According to experts, there are three reasons why the 6.2 magnitude earthquake in Gansu Province caused more severe damage than other earthquakes of the same magnitude.
As reported by Renmin, a 6.2 magnitude earthquake struck at 23:59 local time on December 18 in Zhi Shacheng County, Linxia Prefecture, Gansu Province, China (35.70° N, 102.79° E) with a depth of 10 km.

The 6.2 magnitude earthquake occurred in Zhi Shacheng County, Linxia Prefecture, Gansu Province, China. (Photo: Renmin)
Causes of the Earthquake in Gansu
In response, the China Seismological Network Center convened an emergency meeting for experts to study and analyze the earthquake’s activity. According to specialists, the earthquake occurred in the southeastern region of Gansu Province, which is an important part of the northeastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and is affected by numerous fault zones.

The earthquake occurred due to the collision of the Indian-Australian and Eurasian tectonic plates. (Photo: Renmin).
The earthquake occurred due to the collision of the Indian-Australian and Eurasian tectonic plates. The southeastern region of Gansu Province has long been subjected to pressure from these tectonic plates, resulting in strong tectonic activity and several major fault zones. Scientists explain that a fault is a crack or fracture zone between two blocks of rock. Faults cause the blocks of rock to move relatively against each other, leading to earthquakes if the movement occurs too rapidly. In an earthquake, the block on one side of the fault suddenly slips relative to the block on the other side.
Experts also stated that the angle of the fault relative to the surface, known as dip, and the direction of slip along the fault are used for classification. Faults that move along the dip direction are called thrust faults, while those that move horizontally are referred to as strike-slip faults.

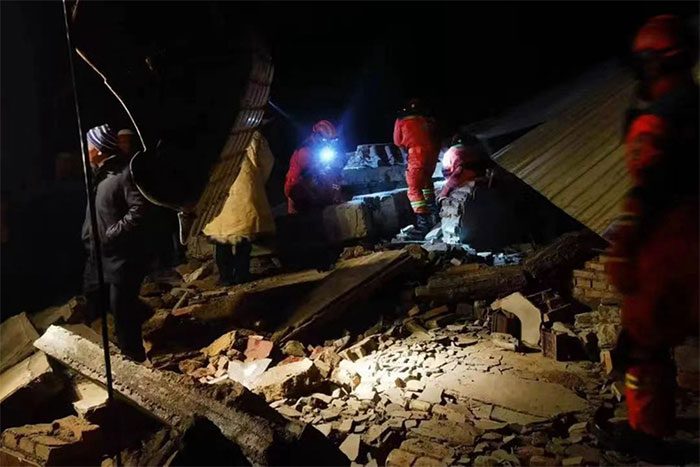
The earthquake caused significant damage to Gansu Province. (Photo: Renmin).
Moreover, oblique slip faults typically exhibit characteristics of both thrust and strike-slip faults. In this case, the earthquake in Gansu was classified as a reverse fault. Specifically, the block above the fault plane moved upward and overrode the block below. This was caused by the earthquake’s location in a compressive area where the Indian-Australian tectonic plate converges with the Eurasian tectonic plate.
Why Was the Earthquake in Gansu More Devastating Than Other Earthquakes of the Same Magnitude?
According to statistics from the Gansu provincial government, as of the afternoon of December 19, at least 111 people in this locality had died, and nearly 400 others were injured in the 6.2 magnitude earthquake that occurred in Zhi Shacheng County. Authorities in the neighboring Qinghai Province reported that 13 victims had died, raising the total death toll from the earthquake to 118 people.
Experts believe that the earthquake in Gansu was more devastating than other earthquakes of the same magnitude due to three reasons.
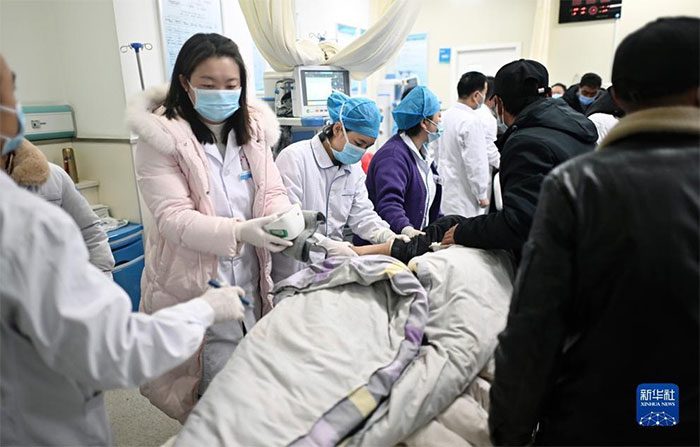

As of the afternoon of December 19, the total number of deaths from the earthquake reached 118. (Photo: Xinhua News)
- Firstly, the earthquake occurred in an area governed by fault zones. This was a typical reverse fault earthquake and had a very destructive power.
- Secondly, earthquakes often trigger landslides and other geological disasters, and the area where the earthquake occurred is prone to such hazards.
- Thirdly, the earthquake struck in the middle of winter, with the lowest temperatures in Zhi Shacheng reaching -14°C, making rescue operations for trapped individuals extremely challenging.
Warning of Strong Aftershock Risks in Gansu
Previously, about 72 km from this earthquake, a 6.7 magnitude earthquake occurred in 1936. Since 1900, seven earthquakes of magnitude 5 or greater have occurred within 100 km of this earthquake. The most recent one was a 5.7 magnitude earthquake recorded at the end of October 2019.
Local officials stated that there is still a risk of strong aftershocks in the area where the earthquake occurred: “Based on characteristics such as regional structure, historical seismic activity, and the type of earthquake sequence of this event, a comprehensive analysis indicates that the area where the earthquake occurred still has the potential for strong aftershocks of magnitude 5 in the coming days.”