He was a Scottish inventor and engineer. With significant improvements to the steam engine, he became a key figure in the Industrial Revolution. He was also honored as the 22nd most influential person in history.
James Watt was born on January 19, 1736, in the coastal town of Greenock, Scotland. His father was a shipowner and a successful shipbuilder. His mother came from an aristocratic family. James Watt’s grandfather was a mathematician and the headmaster of the local school. As a result, young James was educated very carefully from an early age.
Despite showing a talent for mathematics, James Watt could not attend school due to his poor health. Instead, he stayed at home and learned mechanical engineering skills.
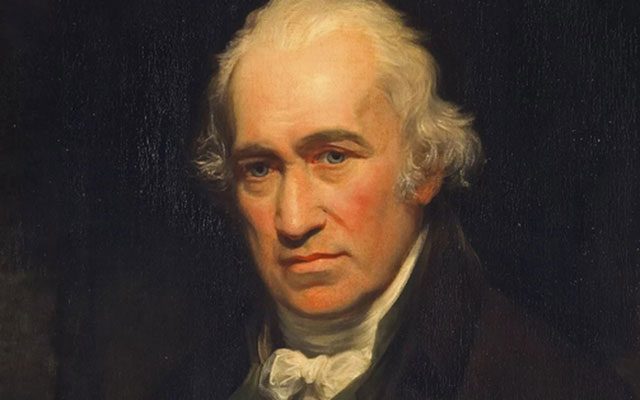

James Watt (1736-1819).
Young Watt was an avid reader and always found something interesting in every book. By the age of 6, Watt was solving geometric problems and using his mother’s teapot to explore the concept of steam.
As a teenager, James Watt began to showcase his abilities, particularly in mathematics. In his spare time, Watt sketched with pencil, carved, and worked on wooden and metal tool benches. He created many intricate mechanical models and enjoyed helping his father repair equipment.
At 17, James Watt’s mother passed away, and his father’s business was no longer thriving. Watt spent a year in London studying the production of mathematical instruments before returning to Scotland to establish a business in Glasgow. However, because he did not undergo a seven-year apprenticeship, his plans were thwarted. Instead, a professor at the University of Glasgow arranged for Watt to set up a workshop at the university.
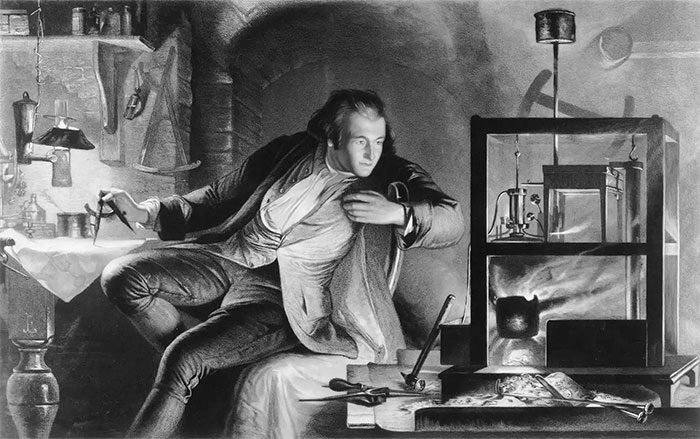
Young James Watt. (Photo: Getty Images).
James Watt began experimenting with steam engines in the early 1760s. At that time, the University of Glasgow had a non-functioning Newcomen steam engine model. Watt studied the model engine in 1763 and attempted to get it working again.
During this process, Watt discovered the issue of steam condensation within the same cylinder. He calculated that 80% of the energy in steam was wasted in heating the cylinder during each cycle. His improvement allowed steam to condense in a separate chamber, enabling the cylinder to remain hot throughout the operation.
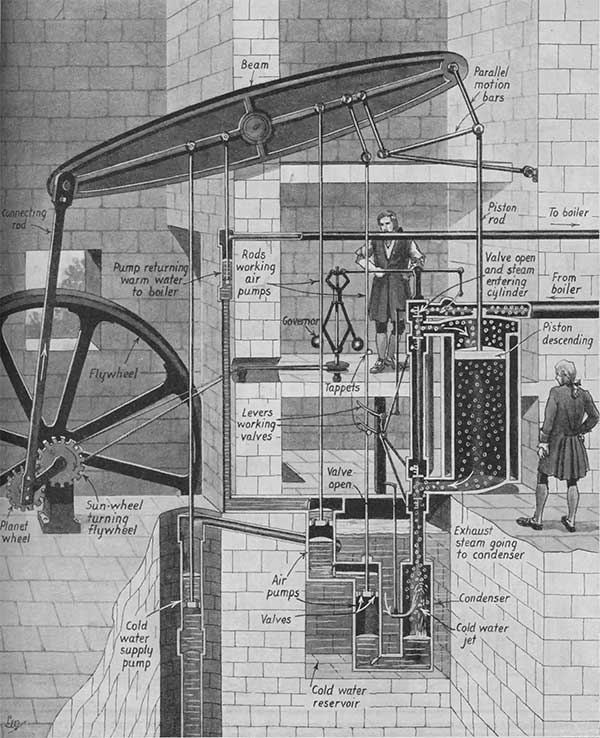
Steam engine improved by James Watt. (Photo: Getty Images).
By 1765, his improvements were completed and demonstrated significant efficiency compared to the simple Newcomen engine. However, it took another decade for the first complete engine to be created.
On his way to London to apply for a patent in 1768, Watt met Matthew Boulton, the owner of a manufacturing company in Birmingham called Soho Manufacturing, which produced small metal goods.
Matthew Boulton had both the facilities and extensive knowledge of language and science. Therefore, Watt partnered with Boulton to manufacture his engines.
In the following decades, Boulton & Watt made a series of significant improvements to their steam engines. By the mid-1780s, their engines were five times more efficient than Newcomen’s. The steam machines that Watt created became increasingly advanced and supplied a large market.
In 1782, the bidirectional steam engine that Watt researched and built was officially launched and granted exclusive patent rights. In 1784, a horizontal steam engine was also confirmed for patent rights. The steam engine became more practical and widely used, referred to as the “universal steam engine.”
By 1790, after making many enhancements and additions, Watt completed his steam engine manufacturing process. This marked a leap in human manufacturing technology, a milestone for the “age of steam.”
From that point on, Boulton & Watt’s company was able to produce various types of operational engines for real-world applications. Innovations and new patents were applied to machines used for milling, weaving, and grinding. Steam engines were also utilized for transportation on land and water. Nearly every successful and significant invention that marked the history of steam power for many years originated from the workshops of Boulton & Watt.
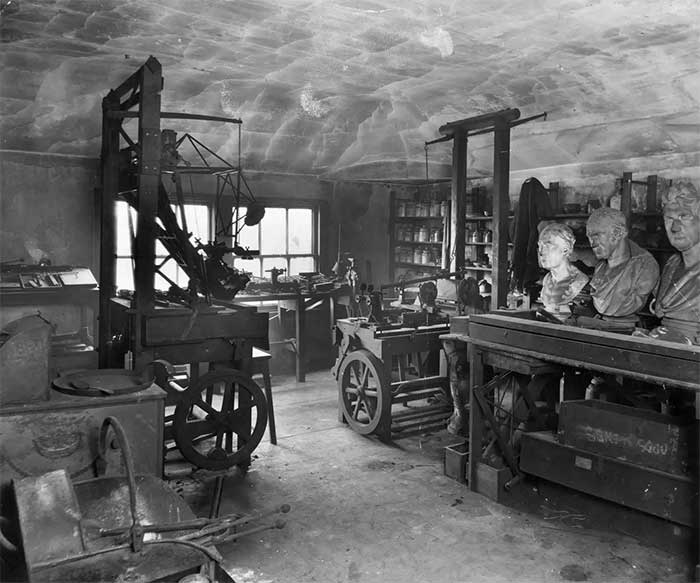

James Watt’s workshop in Heathfield, where he lived from 1790 until his death. (Photo: Getty Images)
Watt ceased steam engine production in 1800 but continued to explore inventions in various fields. Looking at today’s life, we can see the enormous impact of the Industrial Revolution. Therefore, James Watt is also honored as one of the influential figures in human history and has been awarded many prestigious titles.
In 1819, Watt passed away at the age of 85. His inventions propelled the Industrial Revolution and modern innovations, from automobiles and trains to steam ships and factories, not to mention the social issues that arose from them. Today, Watt’s name is associated with measurement units, streets, museums, and schools. His story has inspired books, films, and works of art.





















































