 |
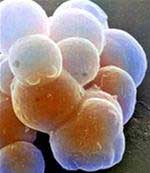
| Increasing scientific research indicates that stem cells can be effectively used to treat many dangerous diseases. |
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) announced yesterday, October 3, that it will establish a national stem cell bank at the University of Wisconsin, where human embryonic stem cells were first isolated.
This national stem cell bank will provide federally approved and funded human embryonic stem cells for research purposes. In the United States, stem cell research has existed since before August 2001, when President George W. Bush banned federal funding for research using stem cells from other sources.
“The national stem cell bank, a reward for the WiCell Research Institute at Wisconsin, will help reduce costs for researchers and maintain quality control of the cells,” according to officials from the NIH.
The NIH also stated that it is funding two other stem cell research centers at the University of California, Davis, and Northwestern University in Chicago. The NIH will allocate $16.1 million over four years for the stem cell bank and $9.6 million for the stem cell research centers.
Stem cells initially have the potential to develop into any cell type in the body. Scientists believe they have the potential to grow into the necessary cells for treating spinal injuries and diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and diabetes.
T.VY

















































