|
| A black hole stretching a star (Image: VNN) |
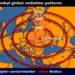
NASA scientists from the American Space Agency have discovered that all nine black holes at the center of the galaxy they observed primarily release energy in the form of matter beams, rather than X-ray radiation as previously thought.
The observed black holes possess immense energy, containing a mass up to three billion times greater than that of the sun. However, the amount of energy radiation emitted is less than any existing object in space, including quasars (which resemble stars but are very distant and emit electromagnetic radiation).
To illustrate, if the heat emitted from a burning campfire is likened to the radiation from a star, then a larger fire, corresponding to a star with higher energy, should emit more heat. Yet, the black holes they observed radiate energy akin to the heat released by the sun, which is comparable to that of a flashlight.
If we consider existing nuclear power plants on Earth as the most efficient structures, these black holes are 20 times more efficient. This figure of 20 is technically not a “normal” number, as achieving this value would require all systems to be absolutely closed and entirely pure, even including the screws in the nuclear power plant.
To visualize this easily, if your motorcycle achieves 30% efficiency, to raise it to 32%, you would need to replace the entire engine with aluminum alloys specially designed for fuel combustion tanks of space shuttles. Achieving a 20-fold increase in efficiency would require your motorcycle to “burn” even the exhaust, which is considered impossible with our current technological level.
The matter beams escaping from black holes remain a mystery, as even light is drawn into them. How, then, can these matter beams—traveling at only 95% of the speed of light, approximately 300,000 km/s—escape? A hypothesis suggests there may be a thrust mechanism or spring-like propulsion helping these matter beams overcome the immense gravitational pull of the black holes; however, everything needs to be thoroughly verified before being announced to the media.
These beams extend for hundreds or thousands of light years, and the energy they contain amounts to trillions of trillions of trillion Watts. This energy source is sufficient for black holes to exist for hundreds of billions of years more, far exceeding the current age of the universe, which is 13.7 billion years. As these beams move, their heat will warm the gas clouds surrounding the galaxy, similar to how material clouds form stars and causing the universe to expand further. This phenomenon is akin to melting a block of butter—while the butter melts and its volume increases, our universe expands rather than flattening out like the butter. Without this heat source, the gas clouds would cool down into stars, which is how stars are formed.
Nguyễn Thử Vương