Chinese scientists have become the first in the world to successfully develop a method for synthesizing starch from carbon dioxide (CO2).
Breakthrough Technology Converts CO2 into Starch, Transforming Air into a Food Source
In recent years, the world has faced increasingly severe environmental issues, with carbon dioxide emissions being one of the most serious challenges. However, scientists have achieved an incredible breakthrough by successfully converting carbon dioxide into starch, bringing new hope for addressing global food shortages. This technology is expected to turn air into a food source and significantly contribute to sustainable development for humanity.
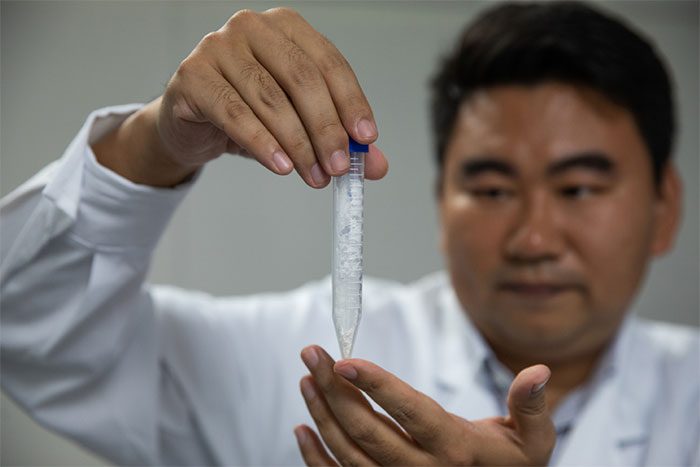

This research was conducted by the Tianjin Industrial Biotechnology Institute under the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Scientists assert that this new method will assist in the transition from traditional agriculture to industrial production. (Image: SCMP).
Carbon dioxide is considered one of the main causes of global warming and climate change. Traditional solutions focus on reducing carbon dioxide emissions from industry and transportation to decrease greenhouse gas concentrations. However, this approach fundamentally fails to address the issue. The technology that converts CO2 into starch can utilize carbon dioxide as a renewable energy source and presents new possibilities for solving food scarcity problems.
This technology is based on the principle of photosynthesis, mimicking how plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight to photosynthesize, converting carbon dioxide into starch. Scientists have discovered that carbon dioxide can be transformed into edible starch using special catalysts and efficient light energy conversion systems.

Starch is a main component of grains as well as an important industrial raw material. In nature, starch is formed through the photosynthesis of crops such as corn and rice. This process involves 60 metabolic reactions and complex physiological regulations, with an energy conversion efficiency of only about 2% in theory. (Image: Zhihu).
The potential applications of CO2 to starch conversion technology are vast: on one hand, it can be directly applied in agriculture to address global food shortages. Currently, the global population is rapidly increasing, leading to a growing demand for food, while agricultural production is constrained by many factors. Implementing CO2 to starch conversion technology will provide a new method of agricultural production that does not rely on the limited resources of traditional farmland but instead converts CO2 into starch to achieve a sustainable air-derived food supply.
This technology can also be utilized in urban areas to provide city dwellers with a more sustainable and environmentally friendly food source. Modern cities face challenges in food supply chains. The CO2 to starch conversion technology will change this status quo, allowing urban residents to synthesize food within the city, thereby reducing dependence on external food supplies.

Ma Yanhe, Director of Tianjin Industrial Biotechnology, stated that the research team has established a method for synthesizing artificial starch that includes 11 core reactions, synthesized entirely from CO2 in the laboratory. The composition of this synthetic starch has been proven to be similar to that of natural starch. (Image: Zhihu).
The technology that converts CO2 into starch also has the potential to manage environmental issues and reduce carbon emissions. Currently, carbon dioxide emissions have become a global environmental problem, and its impact on global warming and ecosystems cannot be overlooked. By converting carbon dioxide into starch, it can not only effectively reduce greenhouse gas concentrations and slow down climate change but also achieve resource reuse.
Although the technology to convert CO2 into starch has significant potential, it is still in the experimental stage and has a long way to go before practical application. Scientists need to conduct further research to optimize catalysts and light energy conversion systems to enhance the efficiency and stability of the carbon dioxide to starch conversion process. At the same time, governments and scientific research organizations need to strengthen support, invest in this field, and promote the commercialization of the technology.
Scientists have discovered that by using specific photosynthetic microorganisms, carbon dioxide can be converted into protein and other nutrients. This method can produce food without the need for land and water, fundamentally addressing the limitations of land and resources that traditional agriculture faces. The Tianjin Industrial Biotechnology Institute has focused on harnessing biological conversion and has been involved in numerous starch synthesis projects since 2015. (Image: Xinhua).
The Future Significance and Viable Application Areas of Converting Air into Food
Transforming air into food holds great significance for the future, primarily in addressing global food security issues. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food also increases. At the same time, issues such as land degradation, climate change, and water scarcity have made traditional agriculture increasingly difficult. If large-scale production can be achieved through air-to-food conversion technology, it could provide a more stable and adequate food supply for the world.
Transforming air into food could also alleviate pressure on the ecological environment. Traditional agricultural production requires large areas of land and substantial water resources, and the overuse of these resources often leads to land degradation and water depletion. The process of converting air into food does not require land and water resources; in this sense, it can better protect natural ecosystems and minimize land development as well as water resource consumption.
Air-to-food conversion could also be used in specific situations, such as urban agriculture in harsh environments. As urban populations continue to rise, urban agriculture has become an important supplementary source. In cities, land is often limited and restricted due to pollution and land degradation. If air-to-food conversion technology can be applied in urban agriculture, agricultural activities could be integrated into urban centers, achieving a more diverse food supply.
To realize the application of air into food, there are still several technical and economic challenges. First, scientists need to explore further ways to optimize this technology to enhance productivity and product quality. Second, appropriate innovation and funding for R&D are also key factors. Only with sufficient investment and support can this technology be developed and further applied.
- China mobilizes nearly 3 million chickens to eliminate an insect species causing 100 billion VND in damage each year
- Why did NASA’s probe almost get ‘swallowed’ while bringing back a ‘clump of soil’ weighing 250g from 6.2 billion km away?
- Two moons of Saturn collide and shatter, creating a mysterious phenomenon?


















































