1. Brush-tailed Possum – Trichosurus vulpecula
The Brush-tailed Possum is a solitary, nocturnal marsupial that lives in trees and has been introduced from Australia. It damages native forests in New Zealand by feeding on various leaves and fruits. Additionally, it eats bird nests and acts as a vector for tuberculosis in cattle.

2. Domestic and Feral Cats – Felis catus
Cats, in various forms and sizes, are found worldwide except for Australia and some Pacific islands. The Domestic Cat, Felis catus, was domesticated around 3000 years ago in the eastern Mediterranean and has since followed humans almost everywhere, becoming feral when abandoned. Feral cats cause significant losses to many native bird species.

(Image: taiko.org)
3. Domestic Goat – Capra hircus
The Domestic Goat is an herbivorous species with a highly diverse diet. Goats consume plant species that sheep and other livestock typically avoid, thus significantly impacting native vegetation and the animals that depend on it. Domestic goats can easily revert to a wild state and transmit diseases to native wildlife.

(Image: museum.vic)
4. Eastern Gray Squirrel – Sciurus carolinensis
The Eastern Gray Squirrel was introduced from South America to the UK, Italy, and South Africa as a pet. In the UK and Italy, they have caused the local extinction of the native red squirrel. They are expected to expand their range from the Alps to parts of Eurasia.

(Image: scarysquirrel)
5. Long-tailed Macaque – Macaca fascicularis
The Long-tailed Macaque is native to South Asia. It was introduced to Mauritius in the early 1600s and thrived on the island due to the absence of competing and predatory mammals. This species has caused significant agricultural damage and is considered a contributing factor in the extinction of many forest bird species.
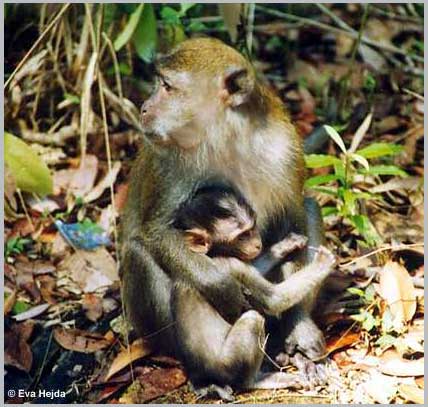

(Image: naturspot)
6. House Mouse – Mus musculus
The House Mouse feeds on various plant parts including seeds, green stems, and leaves, as well as nearly all human and pet food. They cause significant damage, destroying or contaminating food supplies for humans and livestock.
(Image: brain.riken)
7. Nutria – Myocastor coypus
The Nutria is a large semi-aquatic rodent native to South America. However, after being released from fur farms, they have established large feral populations in North America, Europe, and Asia. They burrow and destroy riverbanks, levees, and irrigation systems.

(Image: digitalfotografie)
8. Wild Boar – Sus scrofa
The Wild Boar is a domesticated pig that has escaped or been released into the wild. Introduced in many parts of the world, they damage crops, properties, and spread numerous diseases. Wild boars uproot native vegetation, spread seeds, and disrupt ecological processes such as succession and species composition.

(Image: hlasek)
9. European Rabbit – Oryctolagus cuniculus
The European Rabbit has been introduced to most continents except Antarctica and parts of Asia. They are often introduced by animal husbandry societies to various countries. They have rapidly multiplied in number, damaging vegetation, burrowing, and increasing soil erosion.

(Image: fotoohota.spb)
10. Red Deer – Cervus elaphus
The Red Deer is the largest species of deer, with a shoulder height of up to 1.2 meters. It is a ruminant that feeds on a wide variety of plants, including the stems of young trees. In areas with high densities of this species, they have a severe impact on vegetation and hinder the natural regeneration of native forests.

(Image: macro-photo)
11. Red Fox – Vulpes vulpes
The Red Fox has been introduced to many countries for recreational hunting but has quickly become a pest due to its adaptability to various habitats. As a carnivore, it preys on rabbits, mice, lambs, and kids, as well as small native animals.

(Image: fcps.k12.va)
12. Black Rat – Rattus rattus
The Black Rat originated from the Indian subcontinent and has now spread worldwide. It consumes and destroys everything edible. The Black Rat is a very agile species, often climbing trees.

(Image: algonet)
13. Indian Mongoose – Herpestes javanicus
This species of mongoose has been introduced to tropical islands for sugarcane cultivation. Due to its strong competitive abilities, the Indian Mongoose has driven many native vertebrate species to extinction, harmed livestock, and poses a risk as a disease vector.

(Image: iucn)
14. Ermine – Mustela erminea
The Ermine is now distributed worldwide due to escapes from fur farms. They prey on birds, bird eggs, and small native mammals. Despite being hunted for decades, their populations remain high.

(Image: ittiofauna)
(The species listed here are chosen to illustrate the impacts of invasive species. The absence of other species from this list does not imply they are less harmful.)