Australian Biotechnology Company Proteome Announces Plans for New Prostate Cancer Diagnostic Tool
 |
New Tool for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis |
Proteome Systems has partnered with U.S.-based Egenix Cancer Diagnostics to develop a new tool for diagnosing prostate cancer.
This innovative diagnostic tool will test for the presence of cancer-associated epithelial antigens (HCA) in men’s semen.
Stephen Porges, a representative from Proteome Systems, stated that the tool could be ready for use within one to two years.
It is expected to provide more accurate results compared to current prostate cancer testing methods.
Current diagnostic tools function by testing blood to identify prostate cancer-associated epithelial antigens. They only detect the disease when cancer cells have spread or infiltrated the bloodstream.
There is hope that this new semen-based diagnostic approach will yield higher success rates. The potential for misdiagnosis with this new tool is significantly lower than with existing methods.
However, Proteome Systems also has concerns regarding whether men will be willing to provide their semen for testing.
But it is quite normal to check for cancer signals… and most men will likely need to provide samples for testing instead of undergoing a biopsy.
Meanwhile, a group of American scientists has recently discovered that chili peppers, a familiar spice in daily meals, contain capsaicin, which may inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cells in men.
In experiments with prostate cancer tumors in mice, researchers found that mice treated with capsaicin had tumors that were one-fifth smaller than those not treated with the compound.
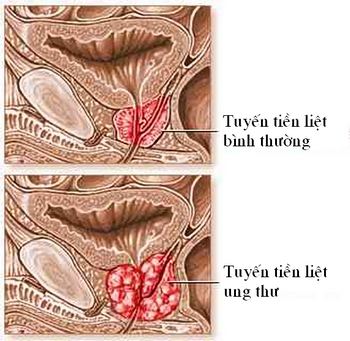
Comparison of Normal and Cancerous Prostate
Dr. Soren Lehmann from the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and the University of California, Los Angeles, stated, “Capsaicin can effectively inhibit the extensive growth of prostate cancer cells in humans.”
Scientists also recommend that individuals diagnosed with this disease increase their chili intake.
Currently, prostate cancer is becoming increasingly common among men in the United States.
It is estimated that about 232,000 men are diagnosed annually, with approximately 30,000 fatalities. Globally, around 221,000 deaths occur due to this disease.
Ngọc Huyền