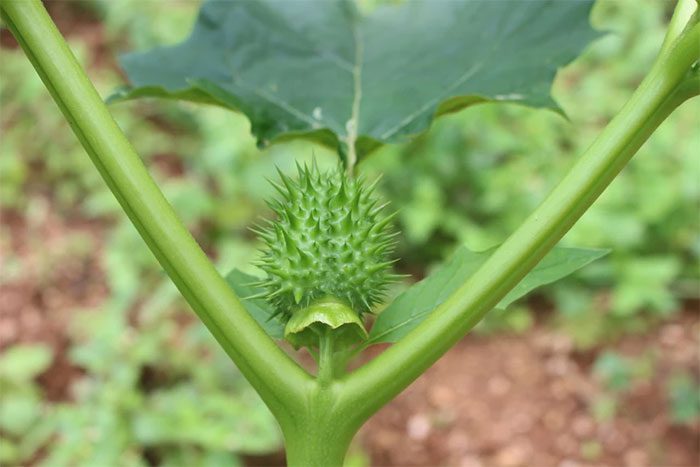
This herbaceous plant typically grows to a height of about 1-2 meters and is perennial. The stems and young branches are purple or green and have leaf scars with fine hairs. The leaves are arranged alternately with a lanceolate shape. Both sides of the leaves are hairy. The flowers resemble trumpet flowers, growing upright and solitary in leaf axils. The petals are white, the calyx is green with five teeth at the top. The fruit is spherical, green, and spiky. When ripe, it splits into four segments. The seeds are brownish-yellow and wrinkled.
In Vietnam, there are three main types of Deadly Nightshade:
- White-flowered Deadly Nightshade with green stems and branches.
- Purple-spotted Deadly Nightshade with green stems and branches.
- A hybrid of the two above types.
The leaves and flowers are commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine. However, this plant is not safe if used incorrectly, so experts advise against self-medication.
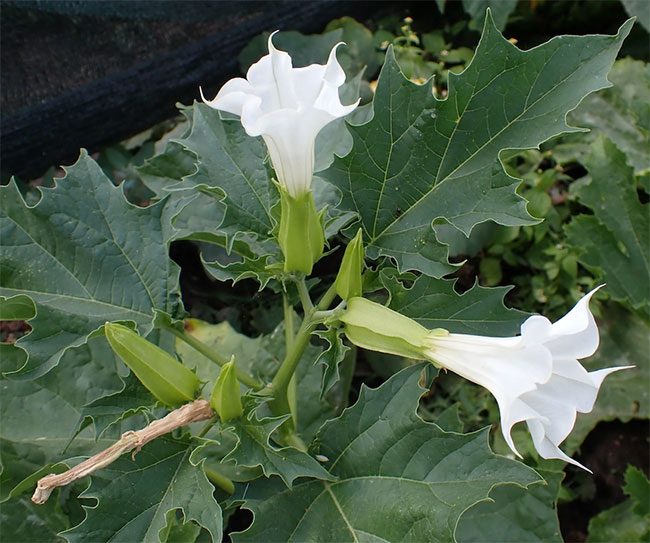

The flower of Deadly Nightshade resembles a trumpet flower, with white petals and a green calyx with five teeth at the top. (Image: Internet).
2. Uses of Deadly Nightshade
According to Traditional Chinese Medicine, Deadly Nightshade has a warm nature and a spicy taste and is classified as a toxic plant. It affects the lungs and stomach and is included in the group of medicines for treating asthma.
The therapeutic effects of Deadly Nightshade are attributed to two alkaloids: hyoscyamine and atropine. These substances can dilate the pupils, relax the bronchial muscles, and cause dryness of saliva, gastric juices, and sweat. Notably, they can reduce intestinal and gastric motility if these organs are in spasm.
Deadly Nightshade is commonly used to assist in treating specific conditions such as:
- Supporting joint and bone health
- Alleviating sciatica pain
- Treating various skin abscesses causing pain and swelling
- Managing nausea and vomiting
- Assisting in sinusitis treatment

Deadly Nightshade is used to treat conditions such as asthma and sinusitis. (Image: Internet)
3. How Does Deadly Nightshade Cause Poisoning?
As mentioned, the therapeutic properties of Deadly Nightshade are due to its alkaloids like atropine and hyoscyamine, but these same components can also lead to poisoning. Both atropine and hyoscyamine are classified as Group A toxins. Therefore, improper use can result in poisoning and even be life-threatening.
- Atropine in toxic doses affects the brain, increasing respiration, causing fever, central nervous system suppression, and paralysis.
- Hyoscyamine in toxic doses can inhibit nerve function.
4. Symptoms and Treatment for Deadly Nightshade Poisoning
The alkaloids in Deadly Nightshade can disrupt the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to intense hallucinations, delirium, and confusion, preventing individuals from distinguishing reality from imagination.
The symptoms of Deadly Nightshade poisoning largely depend on the dosage used. Low doses may manifest as slight dry mouth, reduced sweating, and a slow heartbeat. Higher doses, especially from the flowers and leaves, can lead to pupil dilation, dry, hot, and red skin, prolonged delirium, memory loss, and even death.
In cases of Deadly Nightshade poisoning, it is crucial to focus on supportive treatment (respiratory, circulatory, neurological, etc.), limiting absorption, and increasing elimination through methods such as inducing vomiting, gastric lavage, and using activated charcoal combined with laxatives to promote urination.
If poisoning is suspected, it is important to take the affected person to the hospital as quickly as possible for prompt medical attention.

The alkaloids in Deadly Nightshade can cause intense hallucinations, delirium, and memory loss. (Image: Internet).
5. Important Considerations When Using Deadly Nightshade
To ensure safety, it is essential to use Deadly Nightshade under the guidance of qualified professionals such as doctors and herbalists. When using this plant, one must exercise extreme caution and note the following:
- Only use 1-1.5g per day of Deadly Nightshade in powdered form, dried, or finely cut.
- Individuals who should avoid using Deadly Nightshade, even for medicinal purposes, include: pregnant and breastfeeding women, children, individuals with heart failure, those suffering from constipation, patients with Down syndrome, those with fever, gastric ulcers or gastroesophageal reflux, individuals with gastrointestinal infections, patients with high blood pressure or mental disorders, and those with urinary retention, colitis, narrow-angle glaucoma, etc.
True to its name, Deadly Nightshade is a medicinal herb that contains toxins. Therefore, individuals should not use this plant to prepare food or self-medicate for health issues.