Let’s decode this secret to better understand the requirements set by doctors!
When you go for a routine health check-up, you have likely been asked by your doctor to “fast” before a blood test on multiple occasions.
So why is this regulation in place? Can eating and drinking actually alter test results enough to misrepresent your health condition?
Let’s decode this secret to better understand the requirements that doctors impose!
Why is fasting required before a blood test?
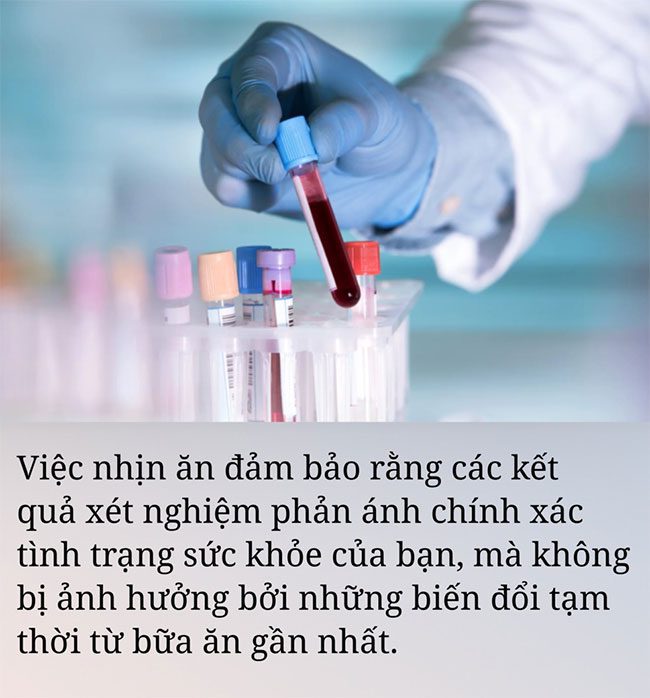
According to information from WebMD: When you eat or drink, nutrients from food quickly enter the bloodstream, altering test parameters.
Fasting ensures that the test results accurately reflect your health status, free from temporary fluctuations caused by your most recent meal.
Some tests that require fasting include:
- Fasting Blood Glucose Test: This measures blood sugar levels accurately, especially for patients at risk or currently suffering from diabetes.
- Lipid Profile: This measures cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood to assess the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Eating before the test can cause a sudden spike in triglyceride levels, leading to inaccurate results.
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel: This test measures liver and kidney function, glucose levels, and electrolytes in the body. Fasting helps eliminate temporary fluctuations in these parameters.
Vitamin and mineral tests such as iron and vitamin B12: These assess deficiencies or excesses that could be affected if you eat before the blood sample is taken.
Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT): This indicates the level of the GGT enzyme in your body. If this level exceeds the normal range, it may suggest liver disease, bile duct issues, or alcohol abuse.
Kidney function tests assess your kidney health: Your doctor may request this test as part of a general health check or if there are issues with your kidneys.
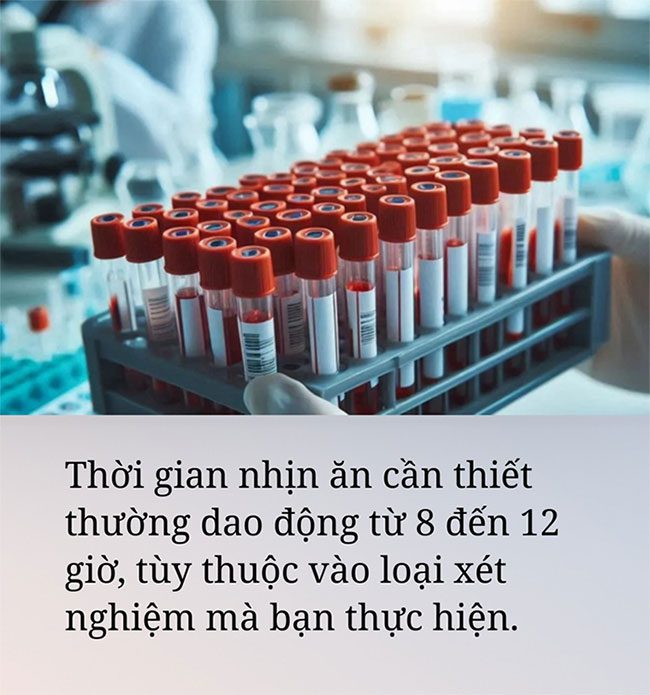
How long should you fast before a blood test?
The required fasting time typically ranges from 8 to 12 hours, depending on the type of test you are undergoing.
For example: For the fasting blood glucose and lipid profile tests, the usual fasting period is 8-12 hours. Other tests, such as those measuring liver or kidney function, also require a similar fasting duration.
Note that you should only drink plain water during the fasting period. Beverages containing caffeine, such as coffee and tea, can affect test results.
Avoid smoking, chewing gum, or engaging in vigorous exercise before the test, as these activities can also alter blood parameters.
What happens if you accidentally eat before the test?
If you unintentionally eat or drink before your test, it’s crucial to inform the phlebotomist or doctor right away. Food can affect the accuracy of test parameters, particularly blood sugar and cholesterol levels. In this case, the doctor may ask you to reschedule your appointment for a later date to ensure the most accurate results.
For example, if you consume a carbohydrate-rich meal before a blood glucose test, your blood sugar levels may spike, leading to a misdiagnosis of diabetes or prediabetes.
Important considerations when fasting before a blood test
- 1. Stay hydrated: Drinking plain water keeps your body hydrated, making veins easier to see during blood draw.
- 2. Avoid coffee, tea, and sugary drinks: These beverages contain caffeine and sugar, which can alter test results.
- 3. Limit the use of supplements and medications (unless instructed by a doctor) before the test.
Strictly adhering to fasting requirements before a blood test is vital for obtaining the most accurate results. If you are unsure about specific requirements, be sure to ask your doctor or healthcare staff before the test.


















































