Earwax is one of the products of the excretory system. Based on the characteristics of earwax, it is possible to determine the health condition of the individual. So, what does normal earwax look like?
What You Need to Know About Earwax
1. Where Does Earwax Come From?
Earwax, scientifically known as cerumen, is secreted and remains on the skin of the external ear canal. It is composed of secretions, dead skin cells, dirt, and sweat within the ear canal. Subsequently, under the influence of the cilia on the surface of the glandular cells, earwax is pushed out of the external ear canal. Earwax will naturally dry and flake off in the outer ear. This process continues within the ear canal, with one layer of earwax replacing another.
As earwax is pushed out by the ear canal, it serves as a shield to prevent bacteria, insects, dirt, and other particles from entering the ear canal. This helps protect the ears from bacteria and fungal spores. Additionally, earwax aids in the transmission of sound waves.
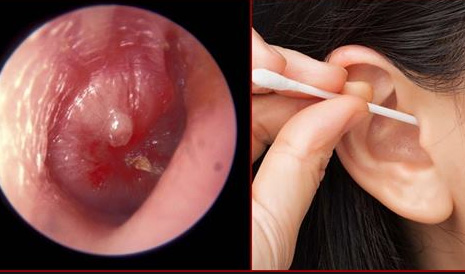
Location of earwax in the ear canal.
2. Characteristics of Normal Earwax
Earwax is composed of cholesterol and fat, so it typically has a yellow color and a slightly sticky texture. Depending on the individual’s health condition, earwax can change in color, texture, and odor.
Earwax can be dry or wet. This characteristic depends on various factors such as individual physiology, diet, living environment, age, activity of the earwax glands, and genetics. Additionally, some individuals may have earwax that forms into flakes. This is not a sign of any serious condition but rather an indication of the body’s aging process, commonly seen in older adults. Thus, these are all normal characteristics of earwax.
3. Health Issues Related to Earwax Appearance
Earwax is Wetter Than Normal and Has a Foul Odor
Foul-smelling earwax is a common symptom of otitis media. At this stage, the ear may be experiencing issues such as infection or damage and needs immediate treatment before it progresses to chronic otitis media. Additionally, if there are unusual symptoms such as tinnitus, fullness in the ear, difficulty hearing, occasional ringing in the head, or loss of balance, the individual should seek medical attention immediately as these are warning signs of problems in the middle ear.
Earwax is Watery and Greenish Like Pus
If earwax is wet or if there is watery discharge during physical activity, it may be due to sweat entering the ear or water entering the ear while bathing. However, if earwax continues to flow or if it appears green or dark yellow like pus, the individual may have an ear infection and should seek early examination and treatment.
Earwax Mixed with Dry Blood
During the process of cleaning earwax, the tool used may have scraped the inner lining of the ear canal, causing bleeding. Sometimes, this symptom may not merely indicate surface damage but could be due to a perforated eardrum. Therefore, if you notice persistent dry blood mixed with earwax, it is advisable to seek early examination to prevent the risk of hearing loss.
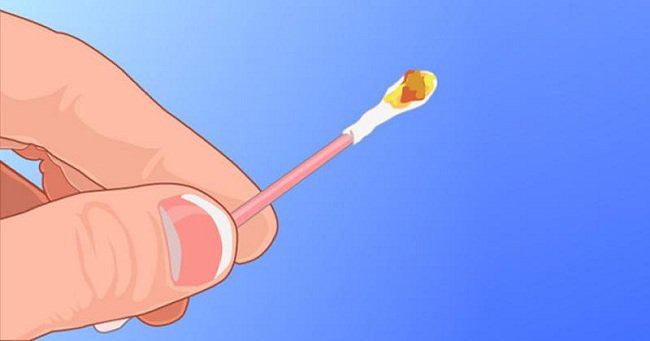
Earwax condition related to certain ear diseases.
Excessive Earwax Production
Is excessive earwax good? In fact, earwax is produced as needed by the brain and serves to prevent bacteria from invading the ear canal. If earwax production is high, it indicates that the brain is stimulating the production of earwax to protect the ear canal.
Individuals who frequently experience excessive stress, have ear defects, or sweat profusely are also likely to produce more earwax. If you feel that you have an excessive amount of earwax along with other unusual symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention and treatment early to avoid dangerous complications.
Sudden Absence of Earwax
If you find that there is no earwax anymore, it is important to pay attention, as this may indicate a condition of keratin buildup in the ear canal. This condition occurs when the mechanism for expelling earwax is halted. Instead of being pushed out, earwax remains trapped in the ear canal, accumulating into a hard plug and causing blockage. Symptoms that patients may experience include fever, ear pain, or inflammation if earwax accumulates excessively.
At this point, patients should not attempt to remove earwax themselves but seek help from a specialist.
Unusual Colors of Earwax
The color of earwax can also be an indicator of abnormalities in the ear. You should pay attention to the color to better understand your condition.
- Gray: If earwax is gray, wet, and sticky, it indicates that dirt has been removed along with the earwax. However, if earwax is gray and dry accompanied by itching, it may be a symptom of eczema infection.
- Light Yellow: Light yellow earwax is commonly seen in children under 8 years old. However, if an adult has light yellow earwax, it may indicate a mild vitamin B deficiency.
- Dark Brown: If earwax is dark brown and sticky, it may be due to excessive sweating or a sign of high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
- Dark Brown, Thick Clumps: This indicates a hormonal imbalance due to stress and anxiety.
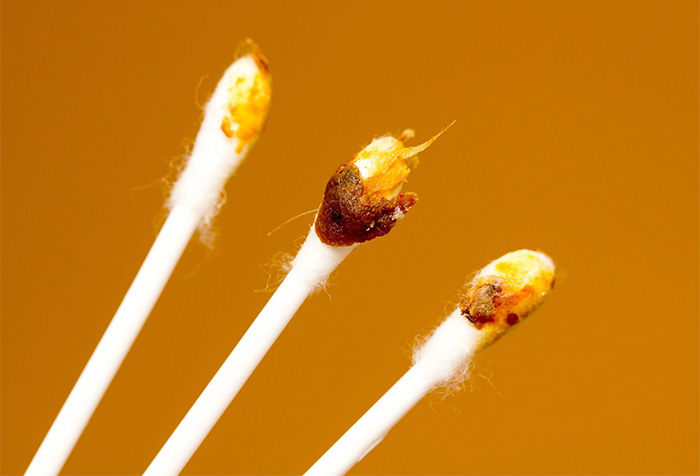

Unusual colors of earwax indicate certain abnormal health conditions.
4. Guidelines for Safe Ear Cleaning
Sometimes, earwax may move out too much, forming a hard plug near the eardrum that needs to be removed. The safe way to remove earwax is as follows:
- Do not insert any sharp objects such as pencil tips, pins, paper clips, etc. into the ear as they can tear the eardrum. Additionally, do not use cotton swabs or fingers to clean the ear (as this can push earwax deeper, blocking the eardrum).
- The correct method is to apply a softening solution (such as hydrogen peroxide, mineral oil, glycerin, or specialized ear cleaning solutions) into the ear. Place 1-2 drops of the solution into each ear. The solution will soften the earwax. After the earwax has softened, prepare a bowl of warm water at about 37°C, gently squirt warm water into the ear, tilt your head to one side to let the earwax flow out naturally, and then gently wipe clean. Note: do not use cotton swabs or towels to scrub hard against the ear.
Note: Do not rinse your ears frequently. Individuals with excessive earwax should only rinse their ears once a month.
Earwax serves to prevent bacteria and dirt from entering deep into the ear canal. The color and characteristics of earwax can also reveal information about an individual’s health. Therefore, it is important to be attentive if earwax shows any unusual signs and to seek medical attention promptly to detect and treat any conditions early.
It is best to consult reputable medical facilities if you notice any unusual colors of earwax, so doctors can examine and provide specific advice regarding your current condition. Additionally, patients should not be complacent, as prolonged neglect may affect hearing.

















































