The viruses causing dengue fever and Covid-19 can lead to similar initial symptoms such as fever and headaches.
Covid-19 is an infectious disease primarily transmitted through small droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or breathes. In contrast, dengue fever is a tropical disease that often occurs during seasonal transitions.
The initial onset of both diseases presents similar symptoms. Both are caused by viruses and share several common signs, including fever, chills, cough, cold symptoms, sore throat, body aches, and severe fatigue. Consequently, you may initially confuse the two illnesses.
How the Viruses Spread
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), both dengue fever and Covid-19 can exhibit mild symptoms, self-resolve, and patients may recover at home. However, they can also progress to severe cases that may be fatal.
Dengue fever is caused by one of four related viruses: Dengue virus serotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4. Therefore, a person can be infected by the dengue virus multiple times in their lifetime. The dengue virus is transmitted to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes, primarily the Aedes aegypti mosquito.
On the other hand, Covid-19 is a respiratory illness caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Currently, scientists have not determined whether the antibodies produced from a SARS-CoV-2 infection can protect against the disease. The virus responsible for Covid-19 spreads mainly through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks.
Both diseases are not age-specific. Anyone of any age can contract either Covid-19 or dengue fever. Patients with various underlying chronic conditions, such as heart disease, kidney disease, or diabetes, are at higher risk for complications.
Dengue fever is not transmitted directly from person to person. In contrast, the virus causing Covid-19 is highly contagious if preventive measures such as wearing masks, sanitizing, and social distancing are not followed.
Dengue fever is considered to pose a higher risk for those living in tropical regions. Covid-19 can affect individuals in any location.
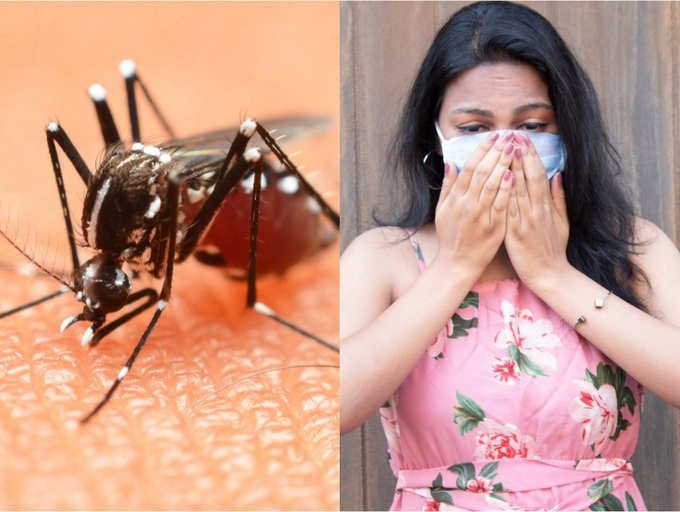

Dengue virus is spread by mosquitoes while SARS-CoV-2 spreads through droplets when talking, coughing, or sneezing. (Photo: IndiaTimes).
Distinguishing Symptoms
According to India Times, Covid-19 can present common symptoms including high fever, chills, cough, cold symptoms, sore throat, shortness of breath, headaches, muscle aches, fatigue, and severe weakness. Common symptoms of dengue fever include very high fever, severe headaches, and joint and muscle pain.
The incubation period for Covid-19 can last up to 14 days, with an average of 4-5 days after exposure to the virus. In contrast, dengue fever has a longer onset period, with symptoms potentially appearing as late as 22-25 days after exposure to the virus.
One of the initial symptoms of dengue fever is weakness and headaches. Most dengue patients also experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and diarrhea.
If you are experiencing symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain, and loss of taste and smell, it is likely not dengue fever. These symptoms are associated with Covid-19.
As Covid-19 is a respiratory illness, some symptoms such as throat inflammation and irritation, changes in voice, and cough may occur. These symptoms are not common in dengue patients.
Dengue patients may also develop rashes on their bodies, from arms to face. In contrast, these rashes are absent in Covid-19 patients.
Notably, if several family members exhibit similar symptoms, it is highly likely to be Covid-19 due to its high transmissibility, whereas dengue fever is not spread through respiratory routes.
Additionally, Covid-19 is inherently more serious and complex, potentially leading to life-threatening complications.
In dengue patients, warning signs of severe complications include: abdominal pain; vomiting (at least 3 times within 24 hours); nosebleeds or gum bleeding; vomiting blood; feeling extremely tired, restless, or irritable.
Meanwhile, signs of deterioration in Covid-19 patients include: shortness of breath; persistent or tight chest pain; confusion, lack of alertness; pale skin, lips, or nails.

Fever is a common symptom in both Covid-19 and dengue fever patients. (Photo: Asianetnews).
What to Do When Experiencing Fever Possibly Due to Covid-19 or Dengue Fever?
Regardless of the cause of the fever, you can treat it at home first. You do not need to be hospitalized if you have mild symptoms of dengue fever or Covid-19.
Typically, complications from dengue fever begin 5-6 days after the onset of fever. Covid-19 can also have complications after 3-4 days of fever.
In the context of the complex Covid-19 pandemic and seasonal weather changes, co-infection (i.e., contracting both Covid-19 and dengue fever) poses a high risk. This can prolong recovery time and lead to many complications for patients.
Here are some ways to reduce the risk of co-infection and keep yourself safe:
- Continue to follow appropriate Covid-19 preventive measures, including wearing masks, frequent handwashing, and avoiding crowded places.
- Avoid using water from sources that may be contaminated and serve as breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
- Use mosquito repellent and wear protective clothing.
- Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle to boost your immune system and protect your health.
Identifying factors that make nCoV easily spread in the air
How will the Covid-19 pandemic end?
No Covid-19 variant has yet been strong enough to defeat Delta