Perhaps this will remain a question for humanity for all eternity, as we cannot truly answer it, but let’s try to imagine what a boundary of the universe would look like if it had one.

Throughout history, humans have always yearned to answer the question of where the vast expanses of space end. (Illustration: Getty).
For thousands of years, the night sky has remained an unchanging mystery. From all corners of the world, people have used the stars for navigation and exploration of the universe.
To the naked eye, the sky appears infinite. However, thanks to the invention of the telescope 400 years ago, we have been able to see much farther.
The telescopes have continuously improved, helping discover new phenomena in the sky. Many new stars have been discovered, and astronomers have noted strange clouds, referred to as “nebulae,” from the Latin word meaning “mist” or “cloud.”

The image of the Large Triangulum Galaxy is a composite of 54 images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. With an impressive size of 34,372 x 19,345 pixels, this is the second-largest photo ever taken by Hubble and published (Photo: NASA, ESA, M.Durbin, J.Dalacanton, B.F.Williams).
Nearly 100 years ago, we established that these nebulae are, in fact, galaxies similar to the Milky Way, in which Earth resides.
Interestingly, no matter which direction we look into the universe, we see more and more galaxies. In a photo taken by the James Webb Space Telescope, even a tiny portion of the sky, like a grain of sand, contains thousands of galaxies.
It is hard to imagine that there could be a boundary beyond which such images no longer exist.
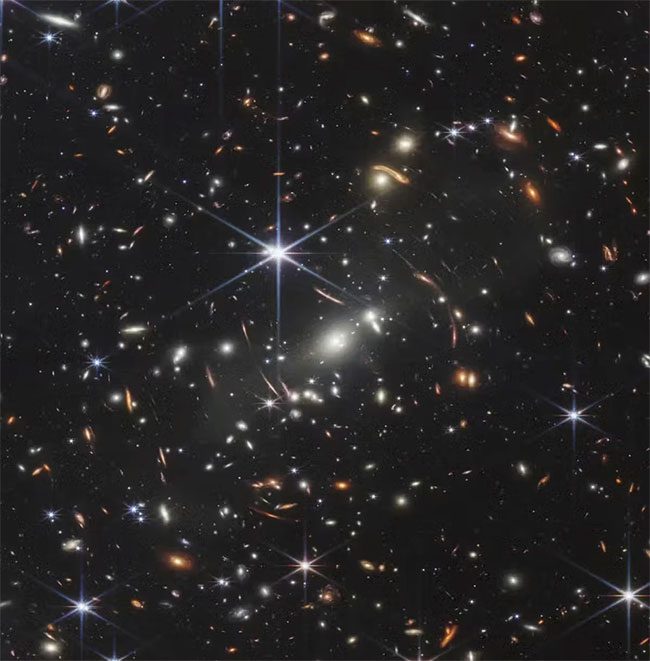

So far, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the farthest and clearest images of the universe. This is the first deep field image from James Webb, capturing the SMACS 0723 galaxy cluster with countless details (Photo: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScl).
Boundary of the Universe
Nevertheless, there is technically a boundary to the universe that we call the “observable universe.” This is because no one really knows whether the universe is finite or infinite, and we may never know due to the speed of light.
We can only see light that has had enough time to travel to Earth. Light travels at an exact speed of 299,792,458 meters per second. Even at this speed, it still takes a considerable amount of time to traverse the universe. Scientists estimate the minimum size of the universe to be 96 billion light-years, and it is likely even larger.
If the Universe Has a Boundary, What Would We See?
Suppose we travel to the very, very far boundary of the universe; what would be there?
Many scientists hypothesize that there would simply be… more universe. But there are also other hypotheses. If our universe is finite and you reach the end, you might transition into an entirely different universe.
While there is no clear answer to the question “Does the universe have a boundary?”, it is precisely such questions that have propelled us to continue exploring and understanding the universe while grasping Earth’s place in that vast expanse.