The Hubble Space Telescope has recently captured a moment of a “lonely” star shining brilliantly with unusual rays of light.
According to Digital Trends, the Hubble Space Telescope has recently documented a remarkable moment in the universe. Based on the results from two separate exposures that were combined, the telescope showcased star BD+17 2217 radiating brilliantly against the backdrop of the anomalous galaxy Arp 263.
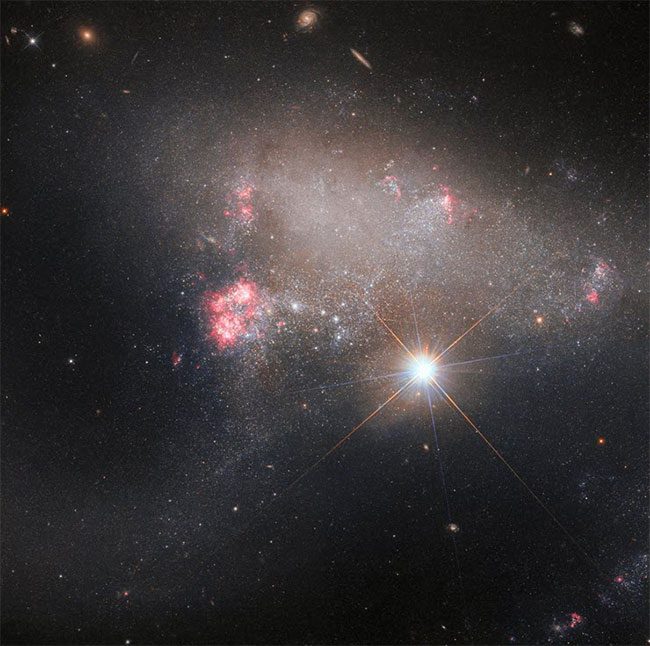

Star BD+17 2217 shining brightly in the anomalous galaxy Arp 263.
Anomalous galaxies have irregular structures, unlike elliptical or spiral galaxies such as our Milky Way. The galaxy Arp 263 has a mottled appearance with numerous clouds, featuring some areas that glow brightly due to new star formation, while other regions appear almost empty.
Such galaxies are often formed due to interactions with other galaxies, which can occur when a large galaxy passes by and distorts the original shape of the galaxy. In the case of Arp 263, it is believed to have taken on its anomalous shape when two galaxies merged.
Regarding the extremely bright “lonely” star, the peculiarity lies in the image it produces and the effect of the special diffraction spikes emanating from bright objects. These spikes are caused by the geometric structure of the mirror that Hubble uses to observe distant objects. Typical bright star images from Hubble usually exhibit four diffraction spikes (compared to six seen in images from the James Webb Telescope), but in this case, Hubble managed to capture an image with up to eight diffraction spikes.
This is due to two different data sets being combined to create the image, each captured at a different angle, resulting in a doubling of the spike count and providing a stunning visual for the Hubble Space Telescope.
Readers interested can access this link to view high-quality images of star BD+17 2217.