According to statistics, Vietnam experiences around 250-500 cases of food poisoning each year, affecting 7,000-10,000 victims and resulting in 100-200 fatalities. The government also spends over 3 billion VND on treatment, testing, and investigations to identify the causes. The medical expenses for each victim poisoned by microorganisms range from 300,000 to 500,000 VND, while cases of chemical poisoning (from pesticides, food colorings, etc.) can cost between 3 to 5 million VND. However, the overall costs borne by hospitals are much higher.
Causes of Food Poisoning
There are many causes:
1. Food contaminated by microorganisms (33-49%) – primarily due to strains of Salmonella, E. Coli, Clostridium Perfringens, and Listeria bacteria.
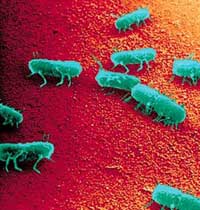 |
Salmonella Bacteria (Image: astrosurf) |
Salmonella bacteria are responsible for 70% of food poisoning cases and can be found in various food items (cold cuts, raw meat, shellfish, undercooked chicken, unpasteurized dairy products…), particularly in dishes made with fresh or slightly raw eggs.
Listeria Bacteria: can develop even at low temperatures (4-6°C) in refrigerated meats, unpasteurized cheese, cold cuts (pâté, Vietnamese pork sausage), and frozen pig tongues. Listeria poses the most significant risk to pregnant women, causing infections in the fetus that may lead to miscarriage.
Toxins account for 20-30% of collective food poisoning incidents. Among these, Staphylococcus Aureus is present in hand-prepared foods (pastries), while Clostridium Perfringens often arises in dishes that are cooked and reheated.
2. Contamination from chemicals (11-27%): CN-, As, Cl-, Hg, Pb, Benladol, food preservatives, and pesticides. 27% of poisoning cases are due to consuming food contaminated with chemicals.
3. Poisoning through: water, food, air…
4.
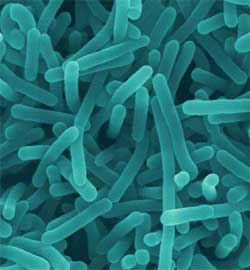 |
Listeria Bacteria (Image: biology.kenyon.edu) |
Natural toxins in food (6 – 37.5%):
- Cyanide (CN) is found abundantly in cassava and bamboo shoots… (the lethal dose for humans is 50-90 mg/kg). Sour bamboo shoots, when soaked, can combine with certain enzymes in the human intestines to form HCN (hydrogen cyanide), causing acute poisoning.
- Phytate in grains (content = 2-5g/kg), is a salt of Calcium Phytic. When receiving 1g of Phytate, the body immediately loses 1g of Calcium.
- Alkaloids (Solanine and Chaconine) in sprouted potatoes or those with green skins, exposed to ultraviolet rays and sunlight, have significantly increased Solanine (toxic substance) levels.
- Oxalic Acid – a calcium inhibitor commonly found in starfruit, tamarind… (5g of Oxalic Acid can be fatal for a 70 kg adult).
- Molds that thrive in Vietnam’s hot and humid environment, especially in grains and oilseeds, can spoil food and produce dangerous toxins. Aflatoxin, a toxin produced by Aspergillus Flavus and Aspergillus Parasiticus in moldy corn, beans, and peanuts, is highly toxic and can cause liver cancer.
- Histamine in spoiled food.
- Poisonous mushrooms, pufferfish, and toad meat, etc., contain Tetradotoxin.
Additionally, there are many cases of poisoning where the cause cannot be identified.
According to an investigation by the food safety authority:
- Ice cream has 55.2% that does not meet quality standards (with 75.4% E. coli; 70.3% Staphylococcus aureus).
- Street food has 87.5% contamination with microorganisms.
- 85.7% of street beverages do not meet standards…
This does not include food contaminated with pesticides (sprayed in high concentrations, not isolated from the harvest date), or additives (borax, industrial dyes, chemical sugars).
Therefore, to avoid poisoning, it is best to buy food directly from markets, choosing live animals (fish, shrimp, chicken, ducks…) that are still moving. For slaughtered and pre-prepared foods, purchase them from reputable places that guarantee the quality of their products, and of course, keep the receipts so that if poisoning occurs, you can identify the source and the seller… for legal procedures and appropriate compensation.
Attention should also be paid to the food preparation practices of each individual and family. Ensure that kitchen utensils are kept clean. Cassava contains cyanide, both in the flesh and the skin (often at higher levels). The best way to eliminate cyanide from cassava is to peel it and soak it in cold water for several hours before boiling; during boiling, keep the pot uncovered to allow cyanide to evaporate. For potatoes, cassava, and peanuts, consumers should not store them for long periods. To avoid solanine poisoning found in potatoes, do not eat tubers that have sprouted, turned green, or have been out of the ground for too long. Be cautious with food that has been stored for extended periods or improperly stored, which may have been contaminated by rats, insects, cockroaches, or flies.
Dr. Bui Manh Ha