Mars, the mysterious red planet, may soon become a “highway” for a swarm of robotic bees buzzing to explore. This project, named “Marsbees”, is initiated by NASA, promising to offer a groundbreaking solution to the challenges posed by the harsh Martian environment.
The NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program aims to utilize Marsbees for more effective exploration of Mars. These small robots are inspired by nature, mimicking the long-distance flying abilities of animals such as monarch butterflies and albatrosses. Monarch butterflies can fly distances of up to 4,000 kilometers, while albatrosses can travel as far as 12,000 kilometers. These species are renowned for their energy-efficient wing movements and adaptability to various atmospheric conditions.
However, flying on Mars presents a significant challenge due to its harsh environment. The air density on Mars is only 1% that of Earth, meaning there is almost no air to create lift for flight. This necessitates that flying vehicles be extremely lightweight and possess special features to adapt.

Mars may soon welcome special “guests”: a swarm of robotic bees modeled after ground bees, tasked with collecting vital data about the red planet.
NASA previously introduced the Ingenuity Mars helicopter, which weighs only 1.8 kilograms and operates on Mars. To compensate for the lack of lift, its rotor spins at 2,800 revolutions per minute (whereas aircraft doing similar tasks on Earth only need to spin at a few hundred revolutions per minute). Due to the distance, controlling from Earth to Mars takes about 15 minutes, so Ingenuity is also designed to operate completely autonomously, capable of handling unexpected situations.
Meanwhile, Marsbees, which are roughly the size of ground bees but have wings resembling cicadas, will face similar challenges to Ingenuity. Each Marsbee is equipped with a color camera and a suite of sensors, including positioning, LIDAR, tilt meters, inertial measurement units, and a communication module. These devices collect and transmit data back to a rover, which serves as the operational base and connects to Earth.
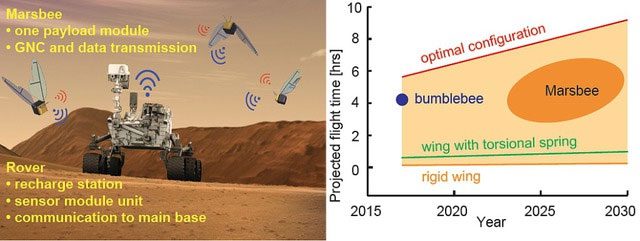
Flying on Mars is fraught with difficulties due to the atmospheric density being only 1% that of Earth. This means that the lift required for flight is nearly nonexistent, necessitating special designs for flying vehicles.
A conventional fixed-wing aircraft on Mars cannot fly for more than 16 minutes without recharging with current technology. However, Marsbees can conserve energy by passively deforming and rotating their wings, resulting in longer flight times.
The mission of Marsbees is to use a multi-agent system to survey the surrounding environment and create a 3D terrain map. In various scenarios, each member of the Marsbee swarm could carry pressure and temperature sensors to sample the atmosphere or small spectrometry analyzers to identify mineral deposits.
The use of Marsbees presents numerous advantages. First, these compact robots can access challenging areas that larger equipment cannot. Second, their ability to fly and survey continuously allows for more detailed data collection on Mars’s terrain and climate. Finally, the multi-agent system of Marsbees can perform multiple tasks simultaneously, from terrain surveying to climate analysis and mineral resource assessment.

Marsbees, the size of ground bees but with cicada-like wings, are designed to overcome challenges similar to Ingenuity but with a different approach and in larger numbers.
The Marsbees project not only represents a breakthrough in exploring Mars but also opens up new possibilities for space exploration. With a combination of advanced technology and inspiration from nature, Marsbees can yield significant discoveries, enhancing our understanding of the red planet and preparing for future missions.
Marsbees are not just a technological solution; they symbolize human creativity and the desire to explore. These tiny robots could become pioneering explorers, paving the way for larger and more complex missions on Mars.
NASA has already succeeded with the Ingenuity Mars helicopter, demonstrating that flight on Mars is feasible. Now, with Marsbees, NASA continues to assert its leading position in space exploration. NASA scientists and engineers are tirelessly working to turn the dream of exploring Mars into reality.
Unlike Ingenuity, Marsbees can conserve energy by passively deforming and rotating their wings, extending flight duration.
In the not-so-distant future, as a swarm of Marsbees flits through the Martian sky, we will have the opportunity to witness a significant advancement in our understanding of the red planet. The data collected by Marsbees will help scientists answer many critical questions about Mars, from its geological structure to climate conditions and the potential for life.
The Marsbees project by NASA exemplifies human creativity and boundless capacity for exploring the universe. With advanced technology and the dedication of scientists, these robotic bees may open a new chapter in Martian exploration, yielding important discoveries and preparing for future space adventures. Marsbees are not just a scientific project; they are a symbol of ambition and faith in our ability to conquer the challenges of the universe.




















































