The liver is the largest internal organ in the body, performing many important functions. It is also the first organ to receive nutrients and chemicals absorbed from the digestive system, acting as a “blood filter” before nutrients are converted into various forms used by the body.
For this reason, what you eat is closely related to liver function. To protect the liver, it is essential to learn about foods that are beneficial for liver health and those that can cause harm. This article will discuss foods to avoid for liver health.
Pastries

Pastries increase triglyceride levels in the body.
Many people enjoy sweet treats like cookies and muffins without realizing that consuming too much of these foods can harm the liver. Pastries are often high in sugar, and excessive consumption can lead to weight gain and obesity, particularly increasing triglyceride levels in the body. These factors can lead to various liver diseases.
Additionally, the main ingredient in many pastries is refined white flour. This type of flour is difficult to digest and can lead to fat accumulation in the liver.
Sugary Drinks

Drinking too many sugary drinks can lead to weight gain and obesity.
Occasionally consuming a sugary beverage won’t cause issues, but regular consumption can be harmful to the liver.
Excessive intake of sugary drinks can also lead to weight gain and obesity, conditions that are often associated with fatty liver disease. Furthermore, sugary drinks contain high amounts of sugar and refined carbohydrates (also known as empty calories), both of which are detrimental to liver health.
Alcoholic Beverages
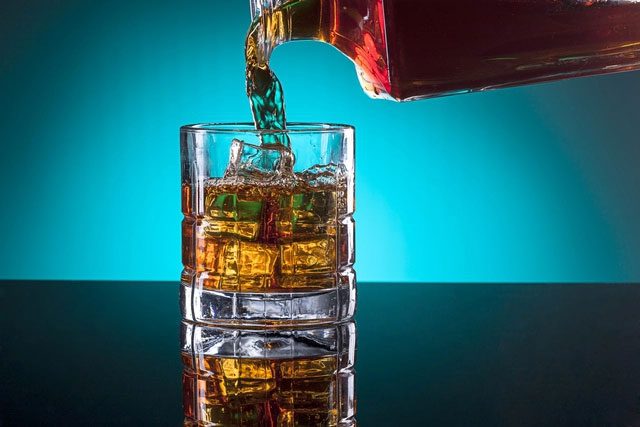

Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages over time can lead to cirrhosis.
Alcoholic beverages are often the first item recommended to limit for maintaining a healthy liver. In Western countries, experts recommend that both men and women consume no more than 14 units of alcohol per week. Drinking too much alcohol forces the liver to work harder to metabolize it. The chemical reactions involved in this process can damage liver cells, leading to inflammation, necrosis of liver cells, and scarring (fibrosis).
Moreover, regular excessive drinking can affect nutrient absorption, further increasing the harmful effects of alcohol on the liver.
Long-term excessive alcohol consumption can lead to cirrhosis, a condition where the liver has significant scarring and cannot recover. Patients with cirrhosis may experience complications such as vomiting blood, jaundice, swelling, and even liver cancer.
White Flour
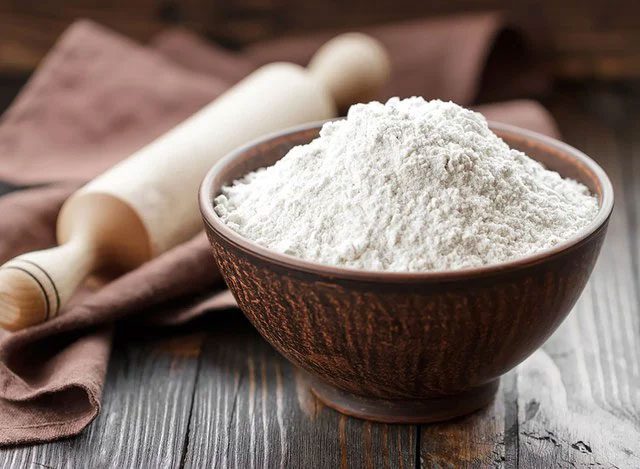

Whole grain cereals are more beneficial for liver health.
As mentioned earlier, consuming a lot of white flour can lead to liver diseases. Therefore, people should limit foods made from white flour such as cookies, pizza, pasta, and white bread. These foods are low in essential minerals, fiber, and vitamins.
Refined grains are more easily converted into sugar and can accumulate as fat in the liver, which is a primary cause of fatty liver disease. Instead of choosing white flour, opt for healthier products that benefit liver health, such as whole grain cereals.
High-Sodium Foods
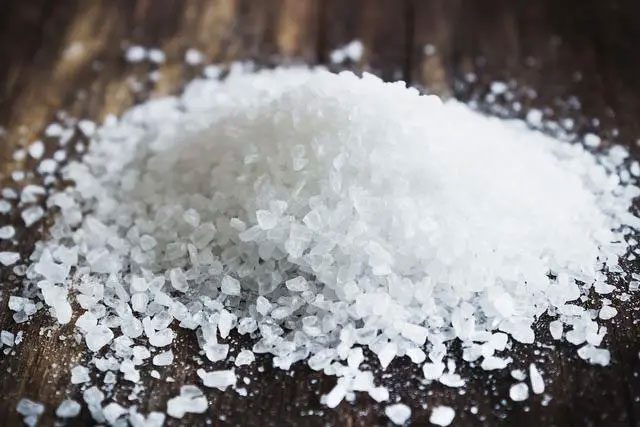

A high-sodium diet can affect the liver’s detoxification process.
Not only sugar, but salt is also a seasoning that can be harmful to the liver if consumed excessively. A diet high in salt can impact the liver’s ability to detoxify, gradually diminishing its functional capacity.
Some high-sodium foods like potato chips, salty crackers, and canned foods also contain high amounts of saturated fats, further exacerbating liver harm by increasing the risk of fatty liver and obesity.
Red Meat
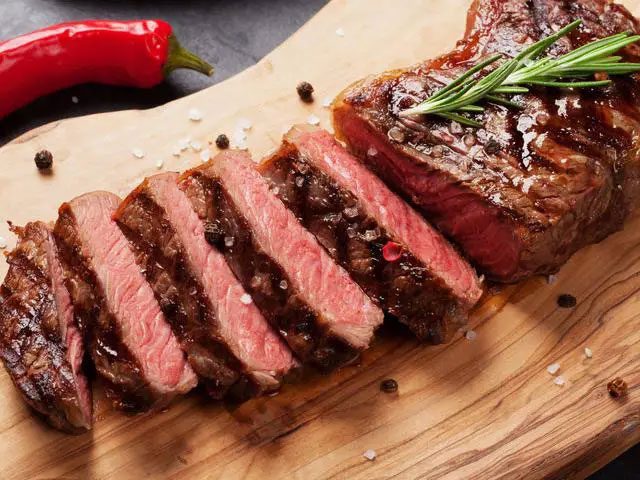

Red meat is high in protein, requiring the liver to work harder to metabolize it.
Red meat contains a lot of protein. Excessive protein intake forces the liver to work harder to metabolize it. Furthermore, the accumulation of excess protein in the liver can lead to fatty liver disease and adversely affect the brain and kidneys.
Similar to red meat, eggs are also high in protein. Overconsumption of eggs can lead not only to digestive issues but can also contribute to liver and kidney diseases.