This marks a breakthrough in the field of medicine, opening up the possibility of remote surgery on humans, especially in areas lacking specialists or in extreme situations such as outer space. This success promises to provide a new medical solution, connecting doctors with patients regardless of geographical distance.
Remote Surgery: No Longer a Fantasy
Remote surgery is not a novel concept in medicine. In fact, many procedures have been performed “remotely” where doctors do not directly participate in the surgery but can control it through technological devices. However, what is remarkable about this surgery is the extraordinary distance between the doctor and the patient. Instead of conducting an endoscopy in the same room as the patient, doctors in Zurich, Switzerland, were able to perform surgery on a “patient” in Hong Kong, a distance of 9,300 km, simply using a video game controller.
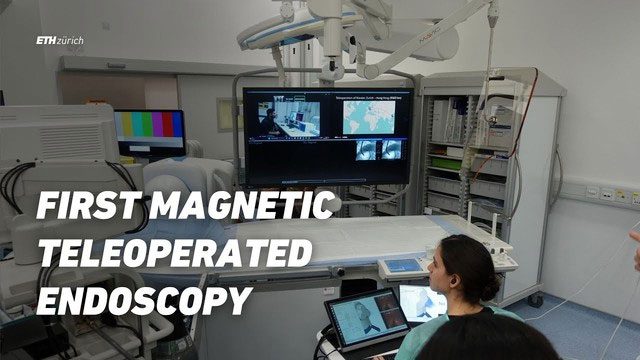
An operating room at the Chinese University of Hong Kong. On the screen is a direct link to another scientific team at ETH Zurich, Switzerland.
Advanced Technology Supporting Remote Surgery
According to a study by the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) and ETH Zurich, the combination of robotic technology and magnetic endoscopy is key to the success of this surgery. The magnetic endoscope is equipped with magnets along its length, allowing it to be controlled by an external magnetic field. This enables doctors in Zurich to operate the device through a robotic system connected to a WebSocket protocol, transmitting real-time data to the control panel in Zurich. More surprisingly, the doctors used an old PlayStation 3 Move controller to perform surgical maneuvers, a tool seemingly intended for entertainment but proving to be highly effective in medicine.
The experimental surgery was performed on a live pig under anesthesia, with the doctor able to manipulate a flexible endoscope inside the body. Notably, they successfully performed a biopsy of the pig’s stomach. Another critical factor of the experiment was that the signal transmission delay was kept below 300 milliseconds, ensuring the doctor’s responses were nearly in real-time, a crucial element for success in complex surgeries.
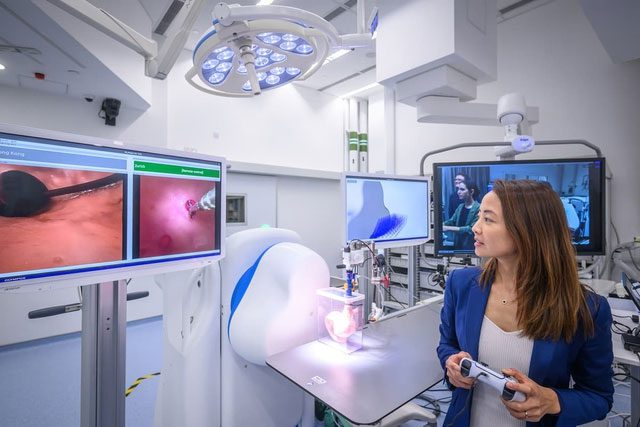
Dr. Shannon Chan using a game controller to operate an endoscope located in Zurich, Switzerland, over 9,000 km from the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
Significance of the Success and Future Potential
The success of this experiment demonstrates that performing remote surgeries on humans in the future is entirely feasible. With advancements in robotic technology, doctors can execute intricate and complex procedures, especially in sensitive organs such as the heart and eyes, from thousands of kilometers away. This promises many benefits for patients in remote areas where medical conditions and the availability of specialists are limited.
Dr. Tim Collins, one of the researchers involved in the project, commented: “Successfully applying this technology could completely transform how we approach modern medicine. It is not only a solution for remote areas but also has the potential to support medical care in space.”
One of the envisioned prospects is to use this technology to perform surgeries on astronauts in space. Given the unique medical conditions in space, access to expertise from Earth is crucial. Remote surgical technology could become the perfect solution to ensure the health of pioneers in outer space missions.
This achievement represents an impressive breakthrough in the field of remote surgery.
Challenges and Prospects
Although remote surgery offers many promising opportunities, it also faces several challenges. Issues such as latency, stable and accurate data transmission remain factors that need further research and improvement. Additionally, ensuring that robotic devices and control systems operate effectively without technical glitches during surgery is extremely important.
Nevertheless, with significant advancements in medical technology, remote surgery is gradually becoming a more tangible reality. No longer mere experiments on animals, in the near future, we may witness complex surgeries on humans performed by doctors located thousands of kilometers away.
“In the next step of our research, we hope to perform remote endoscopy on the human stomach,” said Professor Bradley Nelson from the Multi-Scale Robotics Lab at ETH Zurich. “There is immense potential in this technology. Here, I am thinking of minimally invasive procedures in the gastrointestinal tract, such as cancer screening.”
Distance is no longer a barrier in modern medicine.
The success of remote surgery on a pig 9,300 km away has proven that distance is no longer a barrier in modern medicine. With rapid technological advancements, remote surgery could become a lifesaving method for many patients in remote areas, and even a solution in space medicine. This is a remarkable milestone, promising significant changes in the future of healthcare.
This study has been published in the journal Advanced Intelligent Systems and has attracted great interest from the medical and technological communities.



















































