Paleontological discoveries over the past year reveal that Earth was not merely a dinosaur world during the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods, but a remarkably diverse planet filled with monstrous creatures.
1. Sea Monsters Related to Dinosaurs, Snakes, and Dragons

New species of mosasaur – (Photo: University of Bath)
Pluridens serpentis, a newly discovered species with fossils unearthed in Morocco, resembles a gigantic and bizarre dolphin. It features a long, slender jaw with over 100 razor-sharp teeth designed to seize small prey such as fish and squid, and its body measures up to 8 meters in length.
The research team led by the University of Bath (UK) indicates that this creature is a mosasaur and is related to dinosaurs, snakes, and dragons.
2. The Monster Turtle

Graphic depiction of the monster turtle at hatching – (Photo: University of Calgary)
A farmer in China discovered strange eggs in 2018 and donated them to a university, but it wasn’t until 2021 that the truth about them was revealed. The eggs belonged to Yuchelys nanyagensis, a “monster turtle” species that went extinct alongside all dinosaurs on Earth during the Chicxulub asteroid disaster 66 million years ago.
According to Associate Professor Darla Zelenitsky from the University of Calgary in Canada, a member of the research team, the embryos within the eggs, dating back up to 90 million years, were 85% developed. The embryos allowed scientists to estimate the size of the adult: its shell length could reach up to 1.6 meters.
3. Dragon-headed Pterosaur
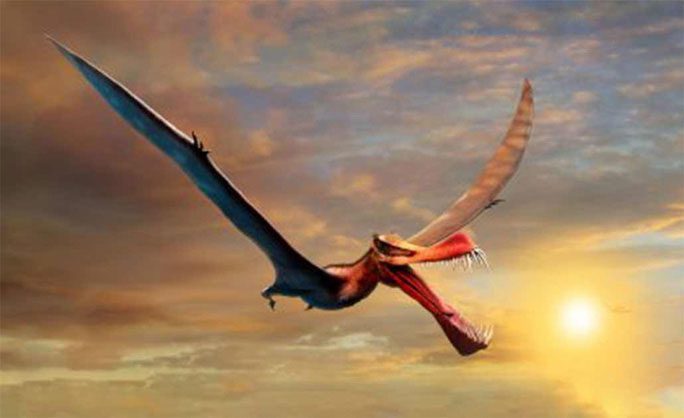

Thapunngaka shawi – (Photo: University of Queensland)
A study published in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology by the University of Queensland (Australia) introduces a terrifying flying creature with a wingspan of 7 meters, a 1-meter long head, and 40 razor-sharp teeth, dangerous as a crocodile. It is a pterosaur named Thapunngaka shawi. Scientists liken it to a real-life dragon.
4. Jurassic Monster with 80 Jaws, Still Alive
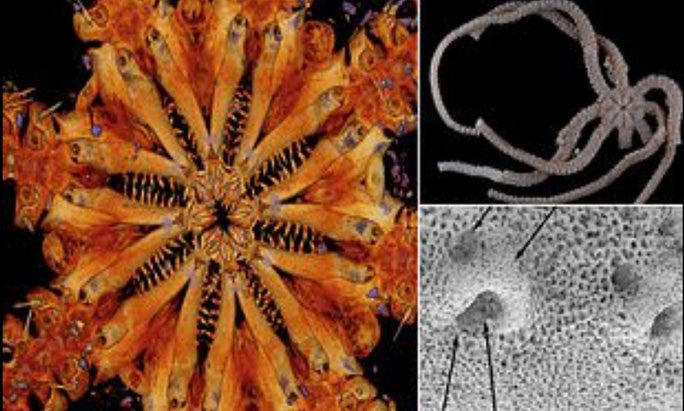
Close-up of the 80-jawed monster – (Photo: Proceedings of the Royal Society B).
Ophiojura exbodi, a distant relative of starfish, branched off from its closest relatives at the beginning of the Jurassic period and has remained evolutionarily unchanged for 180 million years.
This creature was first discovered by scientists from the French National Museum of Natural History in 2011 in the cold, dark waters at the bottom of the South Pacific region, and it took many years to gather further evidence and identify the species.
By June 2021, a comprehensive study about it was published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
5. Giant Ichthyosaur

Close-up of the 10-meter-long ichthyosaur fossil – (Photo: Rutland Water Nature Reserve)
Temnodontosaurus trigonodon is likely the largest ichthyosaur fossil in the world. This monster measures up to 10 meters long and is 180 million years old, discovered at the Rutland Water Nature Reserve (UK).
In the UK, ichthyosaurs are also referred to by a mythical name, “sea dragon.” Ichthyosaurs existed alongside dinosaurs throughout the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods.