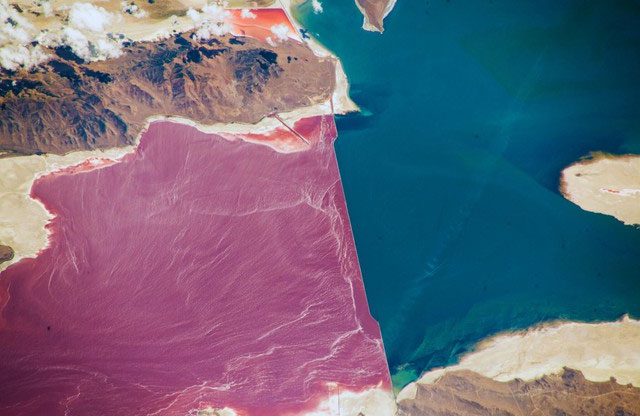
The Great Salt Lake in Utah, USA is a fascinating natural site with a unique landscape: the lake is divided into two parts, one side shimmering blue and the other a vibrant red.
The Great Salt Lake, a vast body of water in Utah, features an astonishing characteristic where one side is a brilliant blue while the other is a mysterious red. The reason for this striking contrast is a massive embankment railway that bisects its center, creating two distinct bodies of water with very different characteristics – the Lucin Cutoff, a 102-mile railway constructed in the early 1900s.
This railway plays a crucial role in connecting densely populated areas in Utah, such as Salt Lake City and Ogden, with destinations in the western United States like California and Nevada.

The Great Salt Lake is famous for its vast area and huge salt reserves.
Located in the west of Utah, the Great Salt Lake is one of the largest saltwater lakes in the Western Hemisphere. Renowned for its vast expanse and enormous salt reserves, the lake also captivates visitors with its unique natural landscape featuring two vivid water colors: blue and red. The unusual color division of the Great Salt Lake is due to a combination of factors, including topography, salinity concentration, and the presence of microorganisms. The railway built in 1959 inadvertently separated the lake into two parts, limiting water flow between the areas, resulting in differences in salinity levels.
Initially, this route was merely a wooden bridge, which obstructed the natural flow of water in the lake. However, by the late 1950s, it was replaced by a solid rock embankment, further restricting the exchange of water between the two sides of the lake and leading to the formation of two distinct branches – the northern and southern sections.
The southern branch, immersed in brilliant blue, receives a continuous supply of freshwater from three major rivers: the Bear, Weber, and Jordan Rivers. This dilutes the salinity, making it much less concentrated compared to seawater.

Over time, the water in this area has become nearly 10 times saltier than the ocean!
The turquoise color in the southern part of the lake is mainly due to the reflection of sunlight from the lake’s bottom. This water area has a lower salinity concentration compared to the northern section, thus it is not salty enough to support the growth of Dunaliella salina. However, the lake remains home to various types of microorganisms, contributing to the characteristic blue color – blue bacteria and algae thrive here, creating the distinctive blue hue of this area.
On the other hand, the northern branch is completely cut off from freshwater, and over time, the water in this area has become nearly 10 times saltier than the ocean! This harsh environment has spurred the development of halophiles and some forms of algae. These tiny organisms create the striking red color of the northern branch.
Moreover, the wetlands along the eastern and northern edges of the Great Salt Lake provide essential habitats for millions of migratory birds and waterfowl in western North America. These areas account for about 75% of Utah’s wetland area.

The distinctive red color comes from the presence of Dunaliella salina.
The characteristic red color in the northern part of the lake comes from the presence of Dunaliella salina, a type of unicellular algae containing red pigments. This type of algae thrives in salty water environments with sunlight, creating a bright red hue for this area. The high salinity in the northern part of the lake also contributes to the proliferation of Dunaliella salina. The colors of the lake can change with the seasons. In summer, when evaporation increases, salinity levels rise, making the red in the north even more vibrant.
The Great Salt Lake is home to many unique plant and animal species adapted to the harsh saline environment. Some representative animals include diving birds, gulls, brine shrimp, and tilapia. The ecosystem of the lake plays an important role in maintaining the ecological balance of the region.

This is also a popular tourist destination with many exciting activities.
The Great Salt Lake is an important source of salt for the region. The salt mining industry has thrived here since the 19th century, providing raw materials for various industries. Additionally, it is a popular tourist destination with many exciting activities such as swimming, sunbathing, kayaking, and bird watching. Visitors can also tour the salt mining facilities to learn about the history and production processes of salt.
The Great Salt Lake is a unique natural wonder with impressive beauty and diverse ecosystems. The color division of the lake is a natural phenomenon that attracts visitors from around the world. The Great Salt Lake is a valuable heritage that needs to be protected and preserved for future generations.

The unique ecosystem of the Great Salt Lake is facing many threats.
Despite its red color, the water in the northern lake is not toxic. The red color comes from beta-carotene, a health-beneficial antioxidant. The unique ecosystem of the Great Salt Lake is facing many threats such as environmental pollution, climate change, and over-exploitation. Conservation of the lake is crucial to maintain biodiversity and ensure valuable natural resources for future generations.