This article was published in the June 2006 issue of the Scientific Activity Journal (Ministry of Science and Technology), detailing the harmful effects of radiation in the atmosphere, primarily from Alpha rays emitted by the radioactive isotope Radon-222.
For a long time, the scientific community has warned about the risk of lung cancer in the community, particularly in mining areas, residential buildings, and especially in bedrooms and workplaces, particularly concerning building materials.
Radon in the Air
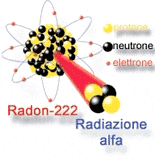 |
| Radon emits radiation (Photo: VNN) |
Radon is a radioactive isotope belonging to natural decay chains. Radon-222 is from the uranium-238 series, radon-220 is from the thorium-232 series, and radon-119 is from the uranium-235 series, commonly known as radon and thoron, respectively. Radon and thoron are inert gases that do not participate in any chemical compounds.
Compared to thoron-220 and radon-119, the radiation hazard of radon-222 is very high due to its half-life of 3.8 days, while thoron has a half-life of 55 seconds and radon-119 has a half-life of 4 seconds.
Radon is a leading carcinogen among lung cancer-causing agents.
In the air, radon and thoron exist in free atomic form. After escaping from building materials, soil, and other minerals, they decay into a series of radioactive progeny, the most dangerous of which is polonium-218.
Polonium decays via alpha radiation with a half-life of 3.05 minutes, sufficient for several respiratory cycles in the human respiratory system.
Polonium-218 travels with dust particles sized in nanometers and micrometers, forming radioactive aerosol particles. These radioactive aerosols, which are several tens of micrometers in size, can be inhaled through the respiratory tract and, more dangerously, can be retained in the alveoli.
In the alveoli, polonium-218 decays via alpha emission, releasing helium nuclei – alpha particles (with a charge of +2e; atomic mass of 4).
These high-energy alpha particles bombard the nuclei of alveolar cells, causing chromosomal damage and negatively affecting the cell division mechanism. A portion of the nuclear decay energy is transferred to the decaying nuclei, causing these nuclei to recoil. The recoil energy of radon nuclei can be sufficient to break down protein molecules in alveolar cells. As a result, the probability of cancer caused by radon is very high.
Thus, determining the concentration of radioactive aerosols caused by radon (i.e., measuring radon) is very important for monitoring and warn of lung cancer risks in the community, in mining areas, residential buildings, and especially in bedrooms and workplaces.
According to the Environmental Law of the United States, the permissible level of radon in residential buildings is
Control Measures, Warnings, and Reducing Radon Concentration
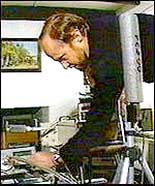 |
| Measuring Radon concentration in the air (Photo: VNN) |
To determine radon levels, specialized measuring devices are required. Radon concentration in the air is expressed in units of pCi/l or Bq/m3.
Places that need to be monitored for radon levels include residential homes, inns, hotels, offices, and areas where radioactive ore is mined.
Radon levels in the air also depend on ventilation. Therefore, bedrooms and offices with air conditioning but lacking ventilation are at significant risk of radon contamination. The exposure risk to radon also depends on the duration of time spent in the living, working, or resting space.
In particular, radon levels greatly depend on the materials used.
Building materials derived from granite will have the highest radon levels, while clay ceramics and coal ash bricks also contain significant radon. Sedimentary minerals such as ilmenite, rutile, zircon, and monazite, which are rich in radioactivity, are also sources of radon.
Hospitals using Ra-226 needles may also cause radon leaks or diffusion into the air.
To minimize radon levels in living and working spaces, low-radon building materials should be used. Offices and bedrooms should be well-ventilated. If working in areas rich in natural radioactivity, consideration should be given to the duration of work in such environments.
 |
| Radon is present everywhere in our environment… (Photo: VNN) |
Who and Where Can Assess Radon Levels in Workspaces?
To measure the activity or levels of radon, specialized equipment is necessary, and the user of this equipment must possess professional qualifications and be authorized by the Radiation and Nuclear Safety Control Bureau.
The Ho Chi Minh City Nuclear Center (located at 217 Nguyen Trai, District 1, Ho Chi Minh City) is one of the authorized units.
This agency has radiation safety experts who are well-trained, certified, and authorized to advise and assess issues related to ionizing radiation safety, including radon. Additionally, other units under the Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute, such as the Da Lat Nuclear Research Institute and the Hanoi Institute of Science and Nuclear Technology, are also authorized in this field.
(According to the Scientific Activity Journal – 6/2006, VietNamNet)

















































