Crystal clear, gemstone-like, or golden yellow, resembling sunspots against the blue sky, and possessing a unique fragrance along with a mysterious chocolate black hue… these fruits are rarely seen, yet they hold the delicious and nutritious essence of nature.
Cactus Pear


Originating from Mexico, the cactus pear features a reddish-purple and yellow color, pear-like shape, with bright-colored flesh that is crystal clear throughout. Not only does the cactus pear have an eye-catching appearance, but it also contains 18 types of amino acids and various trace elements essential for the human body.
It serves not only to cool down the body, detoxify, beautify the skin, and combat oxidation but also enhances the immune system for the stomach and spleen, improves blood circulation, reduces fever, and strengthens muscles. You can peel it and eat it directly or refrigerate it for a softer, smoother taste. If desired, you can mix it with honey for a drink, juice it, or blend it into a smoothie that aids in rapid weight loss. Additionally, cactus pears are used to refine sugar, make wine, or produce milk.
Yellow Himalayan Raspberry


The yellow Himalayan raspberry is a thorny shrub found in Asia, belonging to the rose family. The plant originates from China, Nepal, the Indian subcontinent, Indochina, and the Philippines.
In Hawaii, it is considered an invasive alien species or a weed, but its fruit is sold in local markets in the Himalayas. The plant is cultivated both as a fruit-bearing and ornamental plant in many regions, including Florida, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, and California. Its fruit is sweet and is used to treat colds, stomachaches, coughs, and sore throats.
Holboellia latifolia (also known as August Fruit)
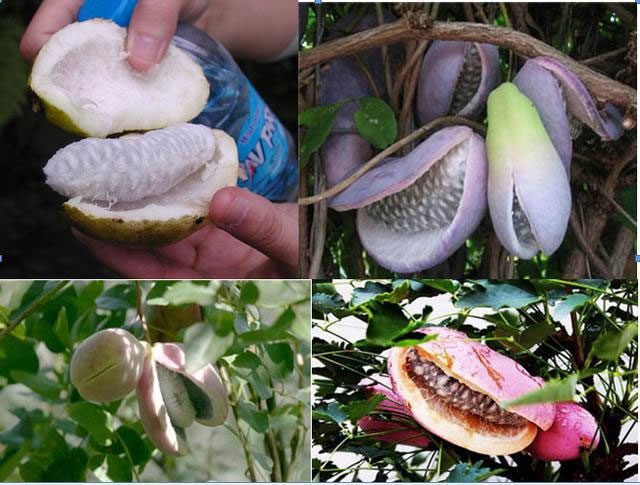
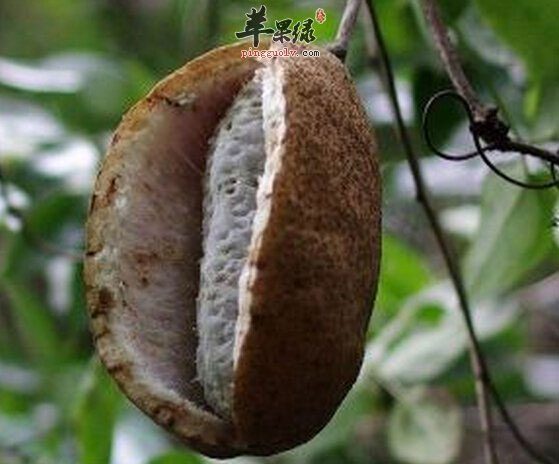
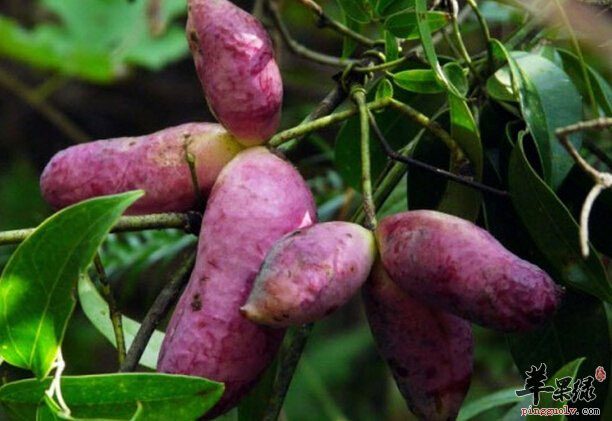



This fruit is distributed in China, India (Northeast), Bhutan, and Nepal, with a presence in Yunnan, Guizhou, Sichuan, Jiangxi, and Southeast Tibet. It grows on hillsides and valleys at altitudes of 600-2600 meters.
The August fruit resembles a banana or purple sweet potato, with a milky white interior that is smooth and sweet, making it very delicious. Additionally, it has a unique fragrance distinct from other fruits. It is yellow when unripe and turns purple when ripe. You can simply pick it up, split it open, and eat it directly or use it to make wine, extract honey, or juice.
Black Sapote
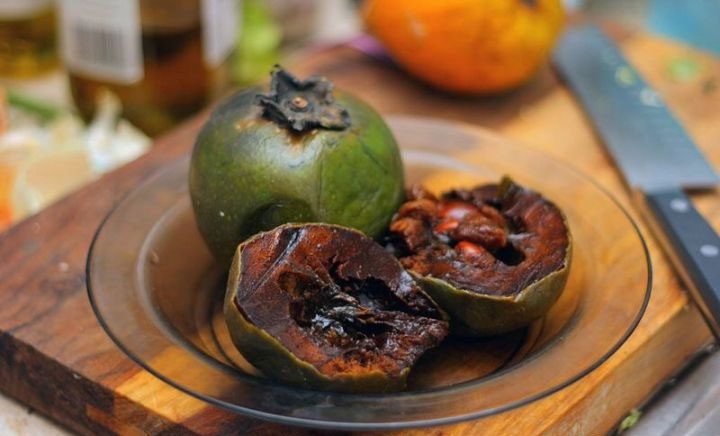
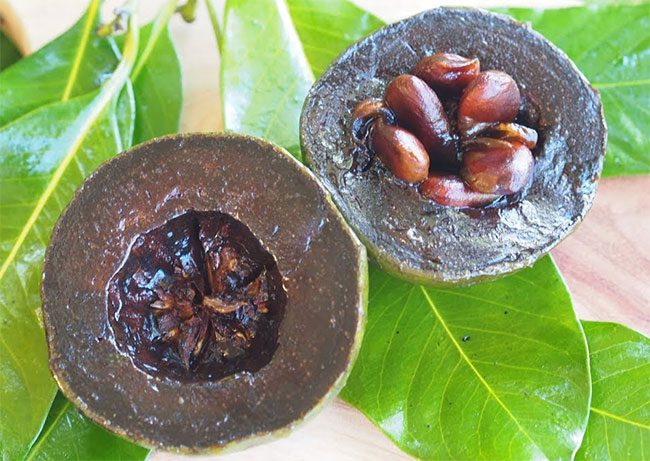


The black sapote, also known as chocolate persimmon, is a tropical fruit tree native to Mexico. The black sapote is found along both coasts of Mexico from Jalisco to Chiapas, Veracruz, and Yucatan, or in lowland forest areas in Central America.
When ripe, the black sapote has a flavor similar to chocolate pudding. The unripe fruit has a shiny green skin. This species is not related to the cacao tree. The fruit resembles a green tomato when unripe and turns yellow-green when ripe.
When ripe, the skin of the chocolate persimmon is slightly “wrinkled” and brown-green. The crushed skin and leaves are used as a poultice for blisters. Additionally, it is used for research into treatments for leprosy, roundworms, and skin itching.
The unripe black sapote has a bitter taste and should not be eaten. To check if the black sapote is ripe, gently squeeze the fruit. If it is soft and leaves an indentation, then it is ripe. It has a mild sweet fragrance that some people may not detect.
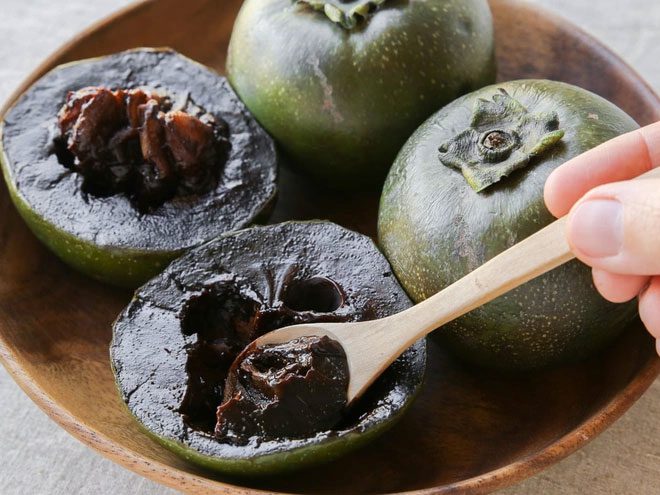

The black sapote can be used to create many delicious dishes.
The black sapote tree has a broad trunk, grows slowly, and can reach up to 25 meters tall, with a trunk diameter of up to 75 cm and black bark. In Mexico, this tree grows naturally in dry forests or clayey floodplain areas near streams or lagoons, where it is frequently flooded. However, it thrives best in moist sandy loam.
In Mexico, black sapotes are harvested from August to January of the following year. Most black sapotes in Florida (USA) ripen in December, January, or February.
Besides being eaten fresh, black sapote can be transformed into many delicious and interesting dishes. In the Philippines, black sapote is used as a dessert when mixed with a bit of milk or orange juice.
Some bakeries have used black sapote mixed with lemon juice as a filling for pastries and other desserts or to make ice cream.
In Mexico, black sapote can be mashed and mixed with orange juice or liquor and whipped cream. Additionally, they sometimes mix black sapote with liquor, cinnamon, and sugar to serve as a dessert.
Some Americans enjoy mixing black sapote with milk and nutmeg. A delicious beverage made from blended black sapote with pineapple juice is also popular. In Central America, fermented black sapote is made into fruit wine.
Black sapote is high in fiber, vitamin C, A, and potassium. It helps build the body’s immune system and boosts resistance. A medium-sized black sapote provides 142 calories and is rich in carotenoids (organic pigments) and catechins that help release fat and convert it into energy. Therefore, it is an ideal fruit for those looking to lose weight.