Almost everyone is aware of heart failure, yet few people understand it in detail. It is one of the leading causes of hospitalization for individuals over 65 years old and is responsible for 35,000 deaths annually in France.
What is Heart Failure?
 |
|
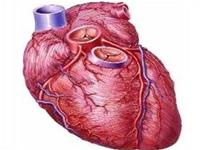
Heart (Photo: TTO) |
The heart becomes less effective at pumping blood into the arteries, which nourishes the tissues in the body to maintain normal function. The heart acts as a pump to circulate blood throughout the body, and heart failure occurs when this pump is no longer functioning properly due to fatigue of the heart muscle (especially the left ventricle).
Many heart conditions weaken the pumping function (primarily as a result of myocardial infarction). Hypertension forces the heart to endure excessive pressure, which is a primary cause of heart failure.
Who is at Risk for Heart Failure?
Heart failure commonly occurs in individuals over 65 who have hypertension, long-term imbalances, and risk factors leading to cardiovascular diseases such as diabetes and high cholesterol. Often, these individuals have previously experienced a heart attack. It is also noted that even very young people can suffer from heart disease, particularly if they are victims of myocardial infarction or viral infections related to the heart. Caution is advised against the excessive consumption of alcohol, which is highly detrimental to health.
Warning Signs to Watch For
Shortness of breath with exertion: Climbing stairs or running requires the heart to exert more effort. Blood must be pumped four times more than normal, leading to the heart’s inability to perform its role effectively. The result is congestion in the lungs, causing difficulty breathing.
Nocturnal dyspnea: Lying flat can cause fluid to accumulate in the lungs. In severe cases, respiratory issues may interrupt sleep.
Unusual fatigue: The organs do not receive adequate blood and oxygen, leading to physical and mental exhaustion throughout the day.
Swelling around the ankles: Fluid in the body is not completely eliminated by the kidneys, resulting in accumulation in the lower legs.
Frequent rapid heartbeat: The heart is forced to beat faster to ensure blood circulation.
Upon noticing these signs, it is crucial not to hesitate and to seek examination from a cardiologist for an echocardiogram. Early diagnosis of heart failure is vital to prevent complications when the condition is detected in the acute pulmonary edema stage. Hospitalization may be necessary.
What Should Individuals with Heart Failure Do?
In addition to taking medications, individuals with heart failure should maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Reduce salt intake:
Excessive salt consumption can lead to water retention. It is best to limit salt intake to 4-6g per day (compared to 12g for healthy individuals), and to avoid canned foods, processed meats, and industrial sauces. Only mineral water with less than 100mg of sodium per liter should be consumed.
Preventive Measures
– Protect your heart: First and foremost, adhere to good habits for a healthy lifestyle.
– Quit smoking: It is never too late to stop smoking for smokers.
– Be cautious about rapid weight gain: It forces the heart to work excessively.
– Monitor cholesterol levels: Consume more fruits and vegetables and low-fat foods.
– Maintain balanced blood pressure and diabetes: Follow prescribed treatment diligently.
– Properly manage heart disease: Take medications as prescribed and have regular check-ups.
Mark the salt container and even potassium salt, as excessive intake can lead to many harmful consequences.
Exercise regularly: The goal is not to run a marathon! Cardiologists recommend walking or swimming for 30 minutes a day, at least three times a week. First, break the cycle of fatigue and breathlessness, which gradually destabilizes homeostasis and leads to muscle tone loss. Subsequently, the benefits of exercise are real: arterial tone normalizes, and cardiovascular issues decrease.
Return to exercise should be done gradually with professional support (cardiac rehabilitation centers, exercise therapy doctors).
Follow Medication Guidelines:
Treating heart failure is often a long-term process, as it involves a combination of three types of medications (including diuretics), but this is essential to prevent abnormal changes in the condition. It is necessary to monitor heart health regularly to adjust treatment accordingly.
Dr. ĐẶNG MINH TRÍ