Satellite Images Reveal a Hot, Dry, and Flooded Earth!
In July 2022, the world witnessed numerous wildfires, floods, droughts, heatwaves, and other extreme weather phenomena triggered and intensified by anthropogenic climate change, leading to significant turmoil globally with thousands of fatalities and millions displaced, Reuters reported.
Satellite images – showcasing scenes of extreme weather from space – have revealed a planet that is simultaneously extremely hot, parched, and flooded in various regions around the world.
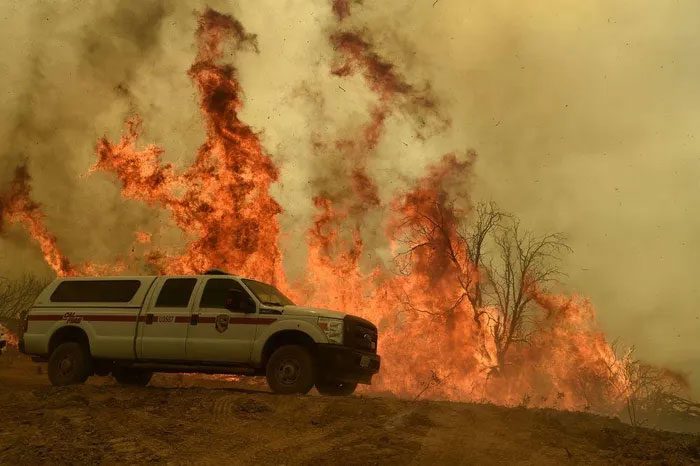

Massive wildfire in California, USA. (Photo: Neal Waters / Anadolu Agency / Getty Images)
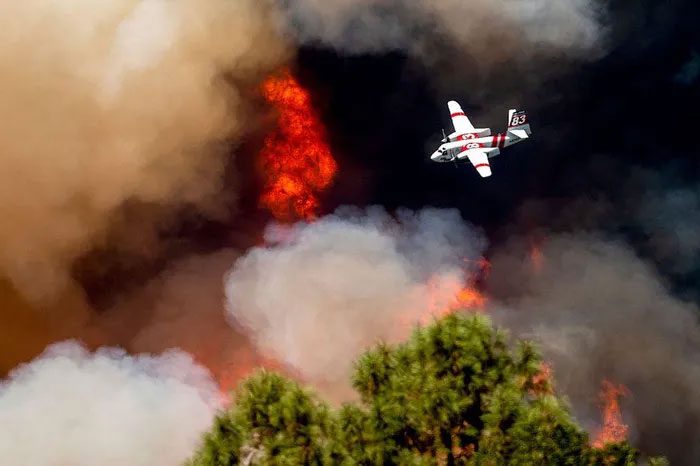

(Photo: Noah Berger / AP)
Weather satellites continuously observe Earth, sending back high-resolution images to provide real-time insights into ongoing events.
Some satellites are in polar orbits, circling the Earth in paths that take them over both the North and South Poles; others circle the Earth in sync with its rotation at an altitude of 35,785 km, known as geostationary orbits.
Atmospheric scientists rely on data from artificial satellites to help make forecasts and warnings while keeping track of global temperature changes.
The Washington Post has shared some of the most striking images from weather satellites operated by American and other space agencies in recent weeks, giving us a panoramic view of the Earth’s weather.
Severe Drought at Lake Mead, USA
Lake Mead, located in southern Nevada and northern Arizona, is the largest reservoir in the USA, formed after the construction of Hoover Dam in the late 1920s to 1930s. Approximately 20 million Americans rely on its water supply, especially in the urban area of Los Angeles.
Since 1983, a combination of increased water demand and persistent drought has left the reservoir below its capacity. As a result, it is currently at a record low level.
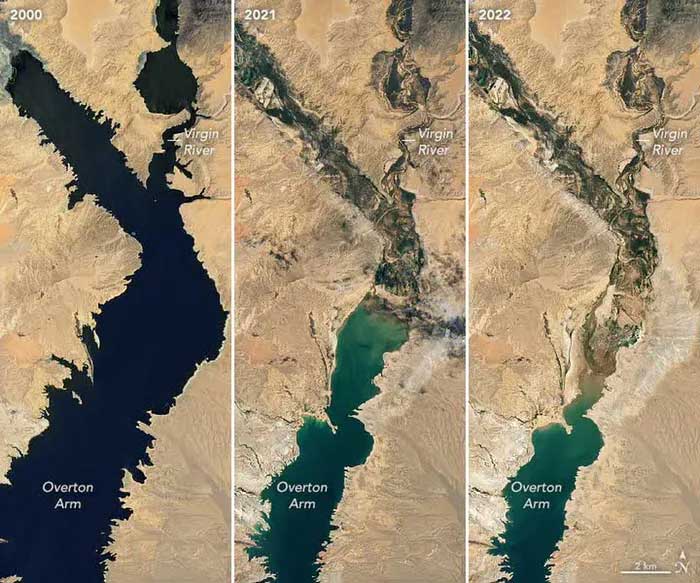

Comparison of water levels at Overton Arm of Lake Mead from 2000 to 2022 using natural color images from Landsat 7 and Landsat 8. (Source: NASA)
NASA stated: “About 10 percent of the water in Lake Mead comes from local rainfall and groundwater each year, while the rest comes from snowmelt in the Rocky Mountains flowing into the Colorado River upstream through Lake Powell, Glen Canyon, and the Grand Canyon.”
This means that Lake Mead not only serves as a ‘barometer’ indicating rainfall amounts but also provides insight into the overall water supply, much of which is stored in snowpack during the winter.
More than one-third of the western United States is experiencing “extreme” or “exceptional” drought – the two most severe levels on the U.S. Drought Monitor scale.
“Reservoir levels are very low,” the U.S. Drought Monitor reported. “Hydroelectric output is limited, alternative power sources are costly; groundwater is declining; water allocations for farmers and ranchers are being cut. Moreover, the survival of ecosystems is under threat.”
Many climate change experts believe that drought in the western U.S. will only worsen in the coming years without any signs of relief.
Wildfires Raging in California, USA
Drought has fostered conditions ripe for explosive wildfires and extreme fire events, both of which have unfolded in the weeks prior across California.
The wildfires in California are occurring near Yosemite National Park, including the Oak Fire, which ignited earlier on July 22, 2022.
Below are images from NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) satellites showing the magnitude of the Oak Fire.
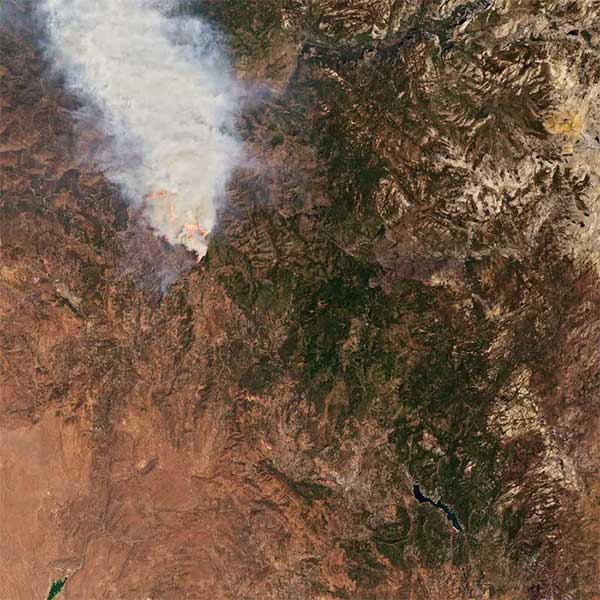

Oak Fire seen from NASA’s satellite. (Photo: NASA)

Image from NASA’s Earth Observatory shows a parched, brown, fiery scene of the blaze in California, USA. (Source: NASA)
So far, the Oak Fire has scorched 18,532 acres in Mariposa County, near Highway 140 and Carstens Road; it has also destroyed over 40 structures and 25 homes, forcing thousands to evacuate, CNN reported.
Cal Fire, the agency responsible for fire oversight, stated: “Firefighting crews still have a lot of work ahead as fires continue to flare up. About 1,440 structures remain threatened as the flames continue to escalate.”
18 of the 20 largest wildfires in California’s history have occurred since 2003. Human-induced climate change is exacerbating drought and extreme heat, contributing to further wildfires.
California is one of several western U.S. states suffering from an extended severe drought, which has been worsened by the climate crisis.
“Hellfire” Rages Across Europe
Over 1,000 people have died amid a record-breaking extreme heatwave that brought relentless harsh temperatures to Western Europe one to two weeks ago, triggering the first-ever “red warning” for heat in the United Kingdom.
Temperatures reached 40 degrees Celsius for the first time recorded in England, with nearly 30 weather stations breaking previous records in many regions of England, registering temperatures of 38.7 degrees Celsius.
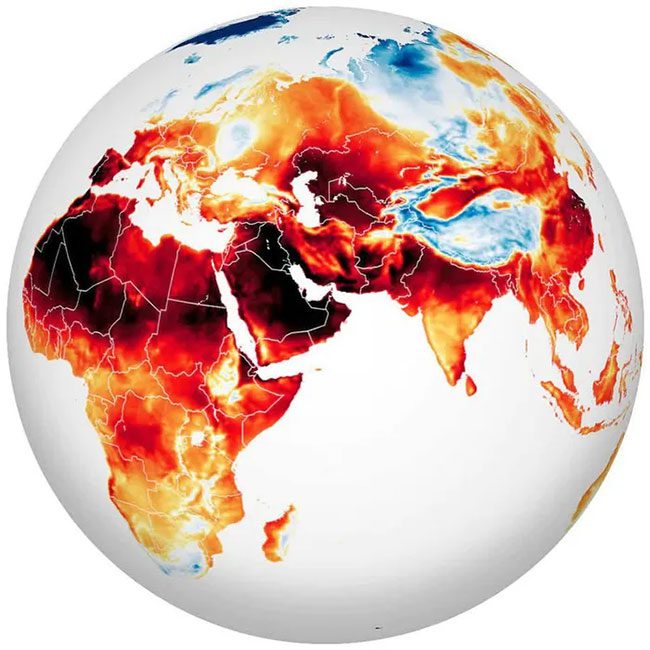
Air temperature on July 13, 2022. (Source: NASA)
Meanwhile, 40,000 residents in France had to evacuate due to wildfires, with additional blazes scorching landscapes in Portugal and Spain.
Climate change has pushed a heat dome into these countries, leading to rising temperatures and parched vegetation that is easily ignited.
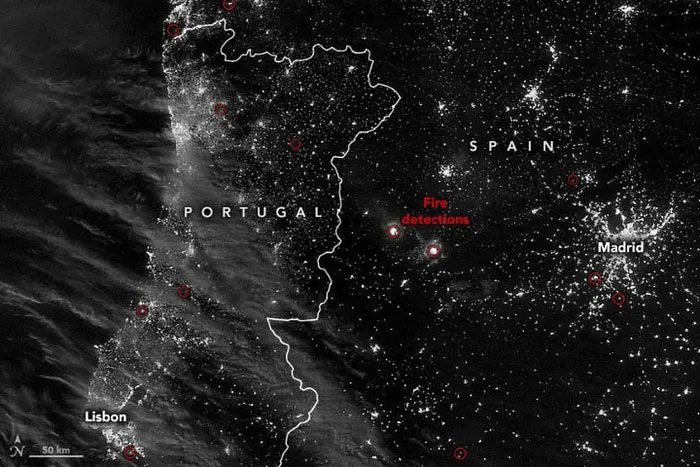
Wildfires occurring in Spain and Portugal. Image captured by the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite – a weather satellite provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). (Photo: NOAA)
The day/night band of the Suomi NPP/VIIRS satellite recorded signs of wildfires raging on the night of July 12, 2022. A fire can be seen west of Madrid (Spain), which has burned 3,700 acres.
NASA wrote: “In Portugal, temperatures reached 45 degrees Celsius on July 13 in the town of Leiria, where over 7,400 acres have been burned. More than half of Portugal is under ‘red alert’ as firefighters battle 14 spreading wildfires.”
Severe Flooding in St. Louis, USA
The impacts of human-induced climate change can exacerbate both flooding and extreme drought. The reason is simple: a warmer atmosphere accelerates the evaporation of water.
In storm-prone areas, such as the Midwest of the USA at this time, additional moisture in the atmosphere translates to downpours. However, in much of the western U.S., the warming atmosphere effectively pulls moisture from vegetation and soil, worsening drought.
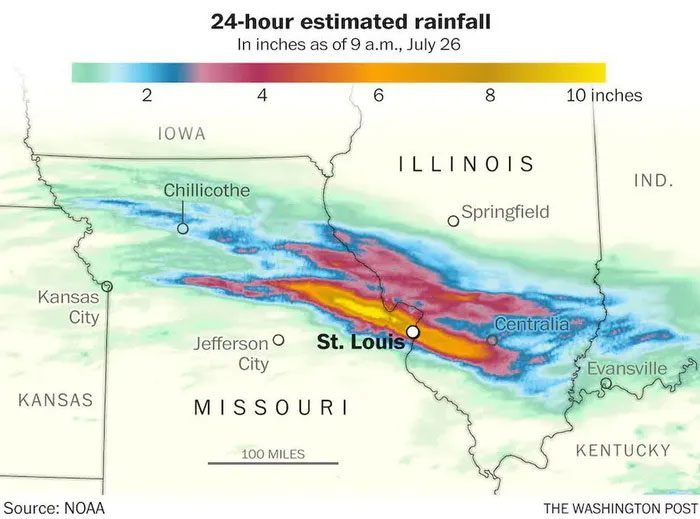
On July 25, 2022, residents of St. Louis (the second-largest city in Missouri, USA) woke up to a flash flood emergency, with several rescue operations underway as torrential rains covered the city for hours.
An astounding 198 mm of rain fell within just six hours, most of it before sunrise over St. Louis.
This historic rainfall, with only a 0.1% chance of occurring in any given year, represents the most extreme weather event recorded for the city. St. Peters in Missouri (near St. Louis) saw nearly 330 mm by 4 PM on July 25.
According to meteorological experts, such downpours are becoming more frequent in St. Louis, The Washington Post reported.
More Intense Tropical Storms
Globally, the frequency of storms has not increased. However, tornadoes are currently more prevalent in the central Pacific and the North Atlantic, while occurring less frequently in the Bay of Bengal, the northwest Pacific, and the south Indian Ocean, according to a study published in the journal Environmental Research: Climate.
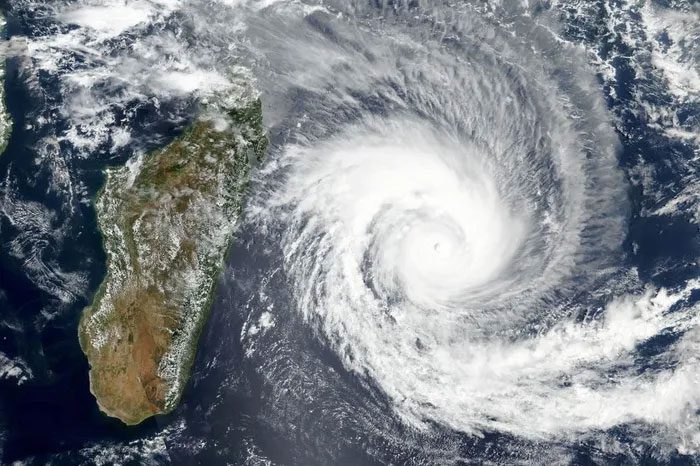

Satellite image of Storm Batsirai from NASA’s Earth Observatory. (Source: NASA)
There is also evidence that tropical storms are becoming more intense and even remain active further inland, where they can cause more rainfall over an area, as exemplified by Storm Batsirai in February 2022.


















































