Many theories have been proposed, but no one can be sure how the stars have disappeared, or where they are now.
We live in a vast universe, filled with mysteries that humanity has yet to explain.
Among these is the phenomenon of stars disappearing without any specific explanation. They clearly do not collide with one another, nor are they leaving the Solar System, yet they vanish in a profoundly puzzling manner.

Image of Barnard 68 Dark Nebula as observed through a telescope. This is a region where stars cannot be seen in visible light due to a massive cloud of dust obscuring them (Photo: ESO).
In 2019, a project named VASCO, developed by the Canary Islands Institute of Astrophysics (Spain), attempted to catalogue the stars that have disappeared from our view over the past 70 years. The results were startling, revealing that over 100 stars are missing without any specific explanation.
“We found no evidence suggesting that the disappearance of a light source is justified,” the study emphasizes. “In particular, the records do not show any evidence of unusual moving sources such as aircraft, asteroids, or fundamental particles.”
“They simply vanished into oblivion”, the study concludes.
Previously, researchers at the Palomar Observatory in San Diego, California, were equally astonished when they observed three stars located close to each other disappearing in less than an hour.
Theoretically, stars can dim or explode as a supernova before leaving a brilliant light for hours or days. However, they cannot simply vanish from sight instantaneously.
One possible theory is that they may not have become supernovae but collapsed into a black hole. However, this is considered extremely rare, with a probability of less than 1 in 90 million, and may not explain why so many points of light have disappeared.
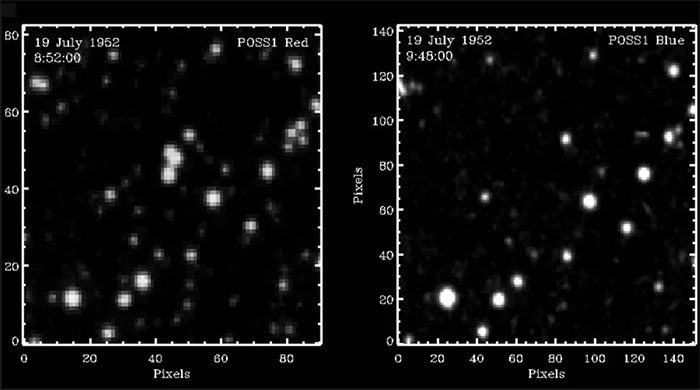
Images taken less than an hour apart showing many stars have disappeared mysteriously. (Photo: Solano).
Another possibility could be gravitational lensing. This occurs when light and electromagnetic waves emitted from an object are deflected on their path due to gravitational forces when near other celestial bodies.
This phenomenon is generally more clearly observed when light passes through black holes or galaxies. Here, objects such as asteroids could also be the “culprits” behind these disappearances.
According to Jamal Mimouni, an astrophysicist at Constantine 1 University in Algeria, research on these disappearing stars might provide clues in the search for advanced extraterrestrial civilizations (SETI).
“This could be a turning point in the SETI search journey,” Mimouni stated. However, he also acknowledged that there is still no evidence or precise answers to describe the aforementioned phenomenon.
“It’s hard to imagine, as this simply raises a series of other questions,” the astrophysicist shared.

















































