Recently, a strange phenomenon appeared in the sky over the Himalayas has been recorded. While many people were in awe of the spectacular sight, astronauts had a contrasting reaction.
In May 2022, the sky above the Himalayas suddenly experienced an unusual phenomenon. Red lightning bolts appeared, which had never been seen before. Many people captured images and videos of these lightning bolts and shared them online. According to the recorded images and videos, the lightning bolts resembled giant red jellyfish with numerous tentacles hovering in the sky.

The sky above the Himalayas suddenly exhibited strange red lightning. (Photo: Baidu).
About a month after the appearance of the red lightning over the Himalayas, a similar grand sight occurred in Guilin, Guangxi, China. A photographer specializing in capturing the beauty of Guilin at night accidentally “caught” this unexpected moment. The unusual phenomenon left many people feeling bewildered, with some suggesting it was a “sign” from the universe. So, what is red lightning? How does this phenomenon form, and is it as frightening as some people worry?
Red lightning was accidentally captured by a photographer in Guilin, China. (Photo: Baidu)
“Red Jellyfish” Appear in the Sky
In fact, red lightning has been recorded in many places around the world, including Asia, America, Europe, and Central Africa. Currently, Antarctica is the only place where scientists have not observed red lightning.
On August 10, 2015, astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) captured a stunning image of red lightning while observing a thunderstorm over cities in southern Mexico. In the photo, on the right side, a column of red lightning extends above a blue-white flash.
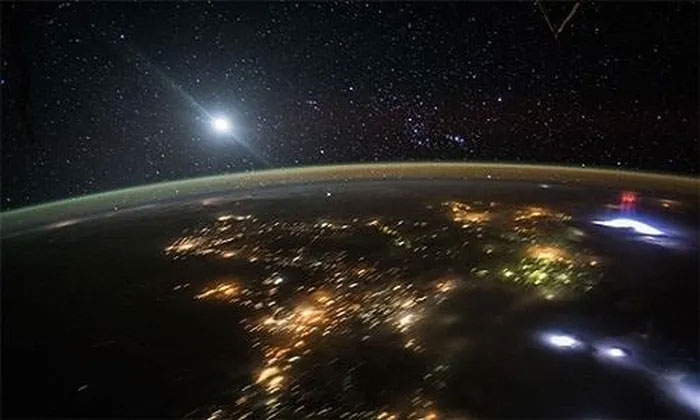

On the right side of the photo, a column of red lightning extends above a blue-white flash. (Photo: ISS).
In 2017, Andreas Mogensen, a Danish astronaut with the European Space Agency, recorded blue and red anomalous lightning several kilometers wide above a thunderstorm in the Bay of Biscay in the northeastern Atlantic using a highly sensitive camera on the ISS. The video provided by Mogensen shows 245 blue and red lightning bolts appearing above the clouds in the Bay of Biscay. These anomalous lightning bolts flashed at an altitude of 18 km above the ground, including one bolt that struck down from a distance of 40 km.
In May 2020, Michael Gavan, a storm chaser, captured rare red lightning resembling a giant jellyfish floating in the sky in Kansas, USA. Gavan reported that he stumbled upon the red lightning while chasing a tornado in the area. Later that year, on July 2, Stephen Hummel, a specialist at McDonald Observatory in Texas, also recorded images of red lightning in the Locke Mountain area.
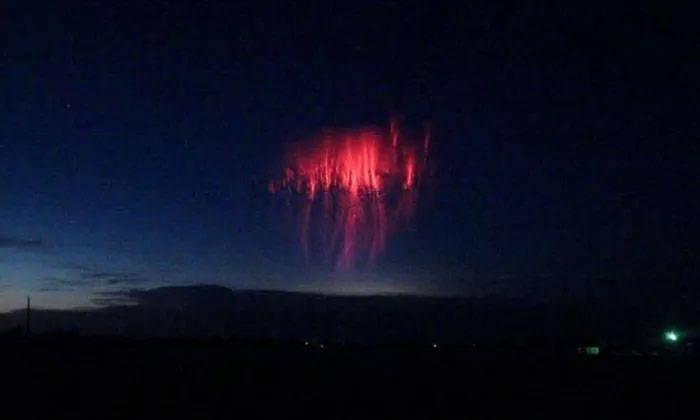

The anomalous red lightning phenomenon recorded in Kansas, USA. (Photo: Baidu)
Red lightning is considered an extremely rare phenomenon. The first photograph of red lightning was taken in 1989. According to historical records, in 1730, the existence of red lightning was identified by Johann Georg Estor, a German historian. He reported observing a strange optical phenomenon occurring above thunderstorm clouds. By 1925, C.T.R. Wilson, a Nobel Prize-winning scientist, argued that there was a discharge of electrical charge above thunderstorm clouds. In 1956, C.T.R. Wilson claimed to have observed red lightning but did not provide specific evidence.
However, it wasn’t until 1989 that actual images of red lightning were captured by a team of experts from the University of Minnesota using a sensitive camera. Since then, the phenomenon of red lightning has become a fascinating research topic for many experts.
The Truth About “Red Sprites”
Scientists have defined that red lightning falls into the category of anomalous lightning. Red lightning, along with black lightning, blue lightning, ball lightning, and bead lightning, are all strange and rare natural phenomena. Red anomalous lightning is also known as Red Sprite. According to the European Space Agency, red anomalous lightning is a rapid discharge phenomenon occurring in the upper atmosphere at altitudes of about 60-80 km. It often appears as branching red strands above areas of active lightning. The electrical discharge into the atmosphere can reach lengths of up to 90 km, with the brightest region located at altitudes of 65-75 km.
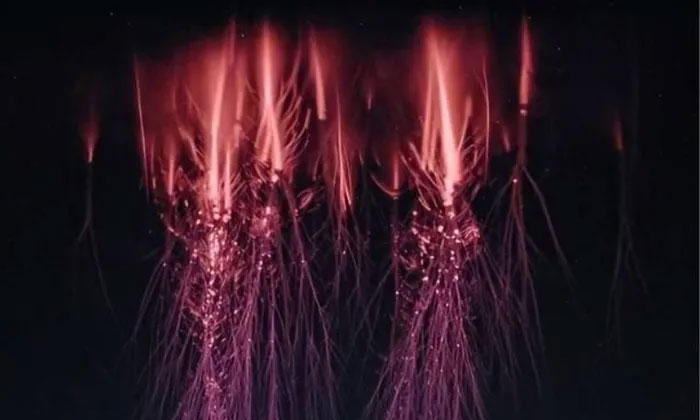

Red lightning is actually a form of anomalous lightning, a rare natural phenomenon. (Photo: Baidu).
Red anomalous lightning occurs due to nitrogen suspended at high altitudes in the Earth’s atmosphere. This gas is stimulated by electrical currents and emits red light. The nature of red anomalous lightning is the release of cold plasma beams, very similar to the discharge process in fluorescent tubes. The lightning bolts are typically red, but they are challenging to observe with the naked eye and can only display their actual colors under the lenses of sensitive cameras and camcorders.
Similar to regular lightning, red anomalous lightning exists in the sky for less than a second. Due to its speed and formation location, red anomalous lightning is difficult to observe from the ground. Astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) are the most likely to observe red anomalous lightning.

Red anomalous lightning often appears in the shape of jellyfish or red beams. (Photo: Baidu)
Some red anomalous lightning resembles jellyfish, while others take the form of red beams pointing towards the ground. Among them, jellyfish-shaped red anomalous lightning is usually the largest. They can reach lengths of up to 50 km and heights of 50 km or more. Some types of red anomalous lightning can be observed from distances of over 500 km. The stronger the thunderstorm and the more electricity it generates, the greater the chance of red anomalous lightning appearing.
The most prominent time for red anomalous lightning is when the Sun is at its minimum phase. This is the period when the Sun is least active in its 11-year cycle. At this time, its magnetic field weakens, allowing cosmic rays from deep space to penetrate the solar system more easily without interference. According to some studies, scientists have found that cosmic rays can promote the formation of anomalous lightning by creating electrical pathways in the atmosphere.
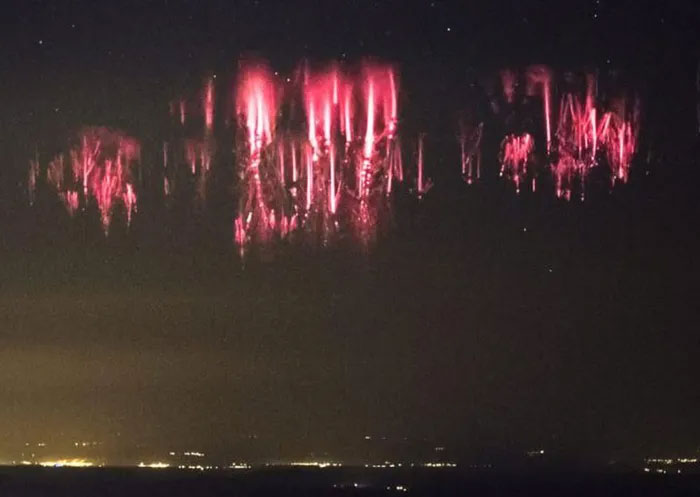

Red anomalous lightning is most prominent when the Sun is at its minimum phase. (Photo: Baidu).
Although red anomalous lightning is a spectacular moment that many people wish to witness in their lifetime, for astronauts, this phenomenon is a nightmare. In the history of aerospace, red anomalous lightning has been a “demon” that has caused many accidents when devices fly above thunderstorm clouds. Among them, the accident of a NASA stratospheric balloon on June 6, 1989, was the most severe. This balloon, after passing through a storm in Texas, suddenly lost serious control at an altitude of 37 km. It wasn’t until 1993 that NASA experts concluded that the balloon had been struck by red anomalous lightning.
Pilots often see red anomalous lightning while flying through thunderstorms. They are challenging to study because they usually occur above storms.