A hyena has successfully stolen food from a pack of African wild dogs multiple times. It thought this time would be no different; however, it was unexpectedly surrounded by them. Can the hyena escape this revenge?
Hyena – The Notorious “Second Brother” of the African Savannah
The hyena, known in English as Hyenas, is a relatively common carnivorous animal in Africa, playing a crucial role in maintaining the ecosystem here. There are currently three species of hyenas: the spotted hyena, the brown hyena, and the striped hyena. Among them, the spotted hyena is the most fearsome, boasting a massive size, cunning eyes, and exceptionally keen hearing.
Hyenas can survive in various environmental conditions, from scorching deserts to the harsh icy terrains of high mountains over 4,000 meters in East Africa. Hyenas are often praised for their teamwork when hunting, as well as their persistent pursuit of prey.

Hyenas are praised for their teamwork when hunting, as well as their persistent pursuit of prey. (Photo: AZ Animals)
Hyenas can kill large animals such as zebras, wildebeests, and buffaloes. However, they rarely hunt on their own and mainly follow other predators like lions and leopards, stealing their food when these animals are unguarded. Due to their body structure not being ideal for hunting like lions or leopards, they find it challenging to control or kill prey, forcing them to rely on other species for food.
In Africa, the spotted hyena ranks just below lions (when they encounter each other alone) in terms of strength. Sometimes, hyenas even “bully” lions when they outnumber them. All leopard species tend to lose to hyenas in encounters, despite the leopards having better hunting skills than both hyenas and lions. Therefore, hyenas often steal prey from leopards.
African Wild Dog – The Ultimate Hunter
The African wild dog (Lycaon pictus) is a mammal belonging to the dog family distributed across Africa. They are also one of the strongest biters among carnivorous mammals. They primarily inhabit eastern and southern Africa, particularly in two large populations in the Selous Game Reserve in Tanzania and a concentration in northern Botswana and eastern Namibia.
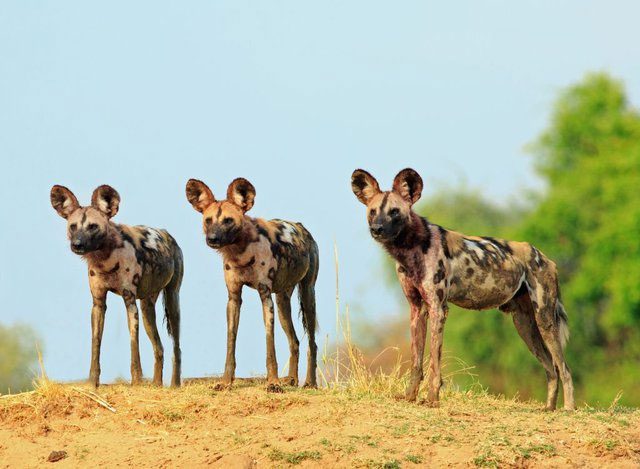

African wild dogs are masters of cooperative hunting on the savannah. (Photo: AZ Animals)
African wild dogs typically live in packs of 6 to 20 and hunt collectively. They are known as masters of cooperative hunting on the savannah, boasting a success rate of up to 80% in each hunt. Each individual wild dog possesses a strong sense of discipline and unity. This is one of the standout traits that help them survive in a harsh environment filled with much larger and more dangerous predators.
With excellent vision and remarkable endurance, wild dogs can chase prey for up to 8 kilometers, reaching speeds of up to 66 km/h. Additionally, their jaws can deliver a powerful bite force of up to 240,000 kg/m2, with their lower jaws being larger than domestic dogs and their molars designed to strip flesh from bones. These factors explain why they are hailed as the “ultimate hunters” of Africa. They even have the audacity to steal prey from apex predators like lions, hyenas, or crocodiles.

African wild dogs and hyenas are both top predators in Africa. (Photo: AZ Animals)
The Relentless Battle Between Hyenas and African Wild Dogs
Both African wild dogs and hyenas are top hunting teams in Africa. Living in the same habitat with limited food resources, these two species inevitably compete daily. So, in their conflicts, which one will emerge victorious: the hyena or the African wild dog?
Africa Geographic, a unit specializing in tourism and conservation, released a video capturing the moment a hyena fled desperately when chased by a pack of wild dogs. Reportedly, this hyena had “attempted multiple times” to steal food from the wild dog pack. With a significantly larger number, the African wild dogs proactively attacked the hyena. After a struggle, the hyena realized it could not withstand the pressure and ran toward a lake. The hyena escaped thanks to its excellent swimming skills. At this point, the African wild dog pack also abandoned their pursuit.

With a significantly larger number, the African wild dog pack proactively attacked the hyena. (Photo: AZ Animals)
Combining data about the two species, it can be seen that the advantages of hyenas are their larger size, stronger bite force, and higher intelligence. The advantages of African wild dogs lie in their speed, good stamina, strong pack unity, and superior hunting skills. In a one-on-one fight, hyenas have an absolute advantage. However, in group fights, African wild dogs have a higher chance of winning. In fights with equal group sizes, unity is crucial; the group that is more flexible and resilient will have the upper hand. When hyenas attack, African wild dogs only need to avoid the attacks and cleverly wear down the hyena’s stamina for a chance at victory.