According to Space, the Hubble Space Telescope has discovered a complex cloud of gas expanding into space.
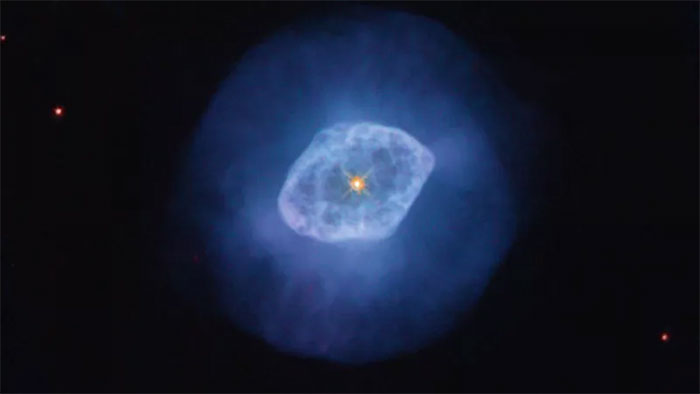
Planetary Nebula NGC 6891 glowing in an image captured by the Hubble Space Telescope. (Photo: NASA)
The Hubble Telescope has captured images of the NGC 6891 gas cloud shining brightly as this space observatory aids scientists in understanding how gas clouds form and evolve.
Astronomers refer to NGC 6891 as a “planetary nebula.” Today, we know that such nebulae form after supernova explosions cause massive stars to release gas.
The high-resolution images from Hubble reveal fine filaments swirling around a white dwarf deep within this gas cloud. The images also show the outer gas rings expanding faster than the innermost part of the nebula. Observations even captured gas shells oriented in different directions.
“From their motion, astronomers estimate that one of the shells is about 4,800 years old, while the outer halo is approximately 2,800 years old,” officials from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) stated.
The luminosity of NGC 6891 occurs when white dwarfs ionize or strip electrons from the surrounding hydrogen gas.
“As the energized electrons transition from a high-energy state to a low-energy state by recombining with hydrogen atoms, they emit energy in the form of light, causing the nebula’s gas to glow,” NASA explained.
The Hubble Telescope is currently being restored after experiencing multiple synchronization errors on October 23. This telescope was last serviced directly in 2009.


















































