Astronauts must undergo a rigorous and strict training process to meet health and endurance criteria before being allowed to fly into space.
Since the first human flight into space on April 12, 1961, when Soviet astronaut Yuri Gagarin orbited Earth aboard Vostok 1, humanity has made significant strides in the quest to conquer space.
Let’s take a look at some impressive and hard-to-break records set by astronauts in the exploration of space.
Astronaut with the Longest Time Living in Space
On February 4, Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko set a new record for the total number of days lived in space, with a total of 879 days spent away from Earth.
Kononenko’s achievement surpassed the previous record held by fellow Russian astronaut Gennady Padalka, who had a total of 878 days, 11 hours, and 30 minutes in space.
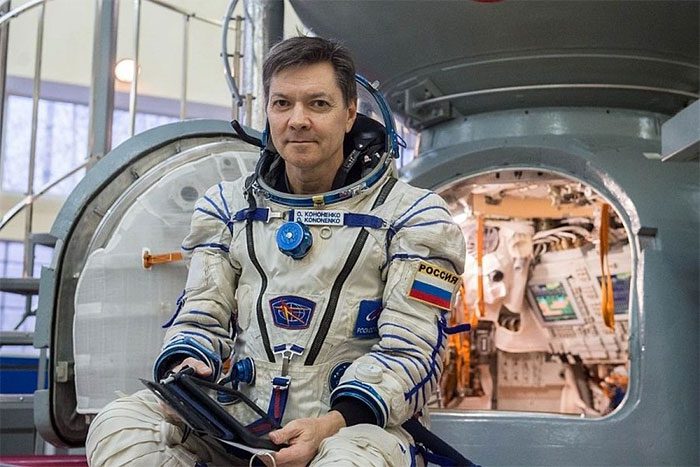

Russian astronaut Oleg Kononenko sets the record for total time lived and worked in space. (Photo: Roscosmos).
Notably, Oleg Kononenko was sent to the International Space Station (ISS) last September, with an expected stay of one year. This means that if everything goes according to plan and no incidents occur, Kononenko will increase his record for time in space to over 1,110 days by the end of his current mission.
“Oleg Kononenko is expected to reach a total of 1,000 days living in space at 12:20 AM on June 5, 2024, Moscow time. After completing the current exploration mission on September 23, his total flight time will be 1,110 days,” shared the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos.
This is Kononenko’s fifth mission outside of Earth. At the end of this month, he will take on the role of commander of the ISS while other crew members will return to Earth.
“I fly into space to do what I love, not to set records. I am proud of my achievements, but I am even prouder that the record for the total time humans have lived in space is still held by Russian astronauts,” Kononenko stated after reaching this remarkable milestone.
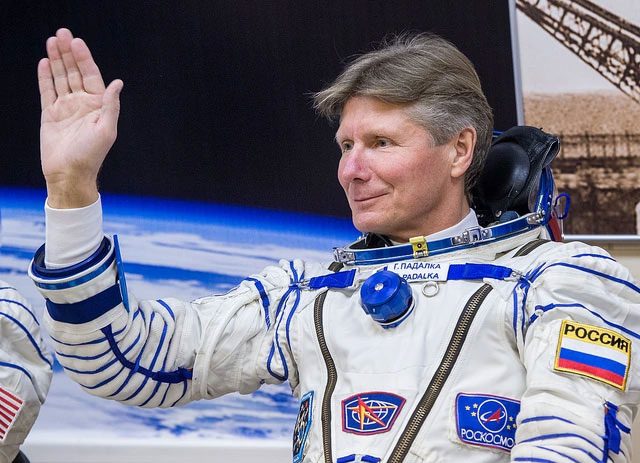

Russian astronaut Gennady Padalka held the record before it was broken by Oleg Kononenko. (Photo: Space Flight).
Both former Soviet and current Russian astronauts dominate the records for time spent living in space. The top eight astronauts with the longest total time spent in space are all from the Soviet Union and Russia. The ninth position is held by American astronaut Peggy Whitson, who spent 675 days away from Earth.
Astronaut with the Longest Continuous Time in Space
The achievements of Oleg Kononenko and Gennady Padalka were made after multiple trips to space for scientific research missions, rather than the longest continuous time spent living in space.

Soviet and Russian astronaut Valeri Polyakov (born 1942, died 2002) still holds the record for continuous time in space. (Photo: TSR).
The record for the longest continuous time in space is also held by a Russian astronaut (formerly Soviet), Valeri Polyakov. He worked on the Mir space station from January 8, 1994, to March 22, 1995, for a total of 437 days, 17 hours, and 58 minutes.
Previously, Polyakov also completed a 240-day mission on Mir from August 28, 1988, to April 27, 1989.
Astronaut with the Most Spaceflights
Two American astronauts, Franklin Chang-Diaz and Jerry Ross, hold the record for the most spaceflights, each with a total of 7 flights.
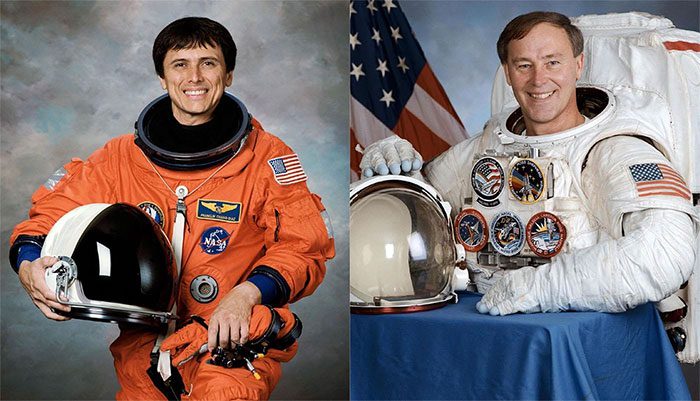

Franklin Chang-Diaz (left) and Jerry Ross hold the record for the most spaceflights. (Photo: WTTW).
Jerry Ross was the first to reach the milestone of 7 spaceflights, completing these missions from 1985 to 2002. His record did not last long as Franklin Chang-Diaz equaled it in 2002 as well.
Astronaut with the Most Spacewalks
Russian astronaut Anatoly Ykovlevich Solovyev holds the record for the most spacewalks (16 times) and also the longest total time spent on spacewalks (82 hours and 22 minutes).

Russian astronaut Anatoly Solovyev holds the record for 16 spacewalks. (Photo: Twitter).
Solovyev’s achievement far surpasses the second place, Spanish-American astronaut Michael Lopez-Alegria, who has completed 10 spacewalks, with a total time of 67 hours and 40 minutes.
Record for the Most People Living in Space Simultaneously
In 2009, the Endeavour space shuttle brought 7 crew members to the International Space Station (ISS). At that time, there were already 6 other astronauts on the ISS. This means that there were 13 people living in space simultaneously, setting the record for the most people living in space at one time.
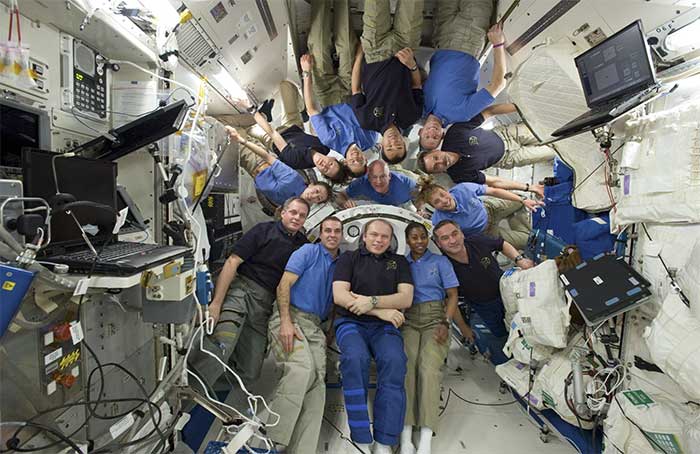

Photo of 13 astronauts present on the International Space Station. (Photo: Space).
This record has yet to be broken.
Youngest and Oldest Astronauts Ever in Space
The record for the youngest man to fly into space currently belongs to Soviet astronaut Gherman Titov. When he made his flight into space in August 1961, Titov was only 25 years old.
The record for the youngest female astronaut to fly into space belongs to Soviet scientist Valentina Tereshkova. When she made her flight into space on June 16, 1963, Tereshkova was just 26 years old. Valentina Tereshkova is also the first woman in history to fly into space.
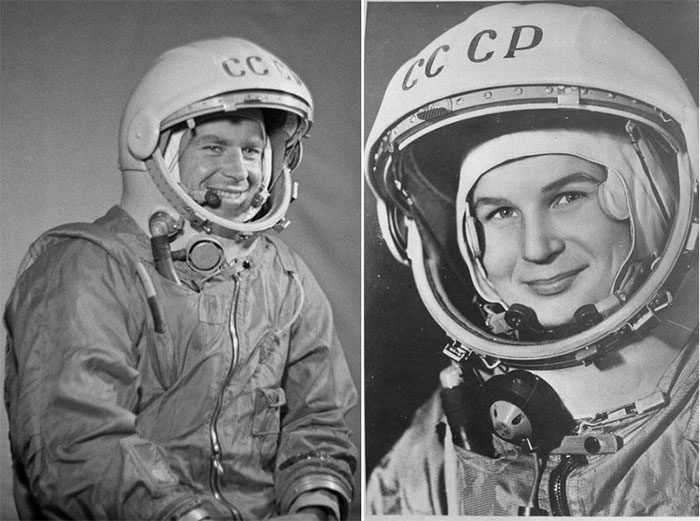

Gherman Titov (left) and Valentina Tereshkova, the youngest astronauts ever in space. (Photo: Getty).
Valentina Tereshkova’s record was later broken by Anastatia Mayers when she flew into space on a Virgin Galactic tourism flight in August 2023 at the age of just 18. However, since Mayers only took a tourism flight, rather than a scientific research mission, many still believe that she has not truly broken Tereshkova’s record set in 1963.
On the other hand, the oldest man to fly into space is American astronaut John Glenn. When Glenn flew into space on October 29, 1998, he was 77 years old. John Glenn was also the first American astronaut to orbit Earth in 1962.
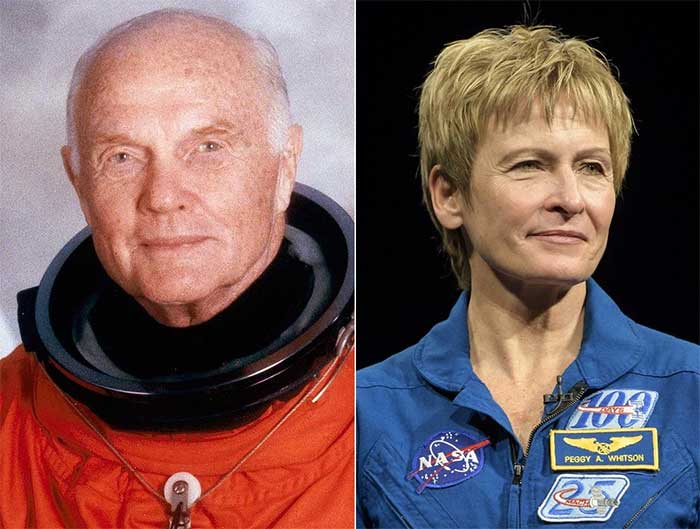
John Glenn (left) and Peggy Whitson are the oldest astronauts ever in space. (Photo: NASA).
The oldest woman to fly into space is American astronaut Peggy Whitson, who was launched into space on May 21, 2023, at the age of 63. She also holds the record for the longest time spent in space by an American and female astronaut, with over 675 days.
The Terrifying Pressures Astronauts Face When Living in Space for Extended Periods
The reason that records for prolonged time working in space are of great interest and highly valued in the scientific community is that these are very challenging records to achieve.
The longer astronauts live in space, the more intense pressures they must endure, affecting their bodies, such as the redistribution of bodily fluids, making it very difficult for them to adapt when returning to Earth.

Astronauts endure tremendous pressure after a long time living in space. (Illustration: NASA).
Many astronauts will face issues such as loss of bone density and muscle atrophy. Although the ISS is equipped with a gym to help astronauts exercise, it cannot completely prevent muscle loss and damage to bones and joints.
Typically, astronauts work for about six months on the International Space Station (ISS) before returning to Earth, where they are replaced by other astronauts.
Astronauts often need several years to fully recover their health after six months of working in space. Despite this, they still face health complications such as a higher risk of bone fractures and an increased risk of cancer.
Another issue many astronauts encounter after long periods in space is psychological and emotional trauma, as they often have to work alone and are separated from their loved ones for extended periods.
As a result, astronauts must be incredibly brave and dedicated to work long durations in space.
The ISS is the largest space station ever constructed by humans, a collaborative project involving five space agencies, including NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency.
Due to political tensions between Russia and the United States, in 2022, Russia announced its intention to withdraw from the ISS by the end of 2024 and build its own space station. However, Russia will continue to support crewed flights to the ISS until 2025.


















































