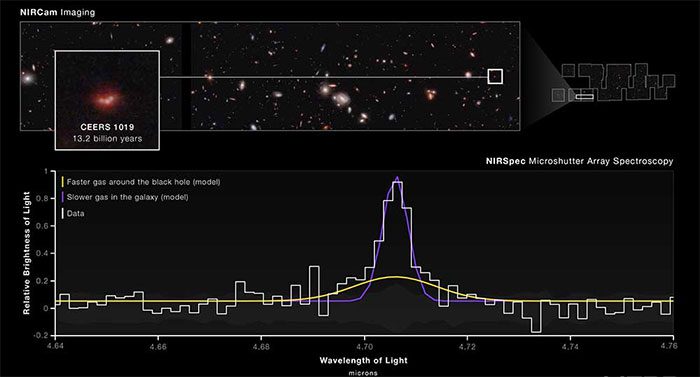
NASA has announced the discovery of a supermassive black hole by the James Webb Space Telescope, located at the center of the galaxy CEERS 1019, which formed over 570 million years after the Big Bang.
The black hole is situated at the center of the galaxy CEERS 1019.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has detected an exceptionally large black hole that is further away from Earth than any previously known.
In a statement released on July 6, NASA indicated that this black hole is located in the center of galaxy CEERS 1019, which formed over 570 million years after the Big Bang.
This active supermassive black hole is not only unusual in terms of its age and distance from Earth but also in its mass, which is only about 9 million times that of the Sun.
This mass difference is relatively small compared to typical supermassive black holes in the early universe, which usually weigh over a billion times the mass of the Sun, making them brighter and easier to detect.
The JWST also identified 11 galaxies that formed when the universe was between 470 to 675 million years old.
NASA stated that the black hole in galaxy CEERS 1019 is more similar to the black hole at the center of the Milky Way, which has a mass about 4.6 million times that of the Sun. This black hole is also not as bright as other larger black holes previously discovered.
According to NASA, despite its smaller size, this black hole appeared much earlier, leaving the mechanism of its existence shortly after the formation of the universe still a mystery.