This Christmas, the United States is experiencing nationwide freezing conditions, impacting millions.
“White Christmas” Claims Many Lives
On December 25, according to U.S. time, many regions across the country reported freezing conditions and snowstorms, with temperatures dropping below -40 degrees Celsius in some areas. According to The Guardian, the severe cold weather has affected approximately 150 million Americans, putting the homeless at particular risk to their lives and health.
According to NBC statistics, there have been 41 weather-related deaths reported on December 25. Nationwide traffic was heavily disrupted; not only roadways but air travel was also significantly affected, with over 3,300 domestic and international flights canceled and 11,000 others delayed on Christmas Day alone.
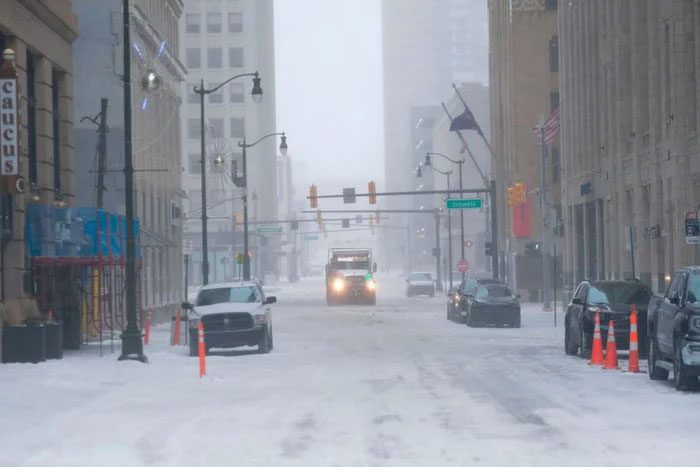

Snowplows in Detroit on December 23.
According to the governor of New York, the snowstorm that swept through Buffalo – an area particularly hard-hit, “will go down in history as the deadliest snowstorm ever.” AFP also reported that the night of December 24 may have been the coldest Christmas Eve in U.S. history.
Al Jazeera reported that the extreme cold may continue to claim more lives as many people could be trapped in their vehicles, not to mention power outages affecting hundreds of thousands of homes and businesses.
Most of the fatalities occurred in and around Buffalo, located on the shores of Lake Erie in western New York, due to snow meeting the “lake effect”, causing it to be colder and thicker. The lake effect occurs when cold air moves over warmer lake waters, creating severe cold that lasted throughout the Christmas weekend.
The scale of the snowstorm named Elliott is almost unprecedented, stretching from the Great Lakes near Canada to the Rio Grande along the border with Mexico. About 60% of the U.S. population was under warnings, and temperatures plummeted well below normal from the eastern Rockies to Appalachia, according to the National Weather Service.
How Do Record Cold and Snowstorms Impact Us?
Climate scientist Daniel Swain stated that the impact of the cold on the human body or infrastructure in the current situation is more severe because, in general, humanity is witnessing rare events of such extreme cold compared to the past.
Deep freeze events have occurred before, but they are becoming more severe. The rapid and extreme shift in weather patterns, from record-high temperatures to sudden lows, can profoundly affect adaptation, especially for plants, animals, and ecosystems.

Both humans and flora and fauna will be severely affected.
Snowstorms may very well have a specific connection to the climate crisis – to what extent is still being discussed. But it is clear that the fundamental impacts caused by global warming could make them feel harsher.
The National Weather Service stated that at freezing temperatures like those recently observed, frostbite can occur in less than 5 minutes.
Alex Lamers, a meteorologist coordinating warnings for the National Weather Service’s Weather Prediction Center, noted that “it is unusual to witness such a rapid temperature drop in such a short period.” This situation becomes even more shocking as many places across the U.S. have been experiencing a record warm December.
Experts say that this situation threatens even species well-adapted to cold.
Brooke Bateman, Director of Climate Science at the National Audubon Society, remarked: “Bird species usually can cope with freezing conditions—especially in areas with low temperatures. But in such cold weather, they need to expend more energy and require more food, putting them at risk of not being able to survive.”
Migratory species may face significant challenges, especially those that linger longer in the North due to previous warm weather. The sudden cold, snowstorms, and food scarcity will pose severe threats to them.
What Caused This “Horrific” Cold Snap and Snowstorm?
According to Bloomberg, this cold snap and snowstorm were caused by a weak North American jet stream that allowed cold air from the Arctic to surge down into the low-pressure area over the Great Lakes and deep into the continental U.S. Jennifer Francis, a senior scientist at the Woodwell Climate Research Center in Falmouth, Massachusetts, stated that this weather may be driven by a “more erratic” jet stream than usual.
The jet stream is a fast-flowing air current in narrow bands that exists in the atmospheres of planets like Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are found at the height of the tropopause, blowing from west to east in a wavy path.
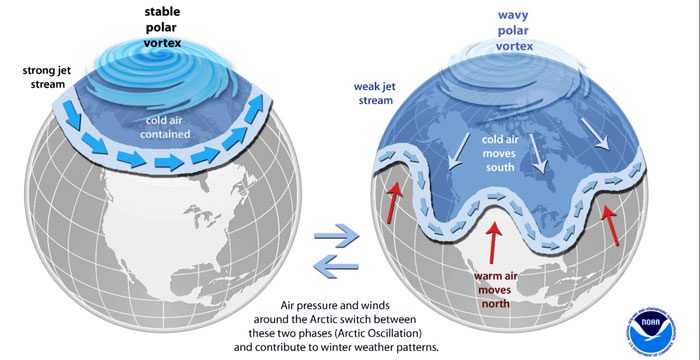
Left image: When the jet stream is strong enough, it causes the polar vortex to circulate stably around the pole. Right image: A weak jet stream allows the polar vortex to “leak” cold air southward.
According to The New York Times, the cold air surge from the Arctic at this time is caused by a jet stream that is not strong enough to keep the polar vortex anchored over the Arctic, allowing it to move southward. The polar vortex is a large area of cold air that typically circulates around the Arctic but can sometimes shift southward.
The polar vortex is also known as the Arctic blast when it is in the Arctic. Besides the Arctic vortex, there is also an Antarctic vortex.
Cold snaps associated with the polar vortex occur frequently in the U.S. One of the most damaging events happened in February 2021, when cold air penetrated deep into Texas, leading to temperatures plummeting 22 degrees Celsius below normal.
Moreover, as it moves southward, the dry cold air from the North collides with warm, moist air from the South, creating a “bomb cyclone”. When a bomb cyclone occurs, pressure in the area drops extremely quickly over 24 hours.
Typically, bomb cyclones occur over water-rich areas to provide energy for the storm. However, in this storm, the massive cold air from the North caused a rare bomb cyclone to occur right over land.
Is It Related to Climate Change?
According to the latest analysis, as global carbon dioxide emissions continue to rise, the Arctic is warming nearly four times faster than other areas on the planet, and the sea ice coverage in the region is shrinking. Therefore, as the polar vortex shifts southward, two fundamental questions arise. What role does climate change play, if any? And will extreme freezing conditions increase as warming continues?
Unfortunately, there are no clear answers.
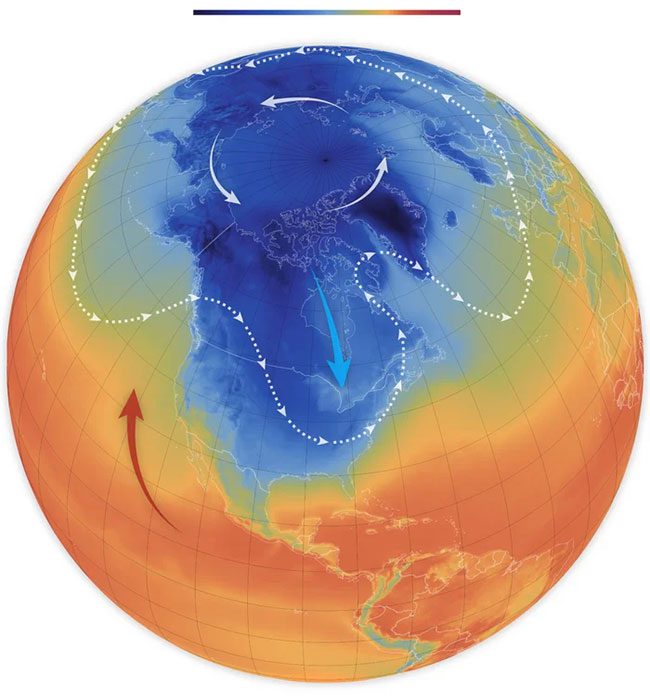
Illustration of cold air from the Arctic being pushed down to North America.
However, one thing is certain: the unusual behavior of jet streams pushing this cold air is related to climate change. Jeff Masters, a meteorologist at Yale Climate Connections, stated, “An event like this could happen naturally. But with the disruption of global weather patterns that climate change is causing, the probability of witnessing unusual weather phenomena (like this) in any season increases.”


















































