The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has just approved the first transdermal patch for the treatment of depression. This marks a new usage of a medication that has long been employed for patients with Parkinson’s disease.
The FDA has approved the selegiline transdermal patch.
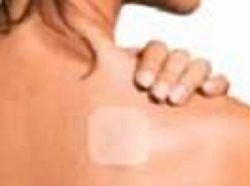 |
|
(Photo: VNN) |
This medication will be marketed under the name Ensam. The pharmaceutical company Somerset Pharmaceuticals Inc., the manufacturer of the drug, along with Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., will market the drug in three sizes, to be used once daily for the treatment of depression.
Peter Dolan, president of Bristol-Myers Squibb, stated: “We believe that the Emsam patch will help physicians treat patients with depression more effectively.”
The active ingredient, selegiline, was approved by the FDA in 1989 for use in individuals with Parkinson’s disease, categorized as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI).
Typically, physicians prescribe MAOIs only when patients do not respond to other antidepressant medications, such as those branded as Prozac, Zoloft, and Paxil.
Although health officials say that MAOI medications are safe when used correctly, they can also cause dangerous reactions, such as a sudden spike in blood pressure, which can lead to a stroke if patients consume foods or drinks containing a substance known as “tyramine.” This substance is often found in barrel-aged beer, red wine, fava beans, sausages, aged cheese, soy sauce, and other products.
Bristol-Myers and Somerset have stated that patients using the Emsam patch with small doses of 6mg or less will not need to be concerned about their food and drink choices.
However, those using larger patches containing 9 or 12mg of the medication daily will need to be mindful of their dietary intake.