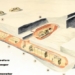
The APS-R spacecraft will provide refueling services for compatible vehicles in geostationary orbit at an altitude of approximately 35,800 km above the equator.
There are thousands of satellites and spacecraft orbiting Earth, but they all face a serious issue: fuel depletion. This problem often forces satellites to cease operations even when their equipment is still in good condition.
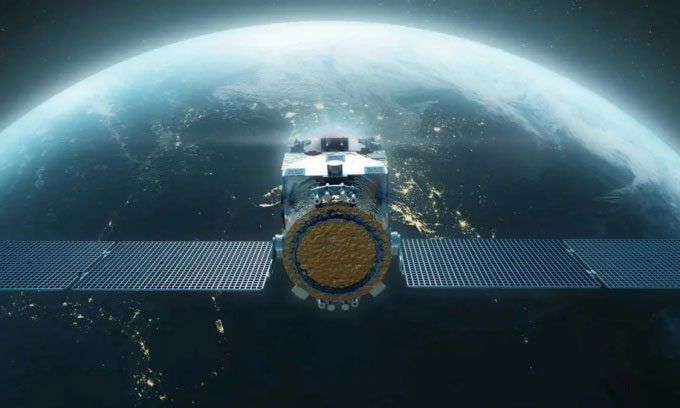

Simulation of the Astroscale Prototype Servicer for Refueling (APS-R) in orbit. (Image: Astroscale US).
To address the fuel issue, the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) in the United States plans to develop a spacecraft that provides refueling services in space. This initiative is part of the Space Mobility and Logistics (SML) pilot project, worth $25.5 million, funded by the U.S. Space Force and managed by aerospace company Astroscale US. They will develop a prototype small spacecraft named Astroscale Prototype Servicer for Refueling (APS-R) to refuel compatible vehicles in geostationary orbit.
Geostationary satellites operate at an altitude of approximately 35,800 km above the equator, primarily for telecommunications purposes. The APS-R will travel in a circular orbit that matches the Earth’s rotation period. The spacecraft will transport hydrazine propellant from storage to satellites in need of fuel. It can provide services to any spacecraft equipped with a compatible refueling port.
SwRI aims to manufacture a “spacecraft bus” to carry the APS-R into space within the next 16 months. “The maximum dimensions are 61 x 71 x 114 cm when folded for launch, and the total launch mass of the vehicle is 198 kg, including the propellant”, said Steve Thompson, project engineer at SwRI.
The development of the spacecraft bus will take place at SwRI’s 6,900 m2 payload processing and new space systems facility. This facility is built for the rapid assembly and testing of small spacecraft.
Once the design and development of the spacecraft bus are completed, SwRI will integrate the payload provided by Astroscale and conduct environmental testing in preparation for the launch. The APS-R spacecraft is expected to be ready for launch in 2026.