Creating glowing cats, fluorescent fish, vaccine bananas, and genetically modified cattle are just a few of the many bizarre gene experiments humanity has conducted recently.
>>> End of the 84-Year Useless Experiment
10. Cabbage-Scorpion

Cabbage is an essential green vegetable for Eastern Europeans, so it’s not surprising that it became a subject of study for biologists.
The Oxford Virus Research Institute in the UK came up with the idea of creating cabbage plants that contain the venom of scorpions as a form of natural pesticide. This allows farmers to reduce pesticide use without worrying about pest control.
In 1994, scientists first tested scorpion venom on cabbage fields. Since then, they have made significant progress in creating cabbage strains capable of poisoning insects without harming humans by injecting scorpion toxins into the cabbage gene pool.
9. Glowing Fish

Glofish – glowing fish is a unique product of genetic technology. Scientists have inserted fluorescent protein genes into zebra fish to create brightly colored fish.
The goal of this project is to minimize environmental pollution. Whenever exposed to contaminated water, the fluorescent substances in the fish’s body will glow, signaling experts to take timely action.
In the near future, canaries will be brought to the ‘surgical table’ to become the next glowing organisms.
8. Grapple – Grape-Flavored Apples

This familiar fruit is actually ordinary apples that taste like grapes. Scientists soaked Fuji apples or Washington Extra Fancy Gala apples in methyl anthranilate (a substance used to create flavor in grape juice and candy) to achieve a Concord grape flavor.
7. Flavr Savr Tomatoes

Flavr Savr tomatoes were the first genetically engineered food approved by the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration), tasting significantly better than ordinary tomatoes.
These tomatoes were sold in 1994 but were withdrawn from the market in 1997 due to difficulties in shipping. While Flavr Savr tomatoes retained their flavor and color longer, they ultimately failed to become a new strain for farmers due to their blandness. Nonetheless, it marked an exciting breakthrough.
6. Super Fast Mice

Researchers at the University of Lausanne have created super mice that are faster, stronger, and healthier than ever. They can run twice as far as normal mice and have an exceptional ability to resist cold.
This is just an initial experimental phase aimed at creating elite troops with unbeatable strength for future government needs.
5. Cancer-Fighting Chicken Eggs

In 2007, scientists at the Roslin Institute successfully produced a breed of egg-laying chickens capable of fighting cancer.
These chickens have human genes in their DNA, resulting in egg whites containing pharmaceutical proteins that can be extracted and purified into medicines.
This idea has been enthusiastically supported by anti-cancer organizations, but seven years later, it seems the project has stalled. However, the initiative for animal-derived medications may be refined in the future.
4. Banana Vaccine
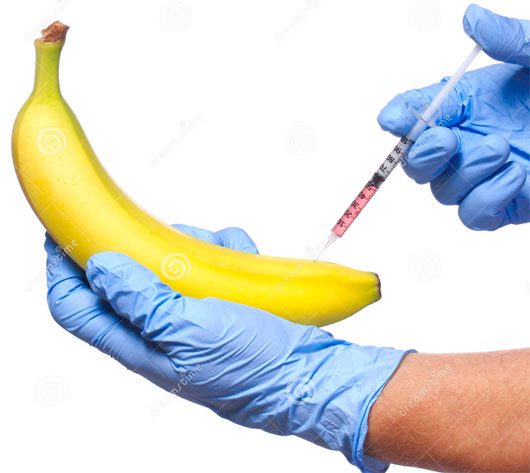
Scientists inject a type of virus into young banana plants, and the genetic material of the virus quickly becomes a permanent part of the plant’s cells.
As the banana plant grows, the cells produce viral proteins – but not the infectious parts of the virus. When people eat these genetically modified bananas, which are packed with viral proteins, their immune systems generate antibodies against the disease, similar to a traditional vaccine.
3. Glowing Cats

In 2007, scientists in South Korea altered the DNA of a cat to make it glow in the dark, creating a breed of glowing fur cats. They then cloned this DNA to produce a set of glowing cat breeds.
Researchers used virus cells to create red fluorescent proteins. They then injected the modified nucleus into eggs for cloning, and the resulting asexual cloned embryos were implanted back into experimental cats, which later became the mothers of glowing litters.
This successful experiment could pave the way for technology to monitor the development of virus-induced diseases. When a virus develops in a certain part of the body, that area will glow, allowing doctors to intervene promptly.
2. Cows with Human Genes

Chinese scientists are said to have attempted to implant human genes into cattle to create hybrid creatures, with the goal of producing milk as tasty as human milk. This raises ethical concerns, as slaughtering these cows would be akin to killing and consuming one’s own kind.
1. Goats that Produce Spider Silk

Spider silk is one of the most valuable materials in nature and can be used to create products like ligaments and ropes. In 2000, Nexia Biotechnology announced an invention: goats that could produce spider silk protein in their milk.
Researchers introduced a gene that regulates spider silk production into the DNA of experimental goats. This way, they could extract spider silk protein from their milk. This milk is used to produce a high-strength fiber known as Biosteel.




















































