Paleontologists have discovered the fossil of a new dinosaur species with a unique horn resembling the iron helmet of the Norse god Loki.
This dinosaur, approximately 6.7 meters long and weighing around 5 tons, has been named Lokiceratops due to its distinctive “helmet.” It belongs to the herbivorous group of dinosaurs known as “centrosaurines,” dating back 78 million years.

Reconstruction of the Lokiceratops dinosaur – (Photo: Fabrizio Lavezzi).
The full name of this new dinosaur species is Lokiceratops rangiformis, which means “the horned face of Loki resembling a reindeer,” according to an article from IFLScience dated June 20.
This dinosaur is also part of the horned dinosaur group known as ceratopsids, which first evolved around 92 million years ago during the late Cretaceous period. Lokiceratops rangiformis is one of the largest and most uniquely horned dinosaurs ever discovered.

The fossilized skull of Lokiceratops on display at the Museum of Evolution in Denmark – (Photo: Museum of Evolution).
The “headgear” of Lokiceratops is quite unusual, even by ceratopsid standards, making it one of the largest plate-like horned dinosaurs seen in the ceratopsid group. However, Lokiceratops lacks a nasal horn.
Archaeologists have known that this group of dinosaurs contains many species with very unique horns, but this recent discovery sheds light on their previously unrecognized diversity.
“A new horned dinosaur species discovered in northern Montana during the late Cretaceous reveals unexpectedly high diversity, indicating a high rate of speciation and regional endemism among members of this group,” stated Mark Loewen, co-author of the study and a lecturer at the University of Utah (USA).
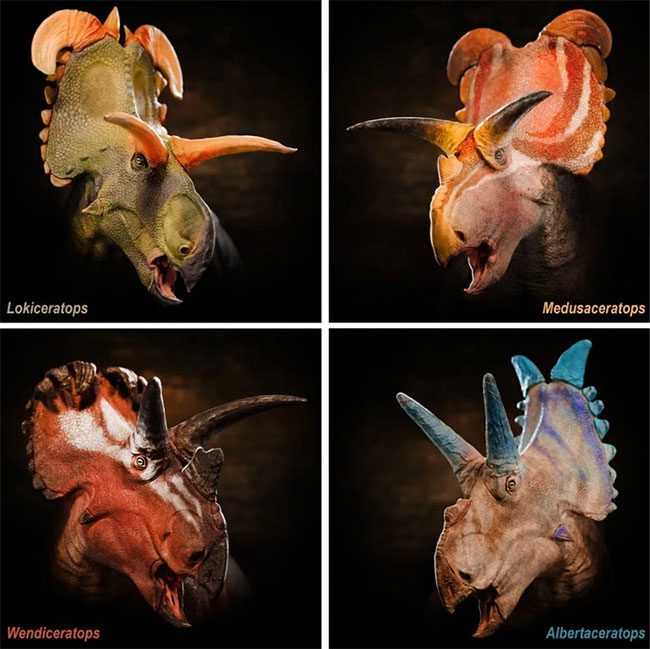
Reconstruction of four dinosaur species that lived together in northern Montana (USA) and southern Alberta (Canada) – (Photo: Fabrizio Lavezzi).
Overall, Lokiceratops rangiformis is the fourth centrosaurine dinosaur species and the fifth horned dinosaur species from a specific faunal assemblage – the animal life of a particular region, habitat, or geological period.
The fossils in the area along the US-Canada border indicate that horned dinosaurs lived and evolved in a small geographical area. The high endemism within the centrosaurine group suggests that the diversity of dinosaurs is currently undervalued.


















































