This discovery not only raises questions about the nature of life but also about evolutionary potential and the hidden threats to our future.
Today, with the rapid advancement of science and technology, the intersection of artificial intelligence and biotechnology is leading to an unprecedented scientific revolution. Recently, a groundbreaking achievement by American scientists has shocked the world – they successfully created the world’s first “living robot” capable of self-reproduction. This discovery not only challenges our understanding of the essence of life but also raises questions about its future regarding evolutionary potential and hidden threats.
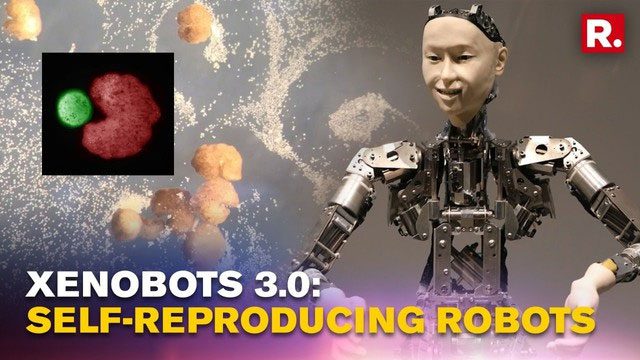
In early 2020, a team of scientists from the University of Vermont, Tufts University, and the Wyss Institute at Harvard University in the United States successfully created the “living robot” – Xenobot, measuring just a few millimeters, using living cells extracted from Xenopus embryos. These tiny robots not only move freely in a petri dish but also have the ability to carry drugs and self-heal. However, what truly made Xenobots famous in the scientific community is their subsequent ability to self-reproduce.
American scientists successfully created the world’s first “living robot” capable of self-reproduction.
Using artificial intelligence technology, scientists optimized the design of the Xenobot and ultimately determined a shape resembling the main character from the video game “Pac-Man.” This design significantly improved the efficiency of the robot during the reproduction process. As these “Pac-Man” shaped robots move around their environment, they use special “mouth” structures to collect stem cells. Over time, these stem cells gather to form new “baby” robots, shaped and moving similarly to them. This process not only marks a significant breakthrough in the self-replication technology of biological robots but also opens a new chapter in artificial life research.
Navigating whether living robots can evolve to become larger is still in its preliminary stages. Based on known test results, the self-replicating system of Xenobots has certain limitations and its replication process typically can only extend for a limited number of generations. This is primarily restricted by various factors such as the culture environment, cell concentration, and temperature range. However, with the ongoing advancements in artificial intelligence and biotechnology, it may be possible to extend the lifespan of the replication system by further optimizing design and testing conditions in the future, even exploring the possibility of increasing its size.
This tiny robot not only moves freely in a petri dish but also has the ability to carry drugs and self-heal.
It is noteworthy that biological evolution is an extremely complex and lengthy process, involving multiple levels such as gene mutation and natural selection. Although current living robots have demonstrated certain self-replicating abilities, the mechanisms behind them rely more on the interaction between cells and the optimal design of artificial intelligence, rather than traditional biological evolution. Therefore, more scientific research and empirical validation are needed to determine whether Xenobots can truly grow and become larger.
Faced with the world’s first living robot capable of self-replication, public concern primarily revolves around whether it poses a threat to humanity. Based on the current stage of research, this concern is somewhat unnecessary.
First, Xenobots currently can only exist and reproduce in a laboratory environment and do not possess the ability to survive independently in a natural setting.
Second, scientists maintain a high level of caution and responsibility in their research on living robots, applying strict monitoring and ethical assessment mechanisms to ensure their research activities do not have negative impacts on humans and society.
However, in the long term, with the continuous development of technology and the expansion of application fields, the safety issues surrounding living robots are also of great concern. Once they acquire the ability to adapt to their environment and possess stronger self-replication capabilities, they may have unknown impacts on ecosystems. Therefore, while promoting research, scientists need to strengthen interdisciplinary collaboration and conduct in-depth discussions about the potential risks and countermeasures of living robots to ensure the healthy and sustainable development of the technology.
The successful creation of self-reproducing living robots is a significant milestone in the history of science. This achievement not only showcases the immense potential of integrating artificial intelligence and biotechnology but also opens a new perspective on the nature and mechanisms of evolution of life. We should feel excited and proud of these advancements, but we also need to remain rational and cautious.
Technological development must go hand in hand with ensuring safety, control, and sustainable growth. Future research and discoveries will continue to expand our understanding of life and artificial intelligence, shaping humanity’s future in an increasingly advanced technological world.


















































