A new discovery about a colossal ancient volcano makes the Noctis Labyrinthus an appealing choice for missions searching for life.
Noctis Labyrinthus – Labyrinth of the Night – is located in the equatorial region of Mars, one of the celestial bodies that NASA and many other space agencies believe may have once harbored life.
In a recent study, a team of scientists led by planetary scientist Pascal Lee from the SETI Institute (Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence – USA) uncovered the astonishing secrets of the Noctis Labyrinthus.
The colossal volcano revealed in the Noctis Labyrinthus – (Photo: Pascal Lee and colleagues).
This discovery came when they traced the remnants of an ancient glacier and recognized the remains of a gigantic, ancient volcano.
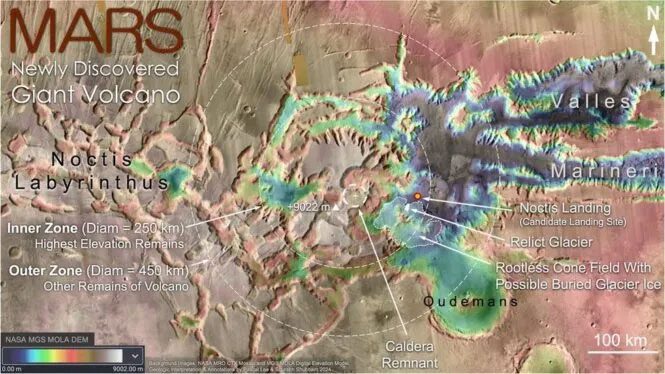
This volcano has been heavily eroded, so initially, scientists did not identify it in remote sensing data. It has been temporarily named Noctis Mons.
“This area of Mars is known to contain various types of hydrated minerals that have formed throughout Mars’ history. There has long been speculation about the volcanic context that led to the formation of these minerals,” explained planetary geologist Sourabh Shubham from the University of Maryland (USA).
Upon further analysis, the research team realized the volcano’s size is extraordinarily vast. It rises over 9,000 meters and spans more than 250 kilometers.
Thus, Noctis Mons becomes the seventh-highest topographic feature on Mars, significantly surpassing the highest inactive volcano on Earth (6,893 meters).
In the central area, scientists have identified a collapsed caldera, which was once a lake of molten lava.
Additionally, several flat-topped peaks in the central region form an arc shape, outlining a volcanic cone that slopes down to lava fields surrounding the geological chaos.
Volcanic deposits also extend across an area measuring up to 5,000 square meters.
More intriguingly, they discovered a vast area containing mounds resembling blister formations, a type of volcanic terrain located in lower regions, which could have been created when lava flowed over a water- or ice-rich surface.
This suggests that glacial sediment layers may be present here and potentially provides evidence of a once-thriving biosphere on the red planet.
The thermal and icy interactions in this area in the past may also have helped create essential minerals that support early life, much like what may have occurred on our own Earth.
Therefore, scientists believe that the Noctis Labyrinthus could also be a labyrinth of life awaiting humanity’s exploration.





















































