A study led by Dartmouth College highlights another potential cause of the mass extinction of dinosaurs, aside from the asteroid impact.
What caused the extinction of dinosaurs 66 million years ago at the end of the Cretaceous period? This question has long fascinated scientists and researchers from around the globe.

The hypothesis that most experts believe is that an asteroid caused the extinction of dinosaurs.
So far, the prevailing theory among experts is that a comet, asteroid, or meteorite struck Earth, leading to the destruction of ecosystems and the extinction of dinosaurs.
However, a recent study led by Dartmouth College suggests that unusual volcanic activity may be the primary cause of mass extinctions, including the disappearance of dinosaurs.
According to researchers, four out of five mass extinctions on Earth coincided with a type of volcanic eruption known as “flood basalt.” These floods inundated vast areas with lava, sometimes covering entire continents in less than a million years.
Their activity has left clear evidence to this day, exemplified by what geologists call “large igneous provinces” (LIP). According to Science, these areas contain at least 100,000 cubic kilometers of magma, equivalent to 400,000 times the volume of an Olympic-sized swimming pool.
Additionally, a common feature of these volcanic eruptions is the release of massive amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, leading to near-total disruption of life.
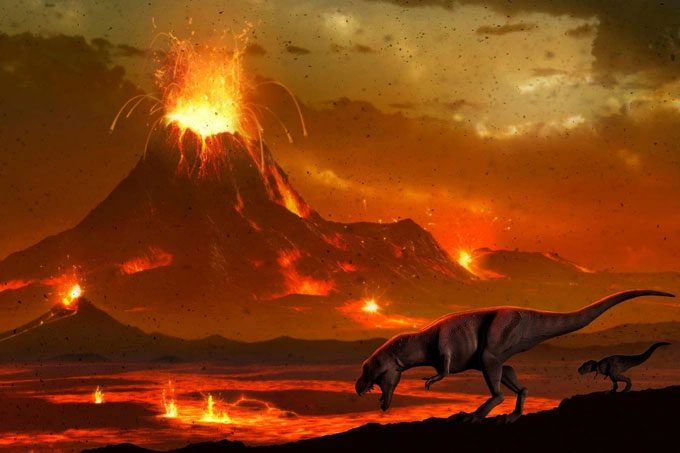

Dinosaurs may have gone extinct due to events that occurred on Earth. (Photo: Getty).
In fact, science has shown that a series of volcanic eruptions in present-day Siberia, accompanied by large amounts of methane from the ocean floor, caused the largest extinction event among mass extinctions about 252 million years ago.
These volcanic eruptions also shook the Indian subcontinent around the time when large dinosaurs were gradually dying out, forming the land area now known as the Deccan Plateau.
This hypothesis is supported by many, as its consequences are similar to those when Earth was struck by asteroids, including widespread global impacts, with the atmosphere filled with dust and toxic smoke.
These factors led to dinosaurs suffocating and other living organisms facing long-term, large-scale climate changes.
Brenhin Keller, an Earth Sciences professor at Dartmouth, stated: “While it is challenging to determine whether volcanic eruptions were the cause of a mass extinction, the results of this study make it hard to overlook the role of volcanoes in extinction events.”
If a causal link is found between “flood basalts” and mass extinction, scientists believe that larger volcanic eruptions could lead to even more severe extinction events in the future.