People in the Middle Ages engaged in many strange and inexplicable practices, such as rarely bathing and diagnosing illnesses using urine…

Medieval people used moss, leather, and fabric as toilet paper. This is a rather surprising discovery about the lives of people in the past.

Medieval people used urine to wash dirty clothes. Soap was rarely used because it was quite expensive.

In the Middle Ages, many believed that diseases were related to water. They thought that water carried diseases that entered the body through the pores. Therefore, some people only washed parts of their bodies. They did not wash their faces because they believed this action was very dangerous and could lead to impaired vision. In fact, many members of the upper class bathed only 1-2 times a year.

People in the Middle Ages did not place much importance on hair washing. While farmers rarely washed their hair, even kings and queens did so only a few times a year. Instead of washing their hair clean, they used wigs, hats, and crowns.
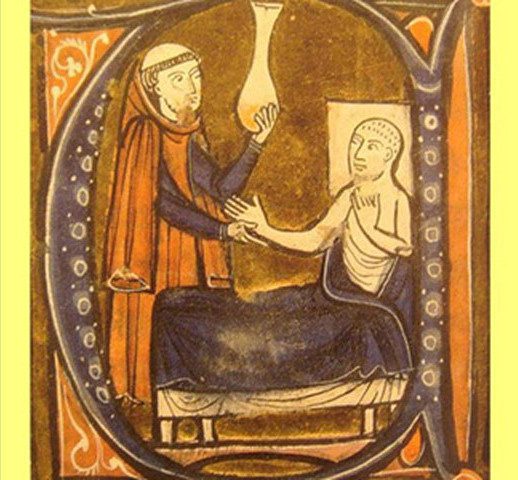
Many medieval doctors used patients’ urine to diagnose illnesses. They would check the color, smell, and even taste of the urine to draw conclusions about the diagnosis.
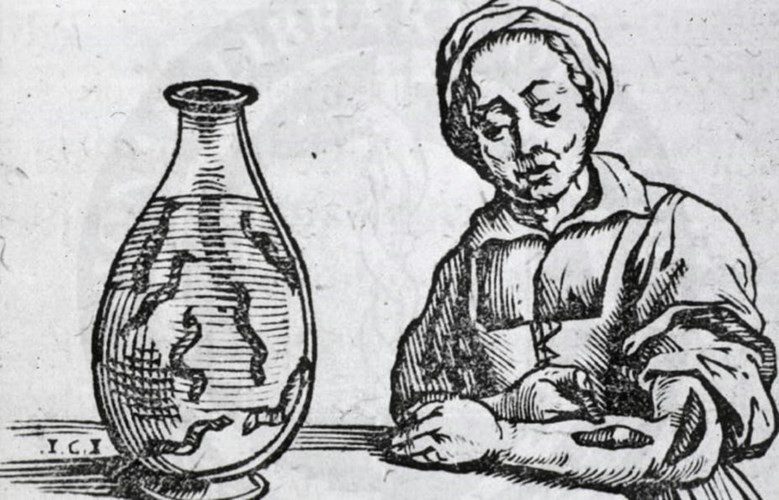

In the Middle Ages, bloodletting was considered an effective treatment. Doctors would let leeches suck the blood of patients to cure their ailments. Many believed in this painful treatment method.
Many medieval people slept on straw mattresses. They would typically replace these straw mattresses once a year. As a result, fleas and lice often infested their sleeping areas. People accepted this as part of life.

In the 1400s, many women preferred an egg-shaped face, small noses, and high foreheads, leading them to shave off their eyebrows. If they suddenly wanted eyebrows, they would use fake eyebrows made from mouse fur. Later, human hair was used.

Medieval women used weasel testicles for contraception. They would wear the testicles around their necks like a necklace during intercourse. They believed that doing so would prevent pregnancy after sexual relations.

Rural women in the Middle Ages occasionally urinated in the streets or public places without hesitation, unlike noblewomen.

An unbelievable trend in medieval England was men’s obsession with pointed shoes. Since the 1330s, this special shoe style was widely adopted by the nobility. To shape the pointed shoes, the toes were stuffed with moss and bent upward for ease of walking. However, these shoes made medieval people uncomfortable, as they often suffered from swollen big toes due to their feet being tightly confined in the narrow shoe tips.

To get married, people in the Middle Ages did not need to organize a large event. Only the consent of the bride and groom was necessary. A couple could marry anywhere, even in a tavern. However, it was advisable to have witnesses present at the ceremony to avoid any mishaps.

By the 16th century, humans had a completely different gait, all due to their shoes. Most people at that time did not have shoes and wrapped rags around their feet or went barefoot. Wealthier individuals wore thick leather boots. However, these shoes had no soles, so they could feel every pebble on the ground. Consequently, people walked as if dancing ballet, constantly checking if the ground was safe.