In addition to being a food source, various types of amaranth are also valuable medicinal herbs that are beneficial to health. So, what are the benefits of amaranth?
Benefits of Amaranth
Common Types of Amaranth
Red Amaranth
Red amaranth is characterized by its deep red color throughout its stems and leaves, and it has a high water content. When cooked, it boasts an attractive bright red hue. This type of amaranth is rich in nutrients such as protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
Grain Amaranth
Grain amaranth typically features flowers at its top. Most of the young shoots, leaves, and tender stems are edible. The roots, tubers, and stems can be used in traditional medicine due to their many beneficial nutrients for body function.
Spiny Amaranth
Spiny amaranth often grows in wild areas or abandoned land. This plant has a good ability to withstand drought and waterlogged conditions and can germinate effectively even in less-than-ideal conditions.
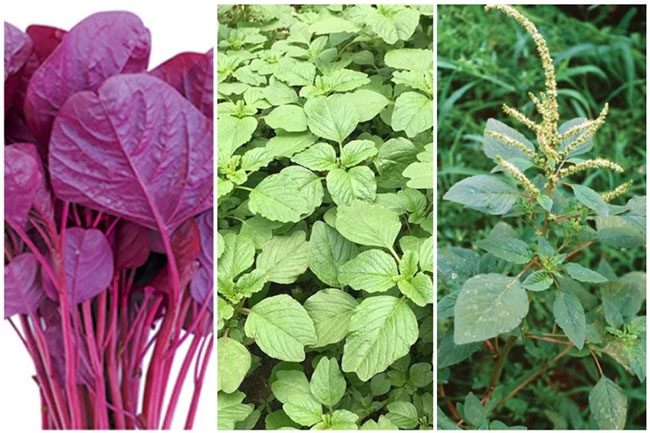

Common Types of Amaranth.
What Are the Benefits of Amaranth?
For a long time, amaranth has been known as a traditional medicine that can treat various illnesses. Below are some of its benefits.
Cancer Prevention
The amino acids in amaranth are quite abundant, particularly the essential amino acid lysine. Additionally, minerals such as potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, vitamin C, and vitamin E found in amaranth play important roles in preventing free radicals caused by aging.
Cardiovascular Health
Amaranth can help reduce cholesterol levels in the body. Tocotrienol—a form of vitamin E present in amaranth—also aids in eliminating bad cholesterol and preventing coronary artery disease.
Improving Anemia
A deficiency of iron in the body can lead to anemia. The rich iron content in amaranth helps increase hemoglobin and red blood cell levels. Thus, consuming amaranth is very beneficial for individuals suffering from anemia.
Joint Health
Few vegetables contain calcium, but amaranth is one of the highest sources. In 100g of amaranth leaves, there are up to 267mg of calcium, which meets 50% of the daily calcium requirement for an individual.
Therefore, amaranth plays a crucial role in enhancing bone density and reducing the risk of osteoporosis and other calcium deficiency-related conditions, such as convulsions.
Calcium in amaranth is three times higher than in spinach and surpasses even cow’s milk.
Reducing Inflammation
The peptide chains in amaranth help reduce inflammation in the body. They also play a significant role in preventing free radicals from attacking healthy cells.
The anti-inflammatory molecules in amaranth can also alleviate symptoms of arthritis, gout, and other inflammatory-related issues.
Enhancing Digestive Health
Amaranth is high in fiber content, so regular consumption can improve digestive health and help prevent constipation.
Moreover, the water boiled from amaranth can assist in treating symptoms of diarrhea, bleeding, or dehydration.
Note: Amaranth has cooling properties and is not suitable for individuals with diarrhea or chronic loose stools, as well as pregnant women experiencing cold symptoms.