A gate or a fence adorned with elegant climbing roses is sure to brighten up any garden, bringing vitality to the home.
Guide to Growing Climbing Roses
Climbing roses, known for their stunning beauty and fragrance, are often grown to decorate gardens in villas or green areas. They produce numerous flowers, especially in summer, and are generally easier to cultivate in the northern provinces. However, flower enthusiasts can also grow them in various regions across the country. Climbing roses come in a variety of colors, including deep red, pale pink, lavender, white, and yellow, blooming primarily at the end of April and early May.
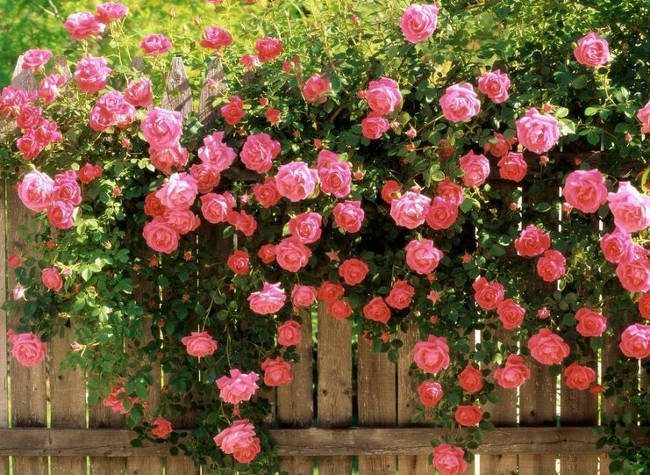

Climbing roses are ideal for decorating gates or gardens. (Illustrative Image)
This type of rose is both beautiful and fragrant, making them a favorite among many. They grow quite rapidly in suitable conditions and do not extend as far as other climbing plants, so they are often planted in smaller spaces such as columns, gates, or fences, or even in elevated flower beds to allow the plants to spread out.
Morphological Characteristics of Climbing Roses
- Climbing roses have a woody, climbing stem with drooping branches. They climb by attaching to other plants or existing structures like walls and fences.
- The base of the stem is woody, dividing into several branches above, all covered with sharp thorns.
- The foliage is dense and can reach up to 3 meters in height.
- The leaves are compound and feather-like, each containing 5 to 9 leaflets. The leaflets are oval with serrated edges.
- The flowers are unisexual, large, and bloom vibrantly in various colors such as pink, purple, red, and white. Each flower has many thick petals arranged around a central core, measuring 6 to 8 cm in diameter. Climbing roses usually bloom in April and May, releasing a gentle fragrance.
- The fruit is flattened and spherical, with a brick-red color.
Ecological Characteristics of Climbing Roses
- Climbing roses prefer airy, cool places and thrive outdoors but cannot withstand harsh sunlight, making them commonly grown in temperate regions.
- This flower species is resilient, robust, and easy to care for.
- They have an average growth rate.
- In our country, the best areas for cultivating climbing roses are in the north or highland regions.
Essential Knowledge Before Planting Climbing Roses
Climbing roses are very easy to plant and care for. When planting them, choose locations with plenty of natural sunlight to ensure faster growth and more blooms.
Climbing roses do not thrive in excessively high temperatures and humidity. Since their branches do not extend as far as other climbing plants, they require a trellis or support to climb. They are often planted in places like columns, gates, fences, or a section of wall, especially next to windows, or can be planted in elevated flower beds to allow for sprawling growth.
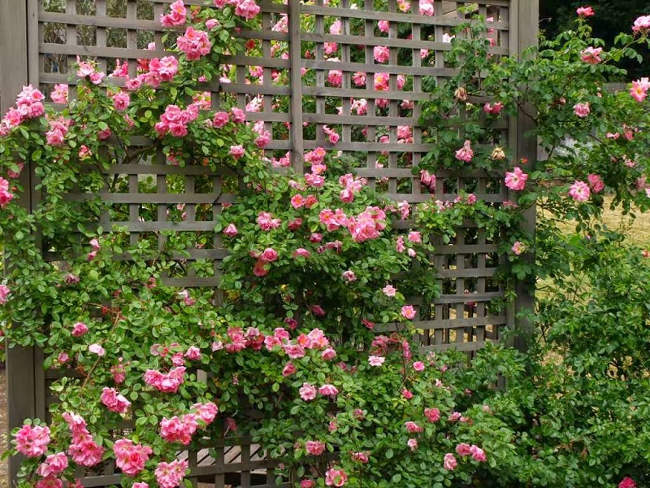

Climbing roses are beautiful flowers loved by many. (Illustrative Image)
Techniques for Planting and Caring for Climbing Roses
Choosing Seeds: The quality of the seeds significantly impacts the quality of the plants and flowers later on.
Soil and Planting Location: The soil should be deep, loose, with clay content, rich in sunlight and moisture. If using sandy soil, mix in organic fertilizer and clay.
Planting Varieties: For roses planted between October and December, only trim them moderately. Weak shoots should be completely removed. For those planted in spring (March to May), leave one outward-facing bud. Trim one-third of the roots. Seeds planted directly might result in weaker plants that do not grow vigorously.

Plant climbing roses in well-drained soil to avoid waterlogging; if using pots, ensure they are large enough. (Illustrative Image)
Planting Method: If planting cuttings, soak the rose cuttings in water for 2-3 hours before planting. If it is too sunny, cover them with a damp cloth. The planting hole should be deep. Bury the woody segment in the middle of the brown roots and the green bud, leaving about three fingers above the soil. Use a mix of soil and organic fertilizer to cover and firmly pack the base. Water lightly to stabilize the plant. During dry seasons, water each morning. Avoid watering on the leaves and flowers, as this can promote harmful fungi.
Caring for Climbing Roses After Planting
Watering: During dry seasons, water the flowers each morning. Avoid watering on the leaves and flowers to prevent the growth of harmful fungi.
Fertilizing: In spring, apply organic fertilizer rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to encourage blooming. In July, avoid nitrogen-rich fertilizers. In September, apply potassium-rich fertilizer to strengthen the woody stems.
Pruning: For climbing roses, only prune some smaller branches to reduce overcrowding. After flowering, cut back about 2-3 leaf nodes. Shoots at these nodes can weaken the plant and produce smaller flowers. For climbing roses, prune excess lateral shoots to ensure strong blooms.
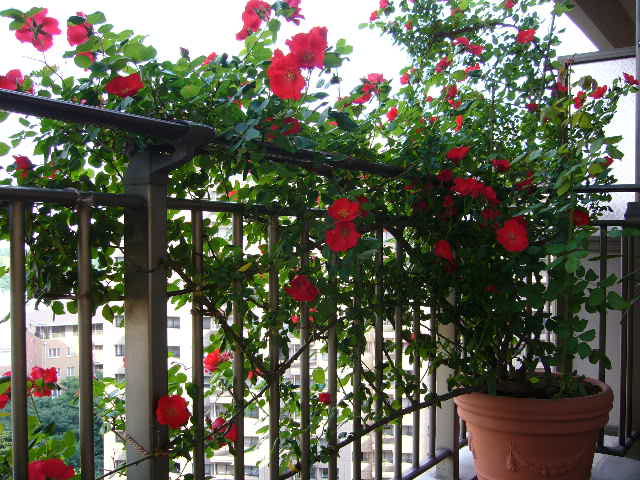

You can plant climbing roses on the balcony.
Ideal Times for Planting Climbing Roses
The best time to plant climbing roses is in early spring, summer, or autumn, allowing the plants to establish strong root systems before winter arrives. Notably, climbing roses planted in spring tend to be more resilient and grow much stronger than those planted in the other two seasons.
Climbing roses prefer sunlight, so the planting location must receive at least 6 hours of sunlight daily. It is advisable to plant them facing east to capture morning sunlight. The planting area should also be spacious, as climbing roses tend to occupy a lot of space as they grow. Avoid planting them too close to other plants in the garden.