Sinuses are hollow cavities filled with air, located behind the cheekbones and forehead. There are four types of sinuses: frontal sinuses, ethmoid sinuses, sphenoid sinuses, and maxillary sinuses.
Among the types of sinusitis, frontal sinusitis is the one most likely to lead to intracranial complications. These intracranial complications include: encephalitis, meningitis, brain abscess, epidural abscess, and cavernous sinus thrombosis.
Frontal sinusitis is the inflammation of the mucous membrane of the frontal sinus, which blocks the sinus drainage openings, causing the accumulation of fluid or mucus within the sinus cavity.
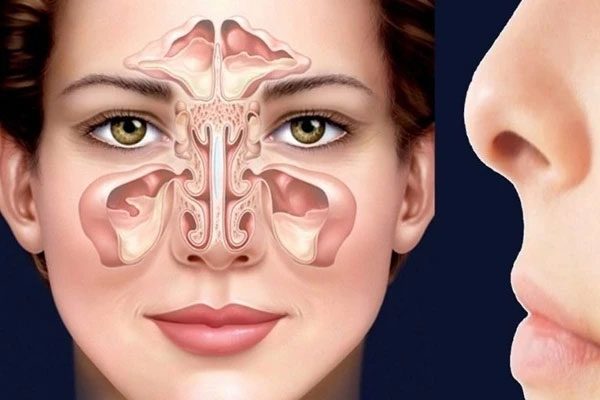
Frontal sinusitis is the type of sinusitis most likely to lead to intracranial complications.
Causes and Risk Factors for Frontal Sinusitis
- Viruses: Typically, sinusitis begins with cold symptoms caused by viruses that lead to nasal mucosal congestion and blockage of the sinus drainage openings.
- Allergies
- Bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae bacteria commonly reside in the nasopharynx. When health issues arise, these bacteria can proliferate and cause illness. A cold can eventually lead to sinusitis.
- Polyps are benign mucosal growths that develop from the nasal or sinus mucosa, leading to sinus obstruction, preventing mucus drainage, and causing sinusitis. These small growths can also limit airflow, causing headaches and reducing or losing the sense of smell.
- Air pollution
- Swimming/diving in pools: Chlorine in pools can irritate the nasal mucosa, leading to inflammation and exacerbating sinusitis.
- Fungi: Aspergillus is a common fungus that causes sinusitis. When the immune system is weakened, fungi can thrive, especially in moist and dark environments like sinuses.
- Overuse of nasal sprays
- Smoking
- Congenital abnormalities in the nasal area
Symptoms of Frontal Sinusitis
The most common symptom of acute frontal sinusitis is pain around the eyes or forehead. This pain is very distinctive and is described as pain above the eye socket and aching along both sides of the brow.
The pain may occur on one or both sides of the sinus and varies throughout the day. When there is post-nasal drip or mucus can be expelled, internal sinus pressure decreases, and the pain gradually subsides.
- Other signs of frontal sinusitis include:
- Runny nose
- Cough, sore throat
- Nasal congestion
- Reduced sense of smell
- Foul breath
- Mild fever or high fever >38.5 degrees Celsius
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue and body aches.
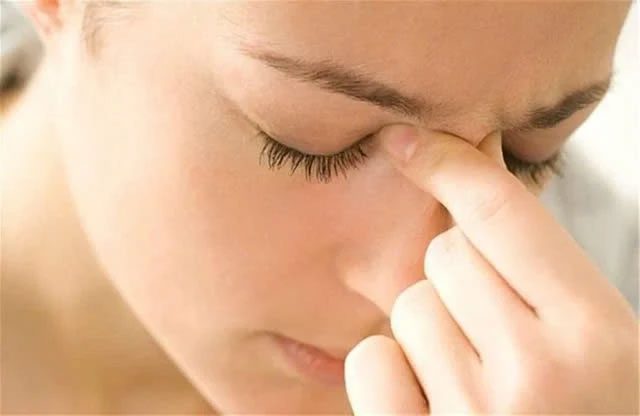

The most common symptom of acute frontal sinusitis is pain around the eyes or forehead.
Preventive Measures for Frontal Sinusitis
- Keep warm during cold weather. When going outdoors at night, early morning, or working outside in cold weather, dress warmly, paying attention to keeping your feet, hands, chest, neck, and head warm.
- Avoid contact with people showing signs of infectious diseases such as flu, respiratory infections, diarrhea, measles, rubella, chickenpox… Limit visits to crowded places.
- Maintain a balanced diet with sufficient nutrients, eat plenty of fruits to enhance nutrition and boost immunity. Ensure a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
- Drink warm water, avoid consuming food or drinks directly from the refrigerator.
- Get vaccinated on schedule for disease prevention…
- Ensure environmental hygiene, maintain cleanliness at home, and keep the living space warm.
- Practice personal hygiene, regularly wash hands with soap, and clean the nose and throat daily with saline solution.



















































